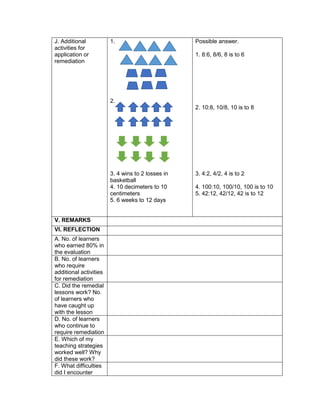
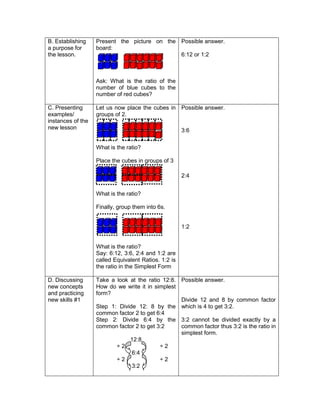
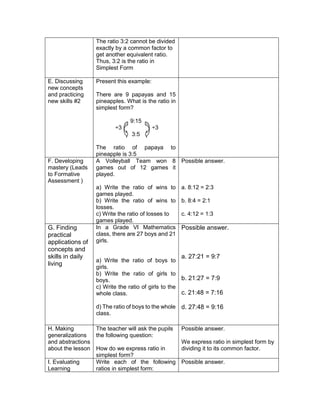
This document outlines a lesson plan on ratios and proportions. The objectives are for students to demonstrate understanding and application of ratios, proportions, and expressing one value as a fraction of another given their ratio. The lesson plan provides examples of ratios of objects and quantities. It discusses different ways to write ratios in word, colon, and fraction forms. Students practice identifying ratios, writing them in simplest form, and applying them to real-world examples like comparing quantities of school supplies. The plan aims to build students' mastery of ratios and their ability to express one value as a multiple of another given their ratio.





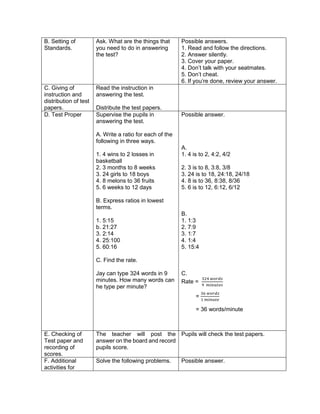





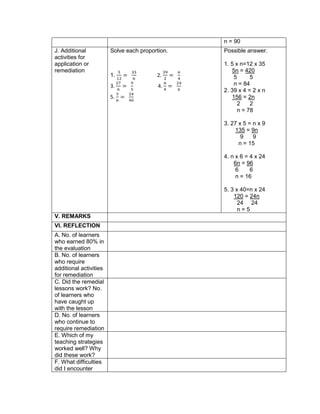




















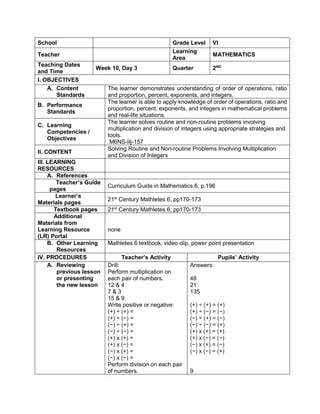
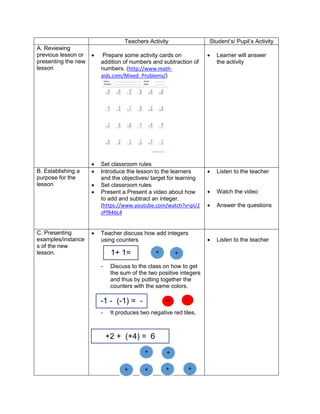
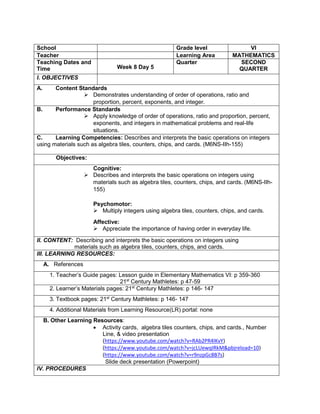
