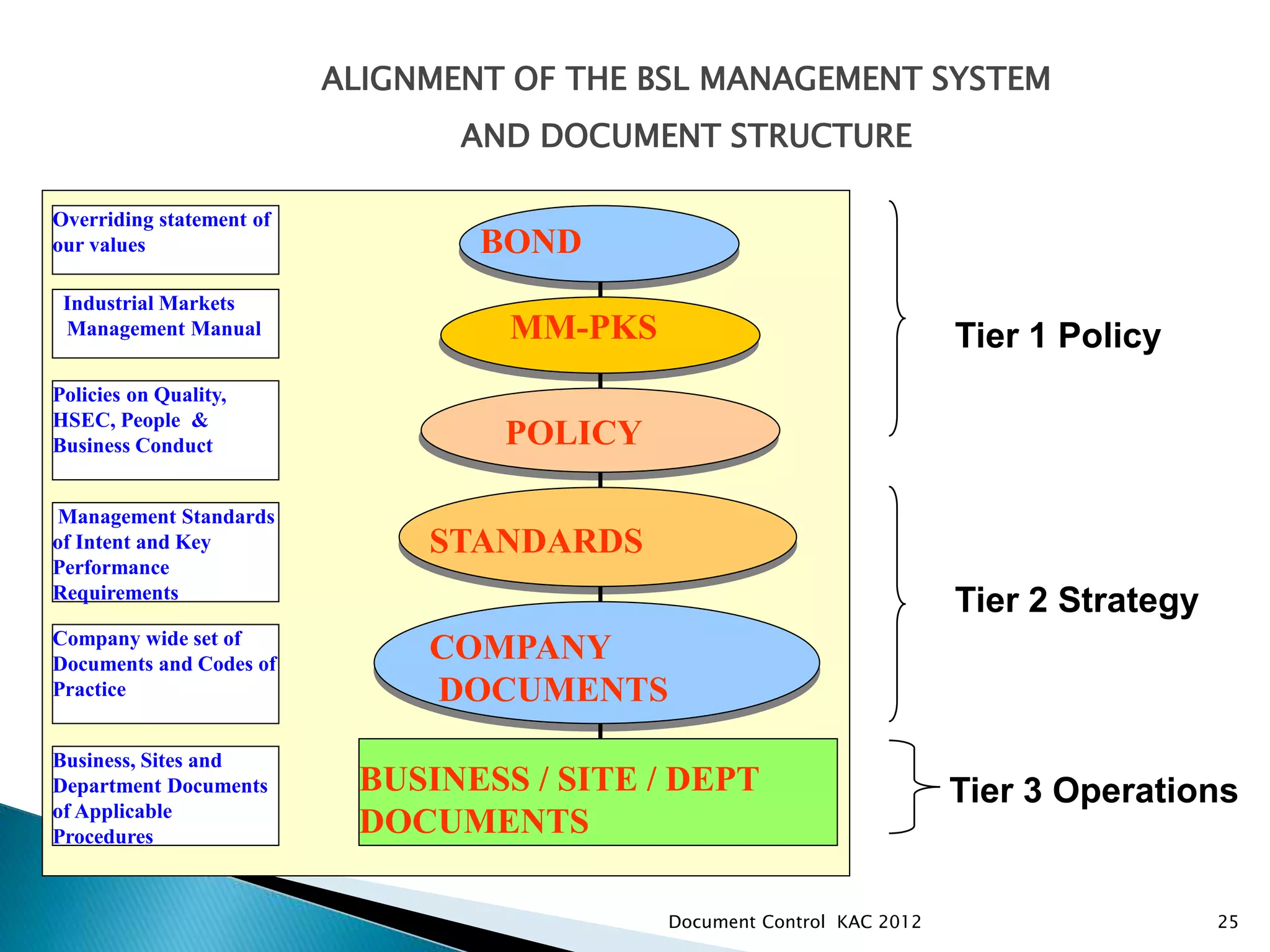
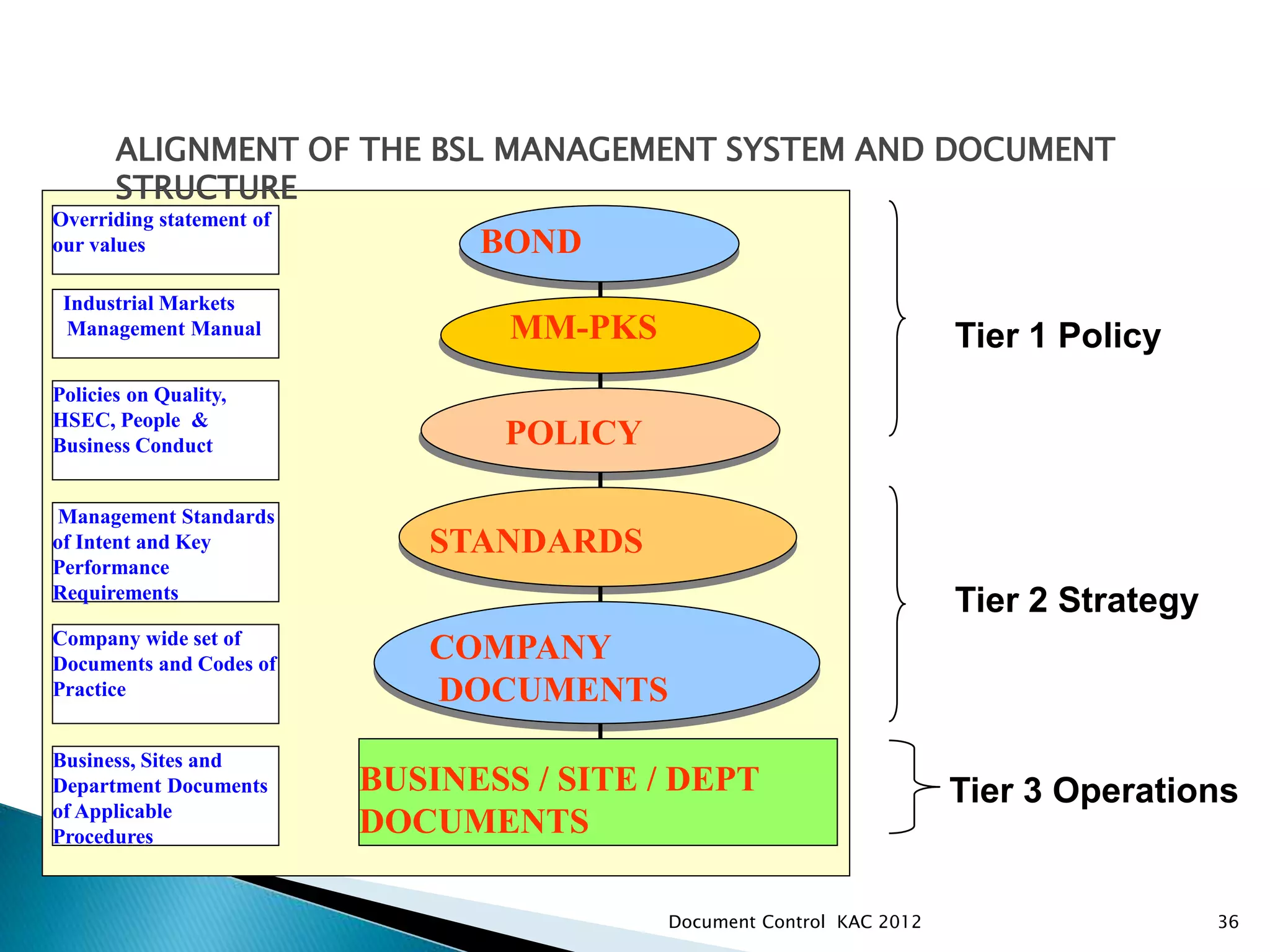
