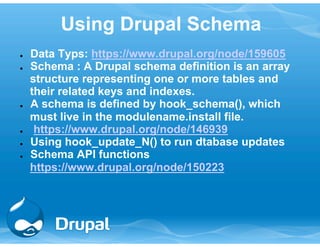
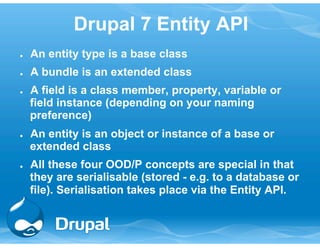
This document provides an overview and introduction to Drupal module development. It discusses Drupal hooks like hook_menu(), hook_permission(), hook_form(), and the Entity API. It also covers creating modules, forms, variables, blocks, and interacting with the database. The event is for a Drupal Global Training Day in Mumbai, India hosted by Drupal Mumbai and Tata Consultancy Services.








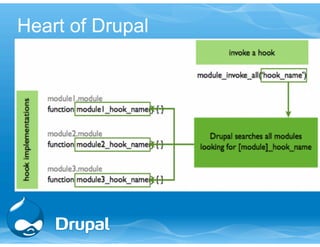
![Menu Example
/**
* Implementation of hook_menu().
*/
function menufun_menu() {
$items['menufun'] = array(
‘title’ => ‘Greeting’,
'page callback' => 'menufun_hello',
'access callback' => TRUE,
'type' => MENU_CALLBACK,
);
return $items;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal7advancedoverviewmoduledevelopmentv32-140915144146-phpapp01/85/13th-Sep-Drupal-7-advanced-training-by-TCS-12-320.jpg)









![Form Elements
# Text Field
# Textarea
# Select
# Radio Buttons
# Check Boxes
# Date
# File Upload :
$form['picture']['picture_upload'] = array(
'#type' => 'file',
'#title' => t('Upload picture'),
'#size' => 48,
'#description' => t('Your virtual face or picture.')
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal7advancedoverviewmoduledevelopmentv32-140915144146-phpapp01/85/13th-Sep-Drupal-7-advanced-training-by-TCS-23-320.jpg)
![# Fieldset : group elements together
$form['author'] = array(
'#type' => 'fieldset',
'#access' => user_access('administer nodes'),
'#title' => t('Authoring information'),
'#collapsible' => TRUE,
'#collapsed' => TRUE,
'#weight' => 20,
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal7advancedoverviewmoduledevelopmentv32-140915144146-phpapp01/85/13th-Sep-Drupal-7-advanced-training-by-TCS-24-320.jpg)
![# Textarea :
$form['keywords'] = array(
'#title' => t('Keywords'),
'#type' => 'textarea',
'#description' => t
('The comment will be unpublished if it contains any of the phrases above. Use a
case-sensitive, comma-separated list of phrases. Example: funny, bungee
jumping, "Company, Inc."'),
'#default_value' => isset( $context['keywords']) ?
drupal_implode_tags($context['keywords']) : '',
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal7advancedoverviewmoduledevelopmentv32-140915144146-phpapp01/85/13th-Sep-Drupal-7-advanced-training-by-TCS-25-320.jpg)
![# Radio :
$active = array(0 => t('Closed'), 1 => t('Active'));...
$form['settings']['active'] = array(
'#type' => 'radios',
'#title' => t('Poll status'),
'#default_value' => isset($node->active) ? $node->active : 1,
'#options' => $active,
'#description' => t('When a poll is closed, visitors can no longer vote for it.'),
'#access' => $admin,
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupal7advancedoverviewmoduledevelopmentv32-140915144146-phpapp01/85/13th-Sep-Drupal-7-advanced-training-by-TCS-26-320.jpg)