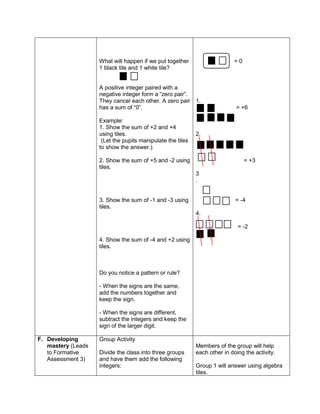
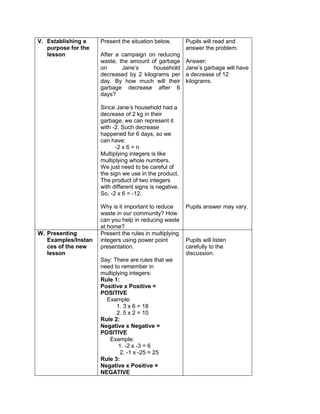
![D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1
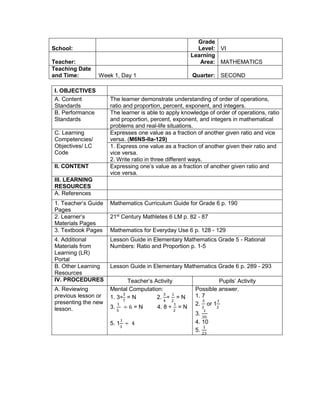
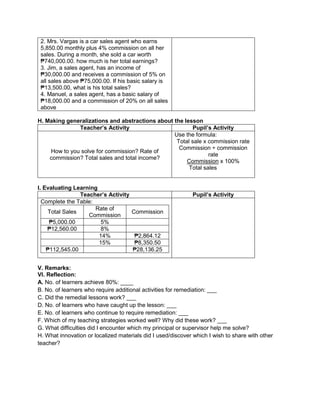
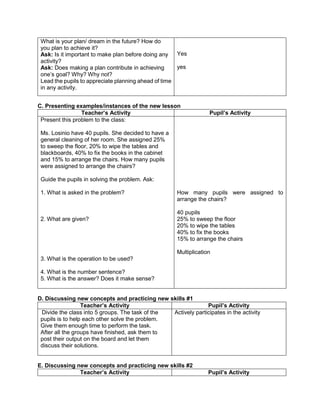
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
Group Activity:
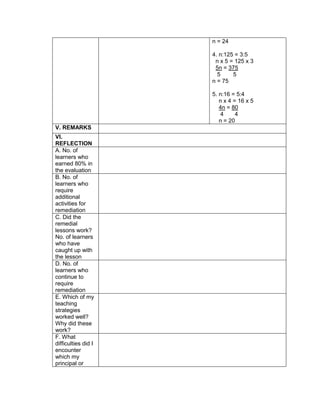
Divide the class into 6 groups with equal number of
members. Give instructions to the pupils on what
they are going to do to complete the activity
Give the following expression for pupils to read and
analyze. With the use of their paper and pen, they
will have to simplify the different expression, thus
answers the questions corresponding the
expression given. Each group is given time to
discuss their answers in front of the whole class
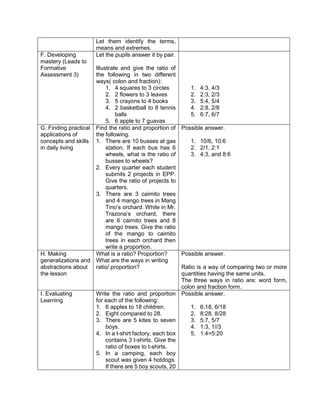
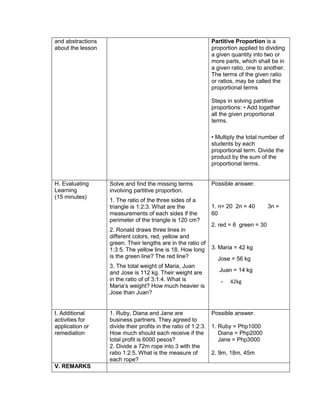
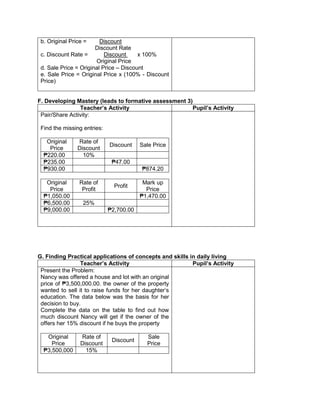
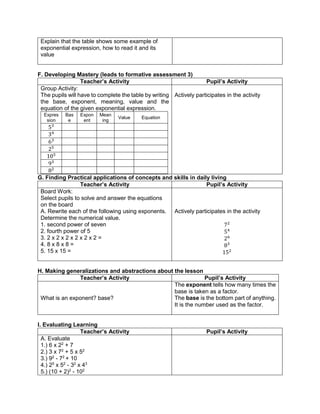
1. Simplify: 2 + (7 x 3) – 5
What is the grouping symbol in the expression?
