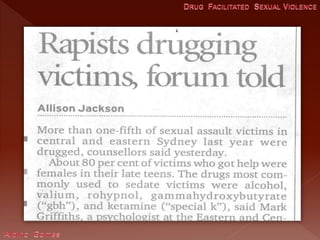
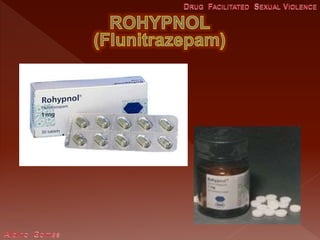
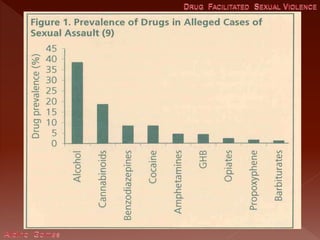
This document discusses drug facilitated sexual assault and provides information about common drugs used, their effects, symptoms exhibited by victims, and challenges with investigating and prosecuting these crimes. It notes that drugs like GHB, Rohypnol, ketamine and alcohol are often used to incapacitate victims and cause anterograde amnesia. Victims may have no memory of the assault and present as confused or disoriented. It stresses the importance of collecting urine and blood samples from victims within a short timeframe to detect evidence of drugs.