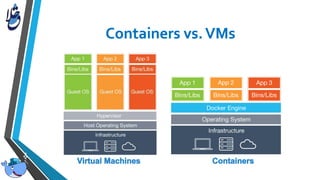
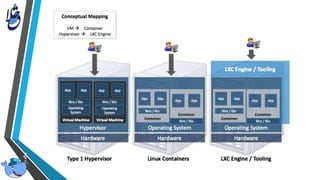
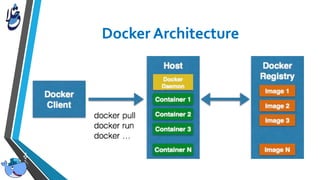
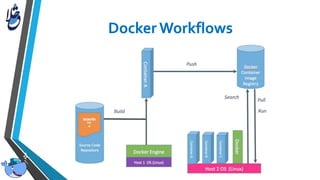
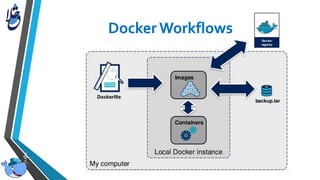
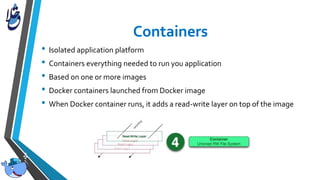
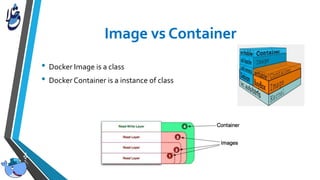
The document outlines Docker, an open-source platform that enables the operating system-level virtualization of Linux systems through containers, allowing for efficient application deployment and management. It covers features such as namespaces, cgroups, and tools like Docker Compose and Docker Swarm for orchestrating and managing container architectures. Docker facilitates rapid software delivery, application portability, and resource efficiency, making it a vital tool for developers and sysadmins.