How many operations do you have to perform to
get the answer?
What operation are you going to perform first?
How are you able to get the correct answer?
What is the answer?
2. Simplify: 3 x 4 ÷ (7 - 5) – 12 ÷ 4
What is the grouping symbol in the expression?
How many operations do you have to perform to
get the answer?
What operation are you going to perform first?
How are you able to get the correct answer?
What is the answer?
3. Simplify: 7 + [ 2 (12 – 5) + 32] – 18 ÷ 3
What is the grouping symbol in the expression?
How many operations do you have to perform to
get the answer?
What operation are you going to perform first?
How are you able to get the correct answer?
What is the answer?
4. Simplify: 4 + [ -1 (-2 – 1)]
What is the grouping symbol in the expression?
How many operations do you have to perform to
get the answer?
What operation are you going to perform first?
How are you able to get the correct answer?
What is the answer?
5. Simplify: 5 – [4 + 2 x 23
) ÷ 10]
What is the grouping symbol in the expression?
How many operations do you have to perform to
get the answer?
What operation are you going to perform first?
How are you able to get the correct answer?
What is the answer?
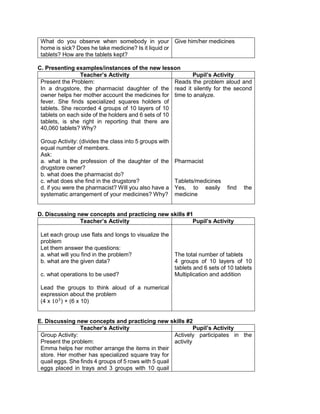
6. Simplify: 42 – 4 x 32
+ 2(5 − 2)3
What is the grouping symbol in the expression?
Performs the activity with their group mates,
discusses among themselves what is the
correct answer…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlp-math-6-240207152821-44927f5c/85/DLP-MATH-6-docx-103-320.jpg)
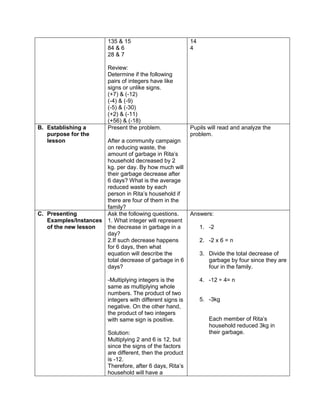
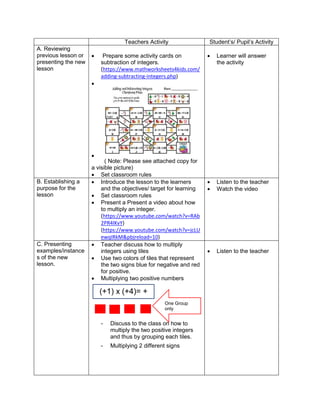
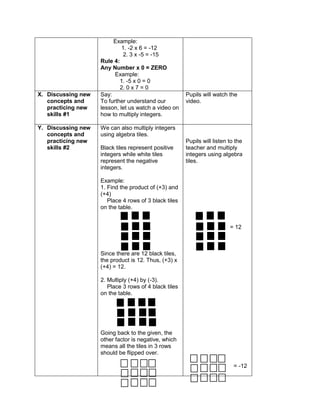
![How many operations do you have to perform to
get the answer?
What operation are you going to perform first?
