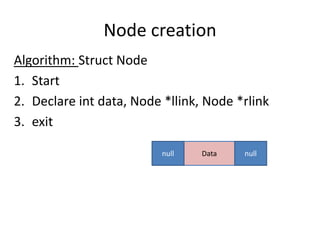
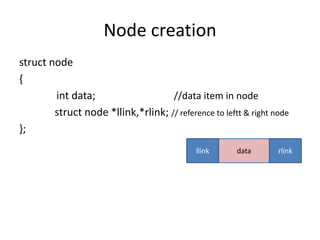
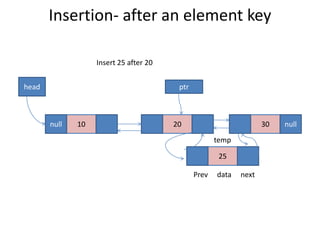
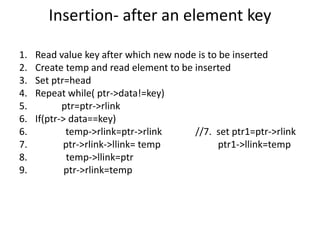
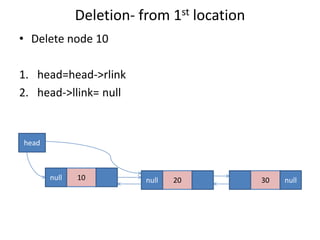
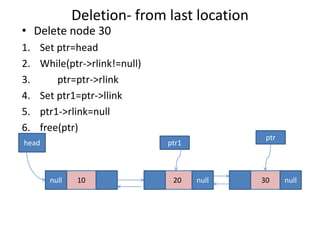
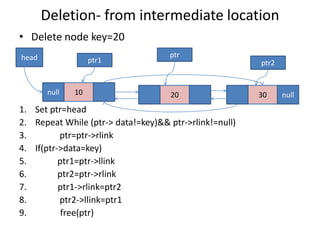
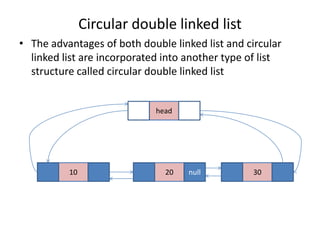
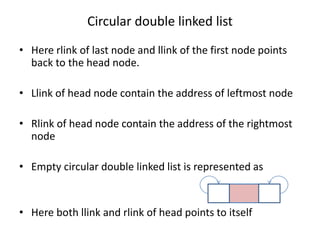
Double linked lists allow traversal in both directions by including a pointer to both the previous and next node. Each node contains data, a left pointer (llink) to the previous node, and a right pointer (rlink) to the next node. Nodes can be inserted or deleted at the beginning, end, or middle of the list by adjusting the pointers of the nodes before and after the target node. A circular double linked list connects the first and last node to the head node to allow continuous traversal in either direction.