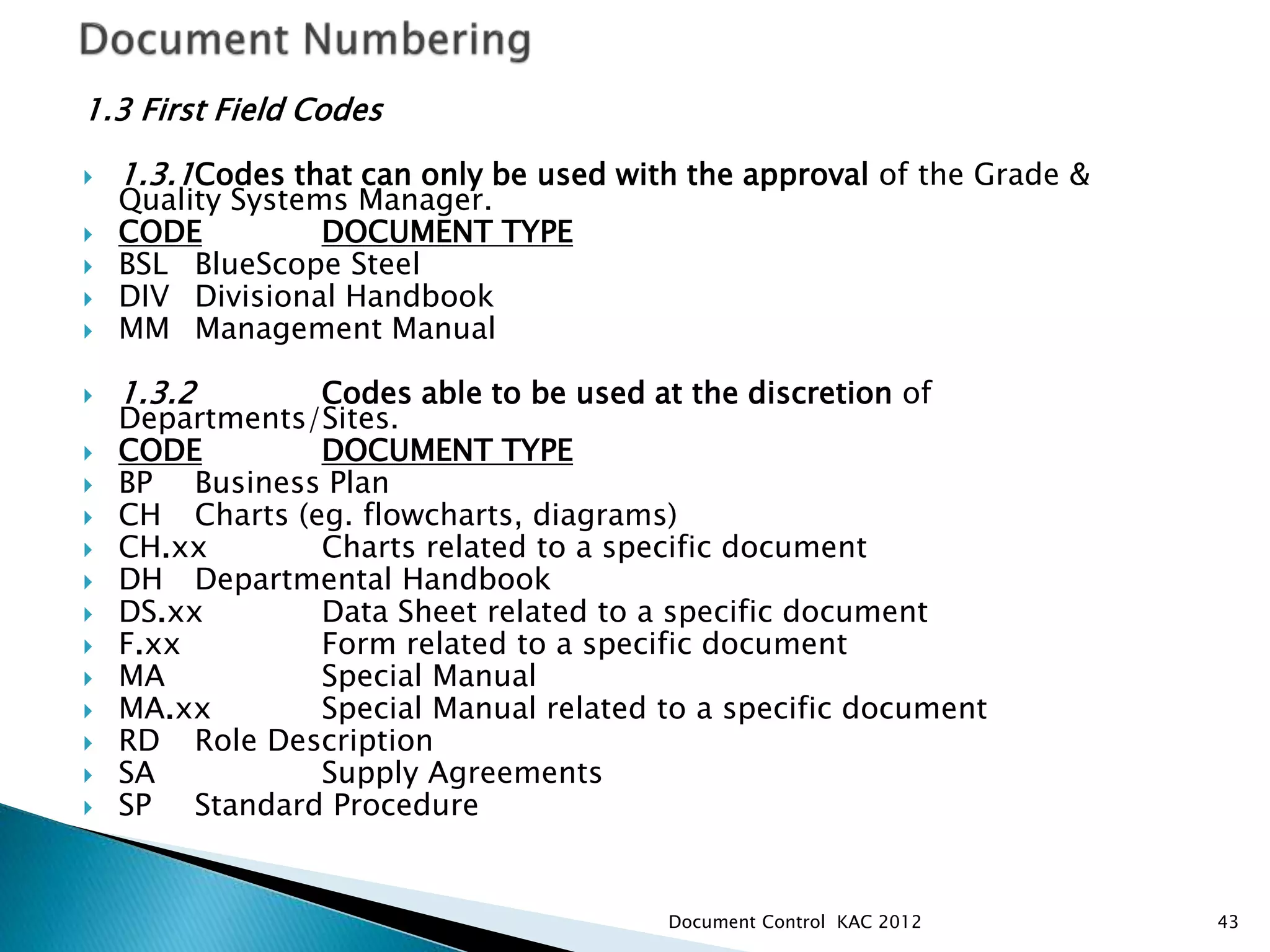
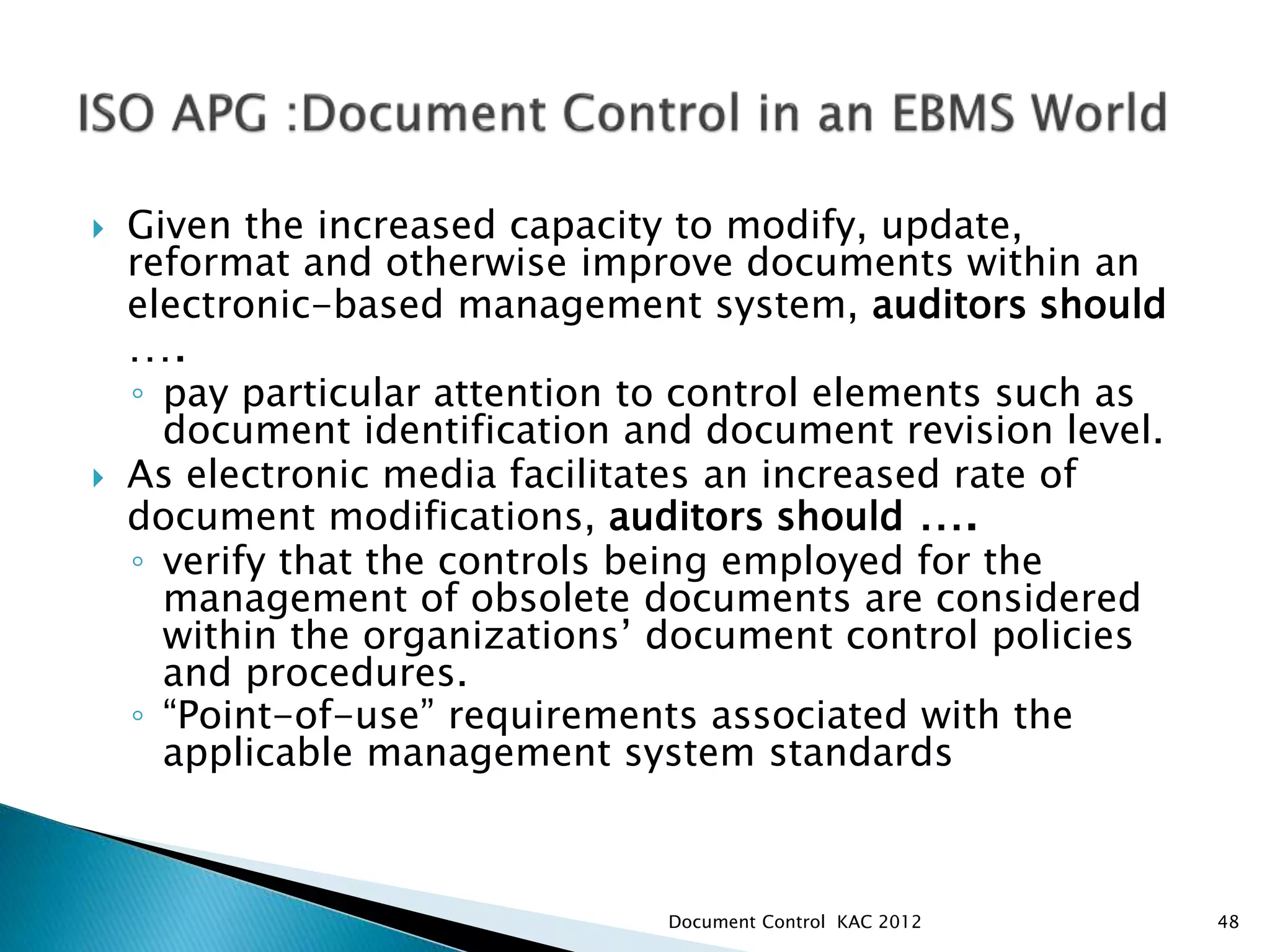
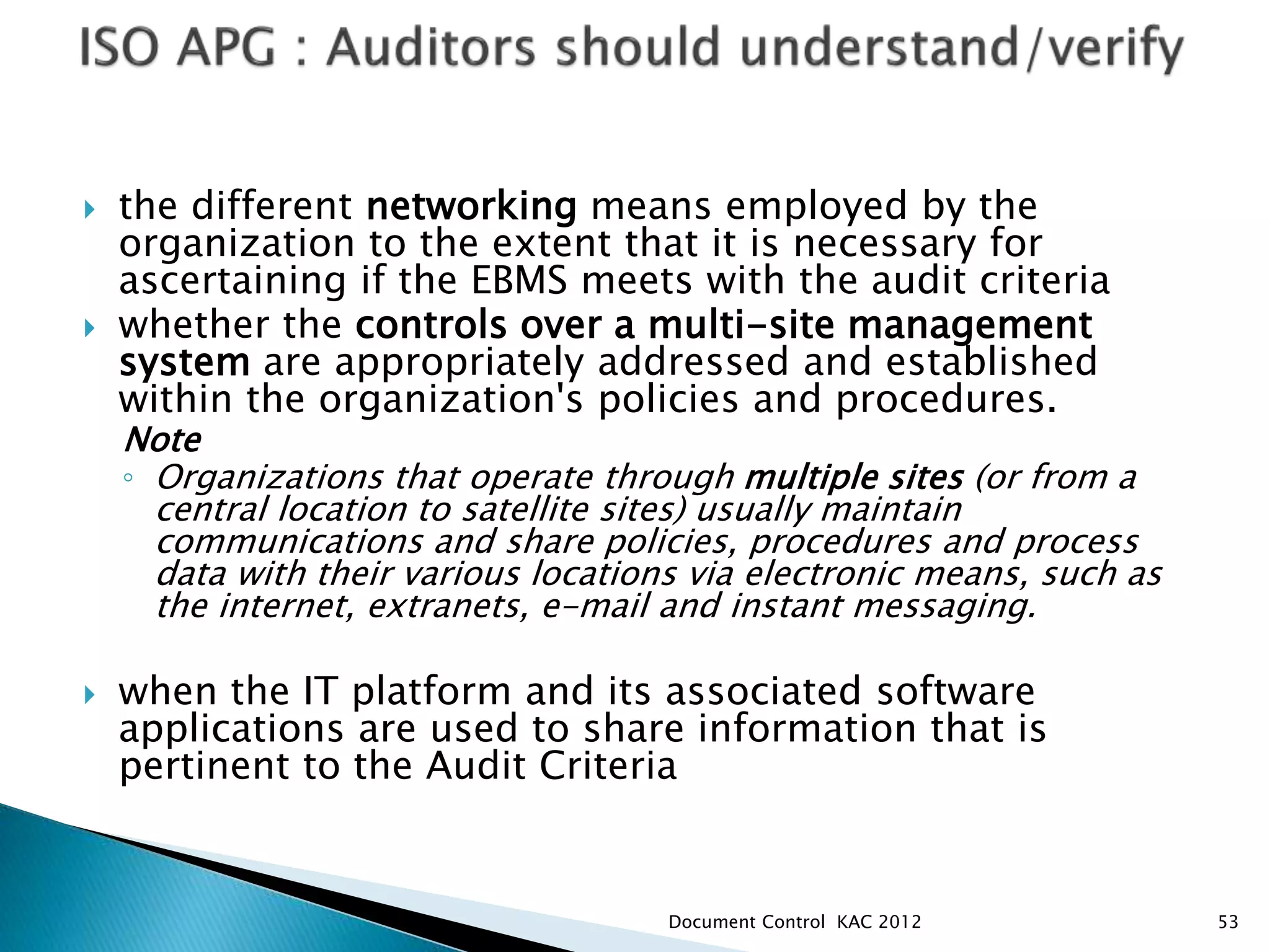