How are you able to get the correct answer?
What is the answer?
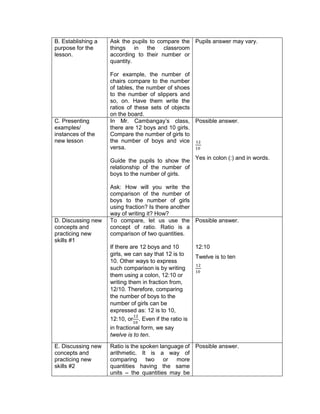
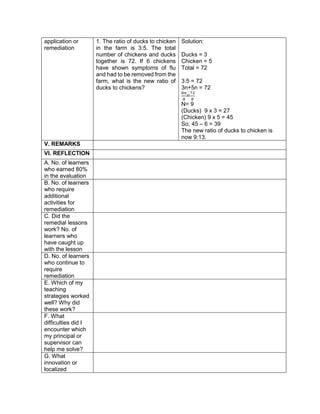
E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
Each group of pupils will be given time to
report/discuss their answers in front of the whole
class. The teacher guides each group. The teacher
helps the pupils on how to simplify the equation. Let
them know what to do in order to arrive for the
correct answer.
Explain about:
How to apply the GEMDAS RULE (grouping
symbols, exponents, multiplication, Division,
addition and subtraction)
group reporting
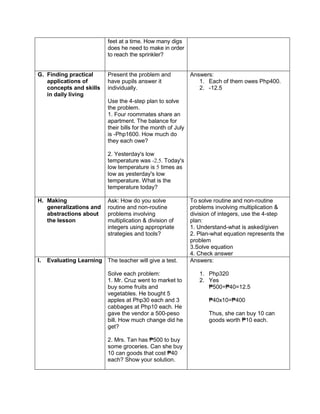
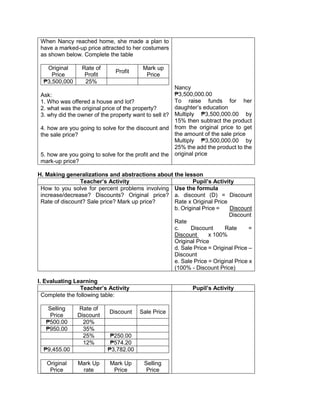
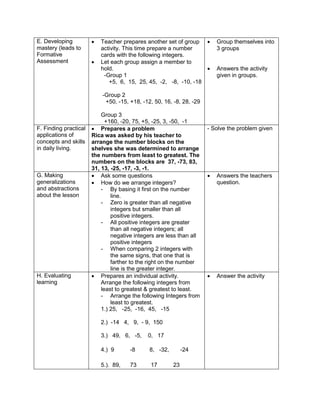
F. Developing Mastery (leads to formative assessment 3)
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
Perform the Indicated operations.
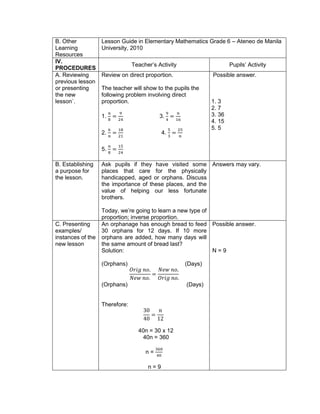
1. 2 ( -5) + (-3) (-7)
2. 27 ÷ (-9) – (3) (-2)
3. 16 + (42 – 2 x 3) – 34
4. 42 ÷ 7 x [37 ÷ 3 – 8]
5. 32 + 2 [5 x (24 – 6)] – 48 ÷ 24
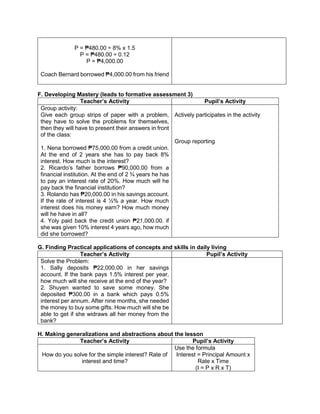
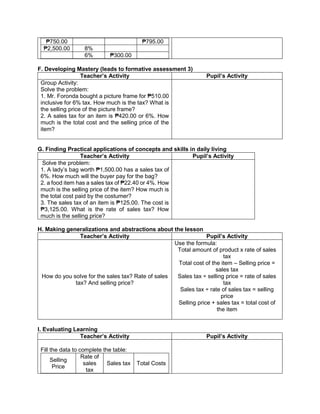
G. Finding Practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
Solve each Problem:
Klein has 42,500.00 in his bank account. Over the
summer period, he made 3 withdrawals of 8,500.00
each and a deposit of 13,250.00 write an order of
operations to represent this situation
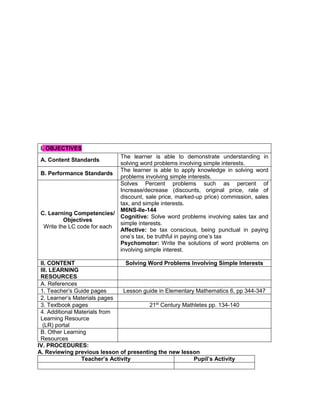
H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
Guide the pupils to give the following
generalizations by asking: What rule would you
follow in order to perform the order of operation?
