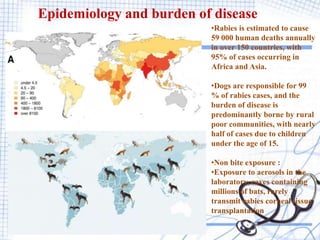
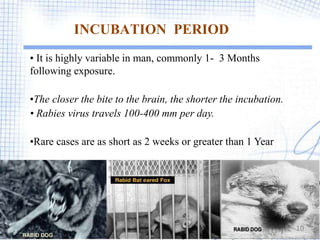
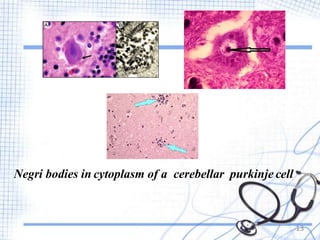
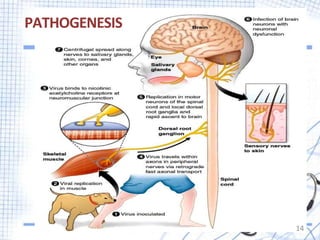
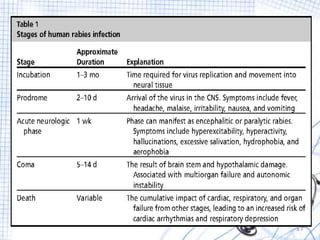
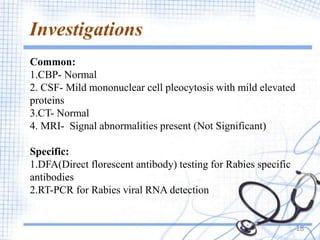
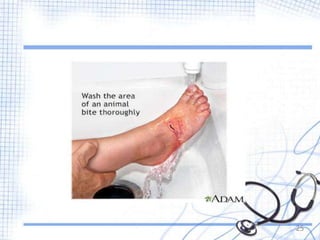
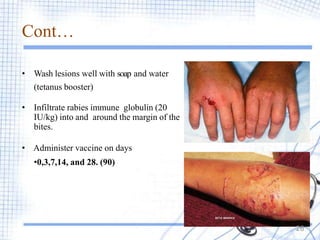
Rabies is a viral zoonotic disease that primarily affects warm-blooded animals, with dogs responsible for 99% of human deaths. Infection occurs through bites or scratches, leading to severe neurological symptoms and nearly always resulting in death once clinical signs appear. Effective prevention includes vaccination and prompt post-exposure treatment, emphasizing the importance of responsible pet ownership and community education to reduce rabies transmission.