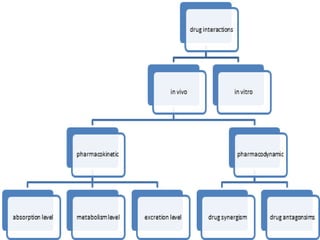
Drug interactions can occur when two or more drugs are taken simultaneously and modify each other's effects. Interactions can be pharmacokinetic, affecting absorption, distribution, metabolism or excretion of the drugs. They can also be pharmacodynamic if the drugs affect the same receptor sites. Common causes of interactions include effects on drug metabolizing enzymes like CYP450 and drug transporters, protein binding displacement, and additive pharmacodynamic effects. It is important for doctors to consider potential interactions when prescribing multiple medications to a patient. While many interactions can be managed safely, they should be avoided if possible due to risks of toxic effects or reduced treatment effectiveness.