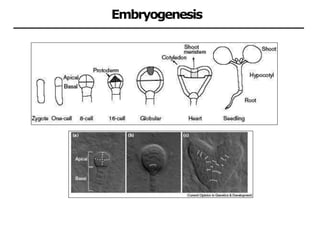
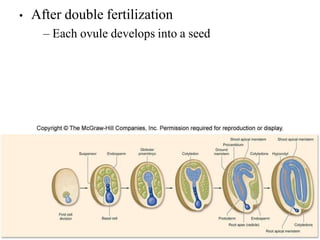
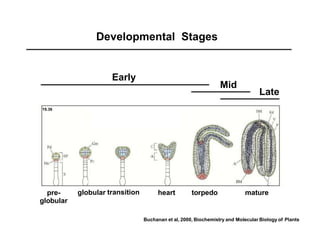
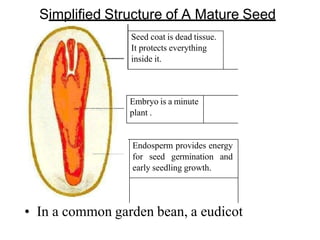
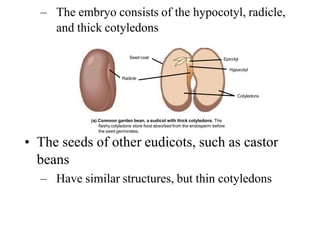
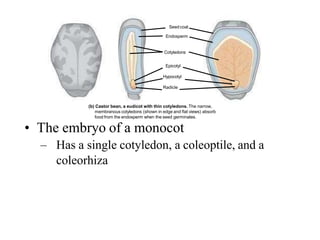
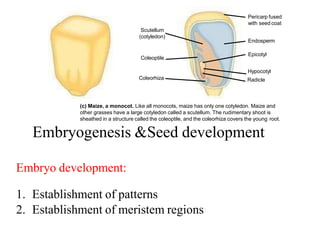
The document discusses embryogenesis in plants, detailing the developmental stages of seeds after double fertilization, including structures like the embryo, seed coat, and endosperm. It differentiates between eudicot seeds, such as common garden beans and castor beans, which have either thick or thin cotyledons, and monocot seeds, like maize, which features a single cotyledon and structures known as coleoptile and coleorhiza. The summary highlights the key components involved in seed development and the establishment of plant patterns.