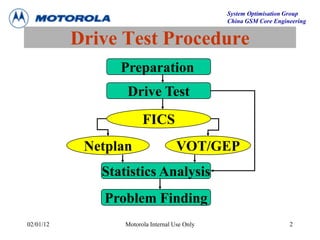
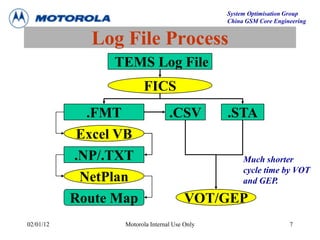
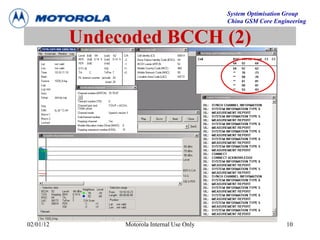
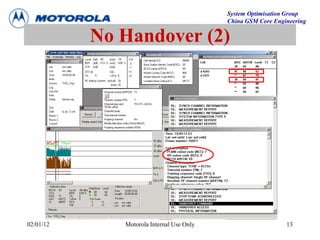
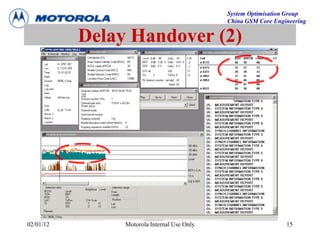
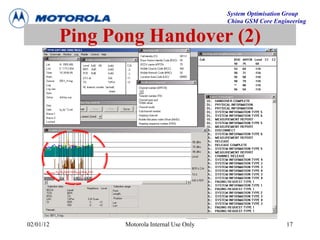
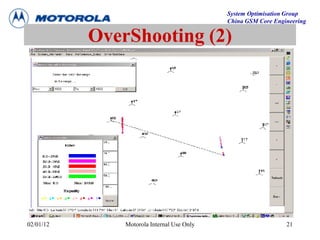
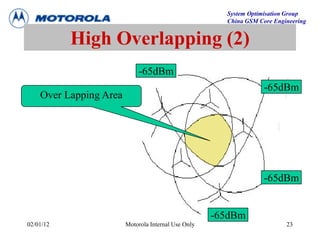
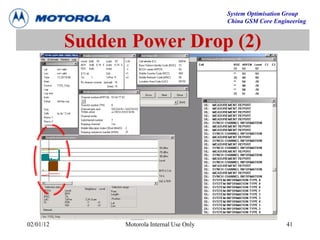
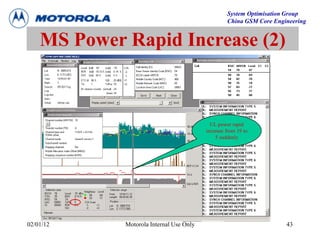
This document provides an overview of drive test procedures and methods for analyzing issues found during drive tests. It discusses preparation steps, how to perform drive tests, and how to analyze log files. Common problems that can be identified include undecoded BCCH, no handover, ping pong handovers, interference, and dropped calls. Analysis tools like GEP, VOT, CM Extractor, and NPM are described for visualizing problems.