What does GEMDAS rule mean?
-simplify the operations in grouping
symbols. Start from the innermost
grouping symbol.
-evaluate exponential expressions
-multiply and divide in order they appear
from left to right
Add and subtract in order they appear
from left to right.
Means grouping symbols, exponents,
multiplication, division, addition, and
subtraction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlp-math-6-240207152821-44927f5c/85/DLP-MATH-6-docx-104-320.jpg)


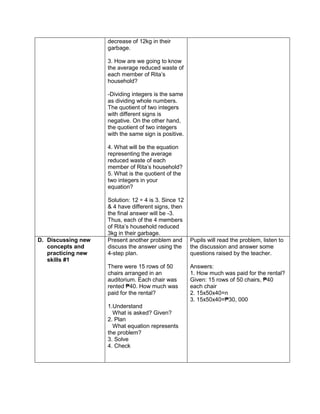
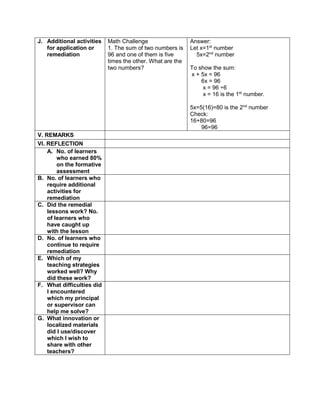
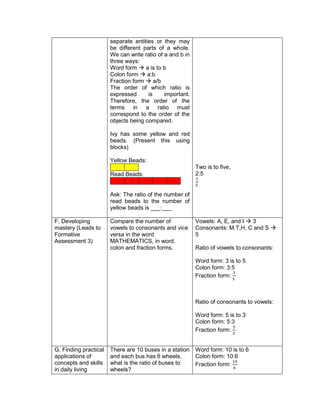
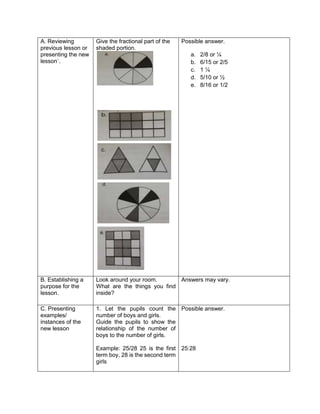
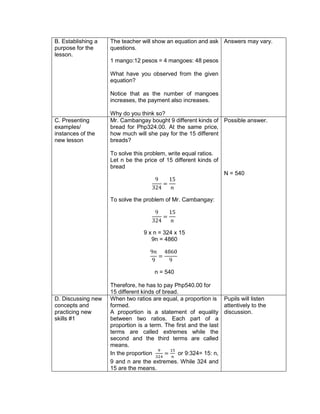
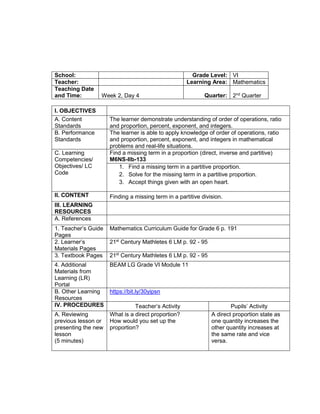
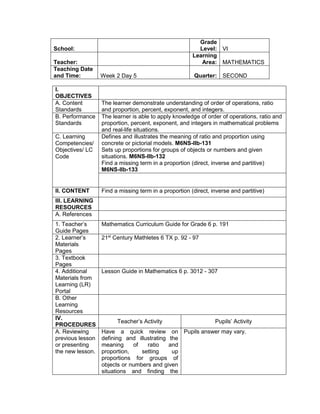