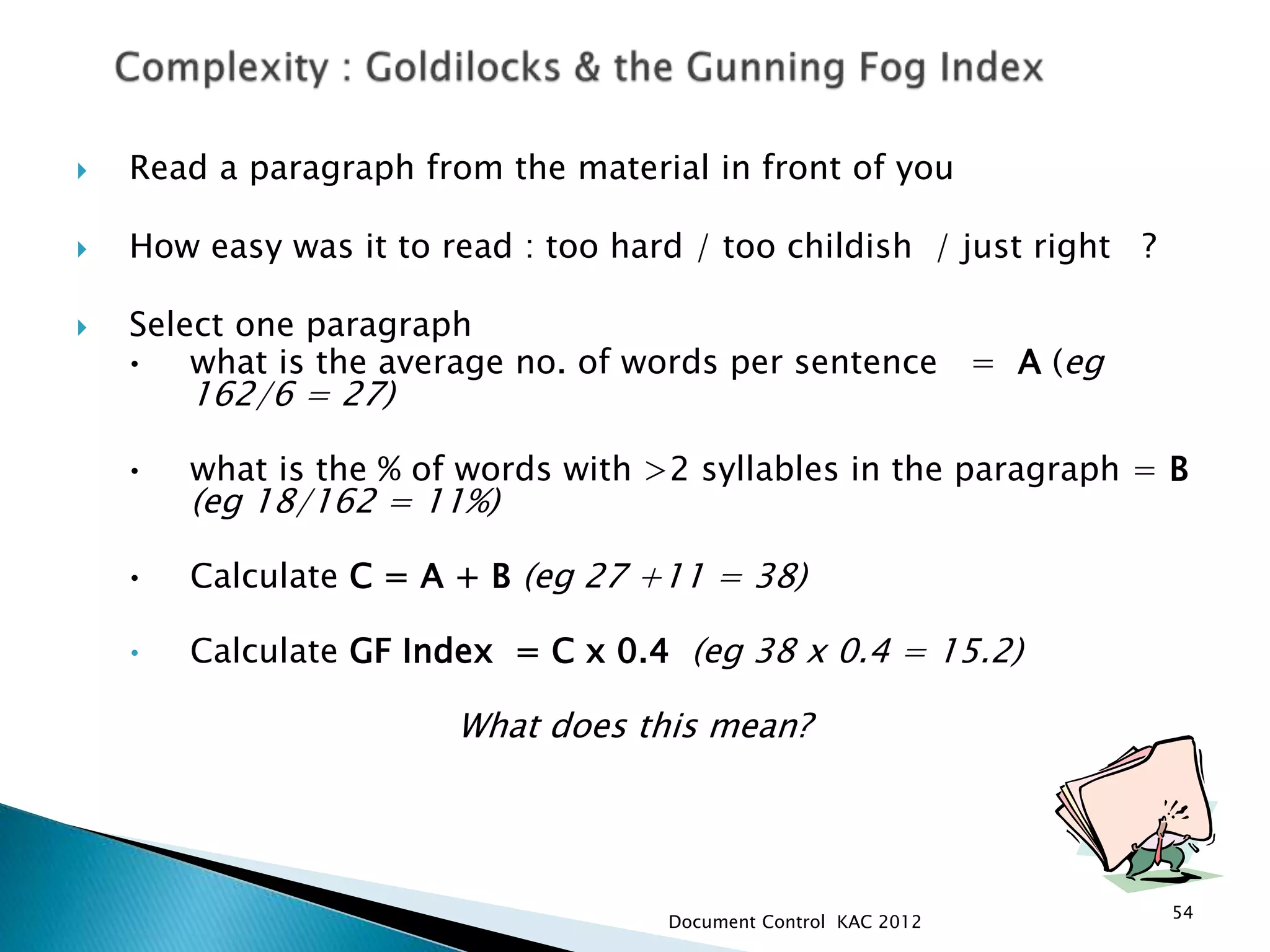
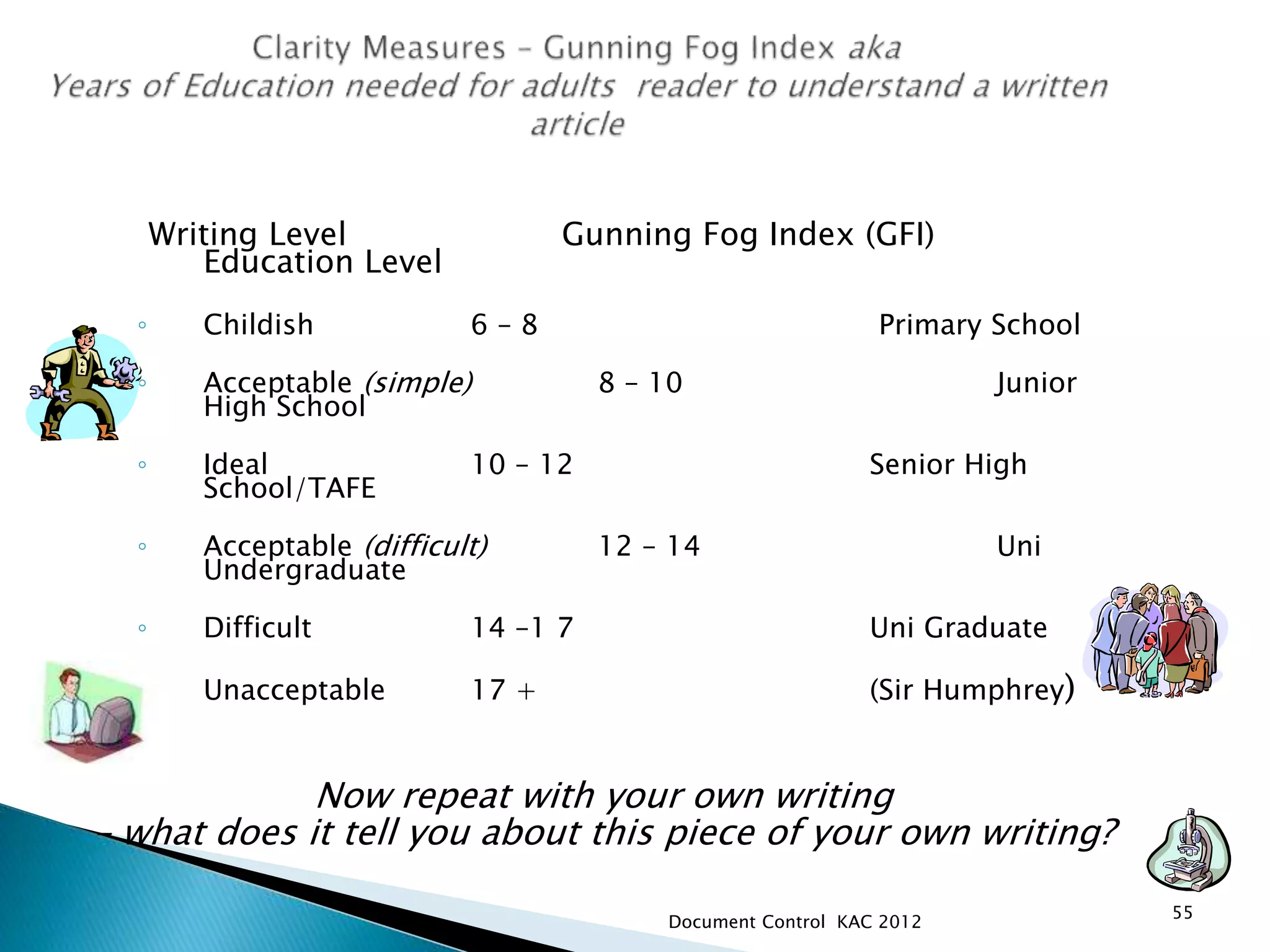
