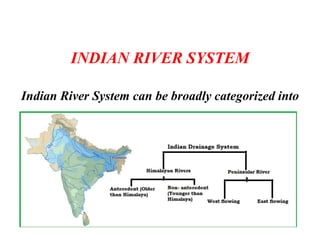
The document summarizes India's river systems. It describes how rivers originate and flow through different stages from youthful to mature to older. It notes that India's river systems can be categorized as Himalayan or peninsular rivers. Himalayan rivers originate in the Himalayas and are longer and perennial, while peninsular rivers originate in the Deccan plateau and are shorter, drying up in summer. It provides details on the Indus river system, the longest in India, describing its source, tributaries, and flow through India and Pakistan before draining into the Arabian Sea. It mentions the Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan that allocates water rights.