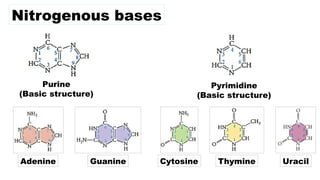
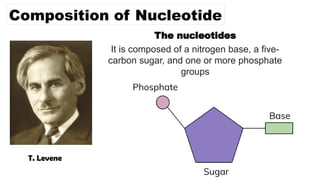
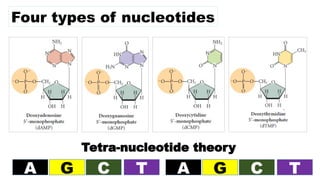
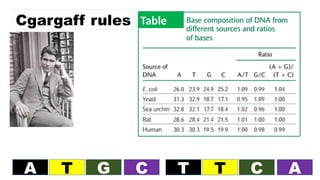
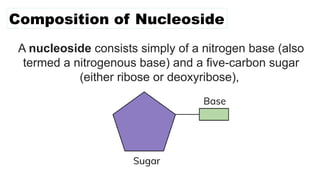
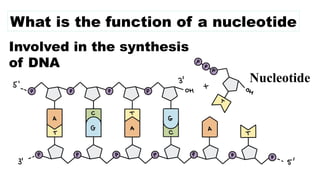
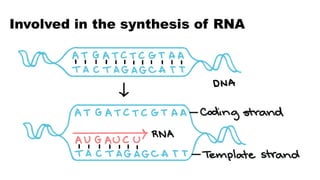
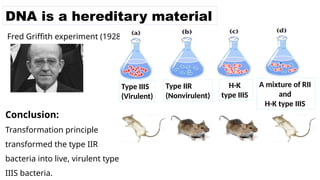
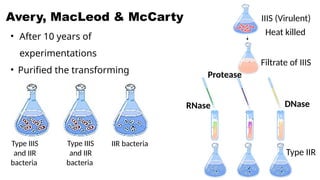
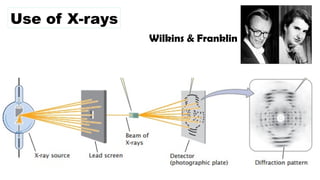
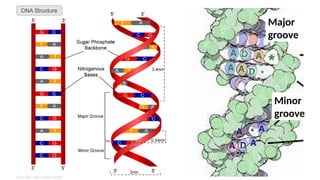
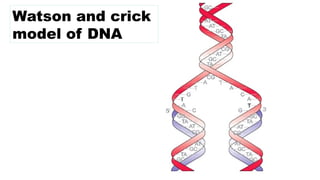
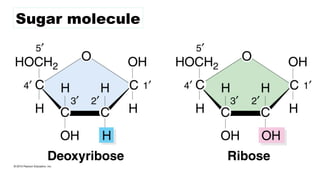
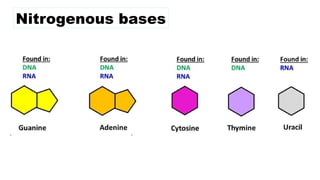
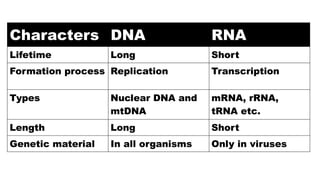
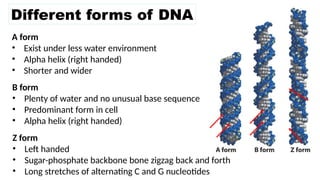
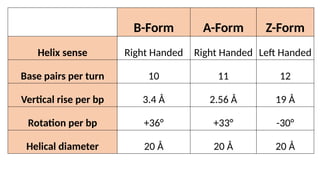
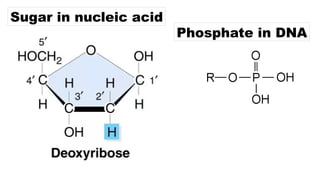
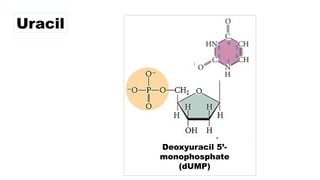
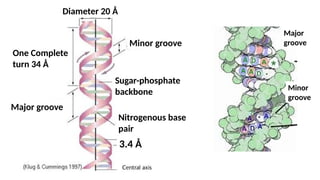
The document discusses nucleic acids, focusing on their structure, composition, and functions in genetics and biotechnology. It covers the components of nucleotides, the transformation principle established by Griffith, and the structural models of DNA proposed by Watson and Crick. Additionally, it differentiates between DNA and RNA and describes various forms of DNA, highlighting their characteristics.