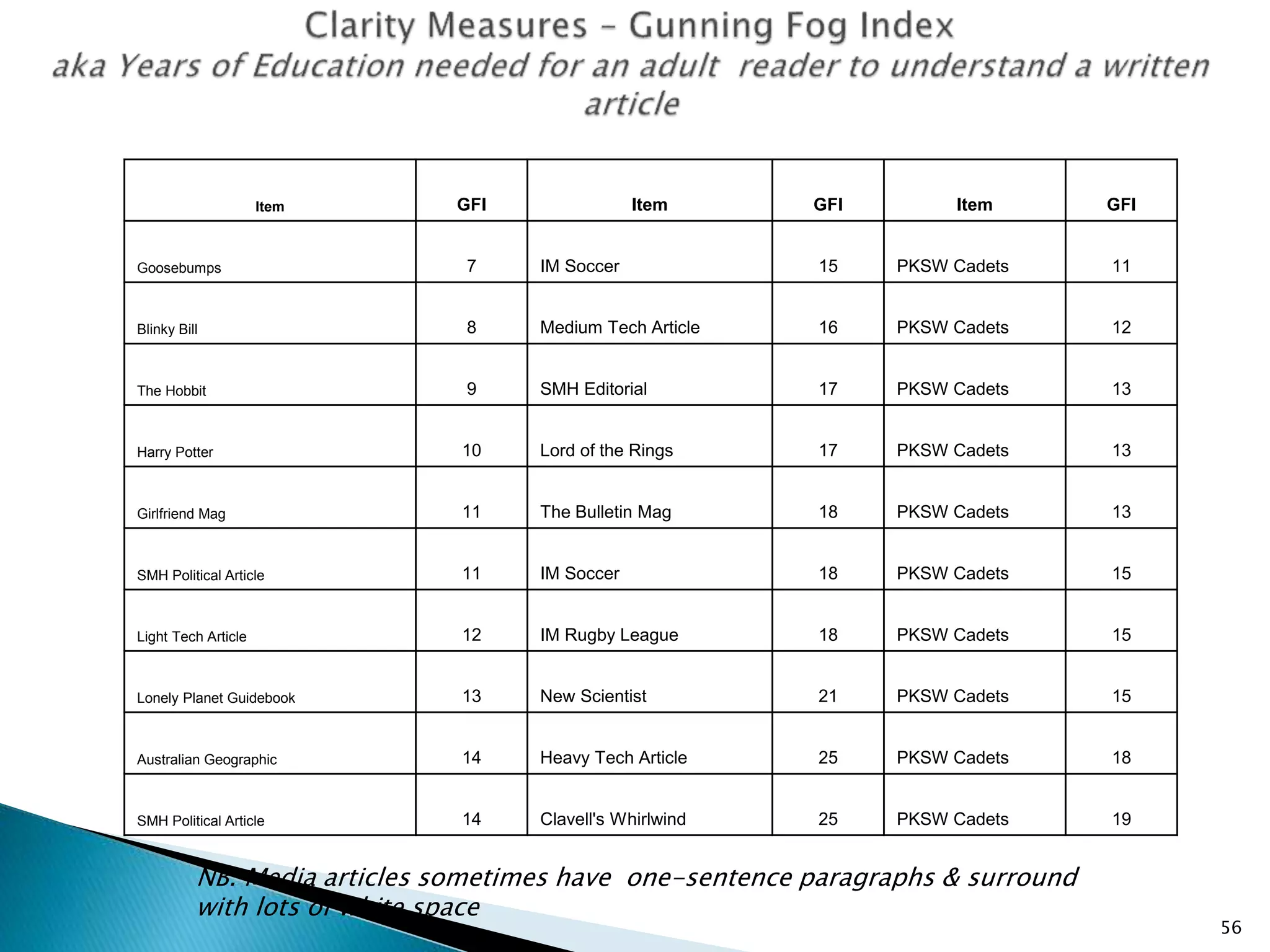
The document discusses various aspects of document control systems, including typical structures, procedures for control, and verification. It notes that effective document control is important for integrated management systems covering activities like manufacturing, health and safety, and environmental management. Controlled documents must be properly numbered, approved, maintained and obsolete versions removed from circulation.