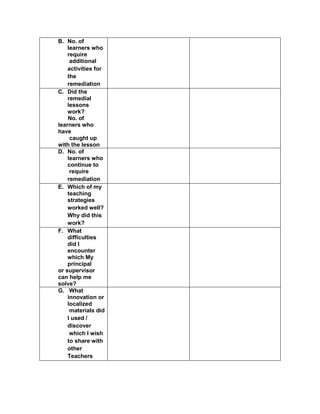
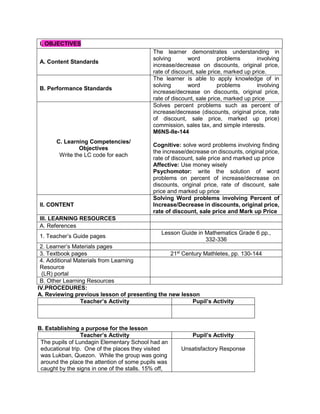
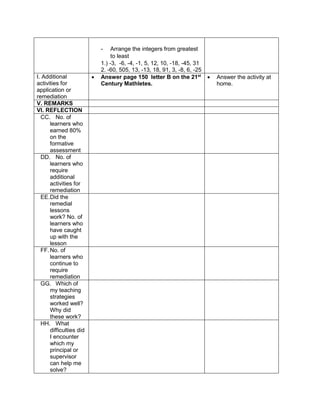
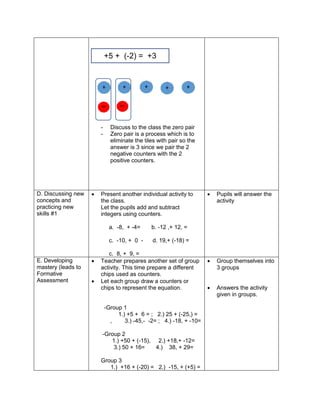
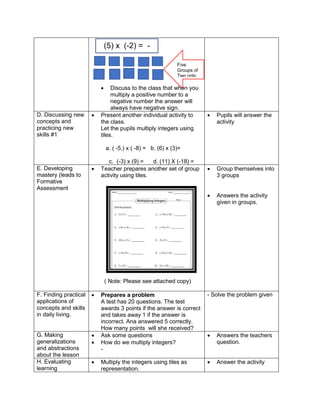
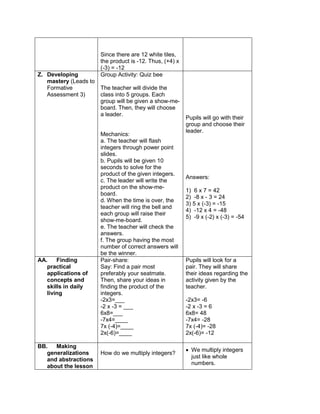
![eggs. She informs her mother that they have 1030
quail eggs. Is she right? Why?
Ask each group to answer the following questions:
1. Who helps her mother in the store?
2. What does Emma do to help her mother?
3. What facts are given?
4. how are you going to solve for the answer?
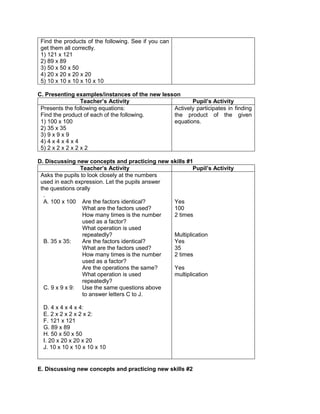
5. ask them to evaluate the numerical expression:
(4 x 52
) + (3 x 10)
(4 x 25) + (3 + 10)
100 + 30
130
Have the pupils analyze which operation should be
performed first, second, next to arrive at the answer
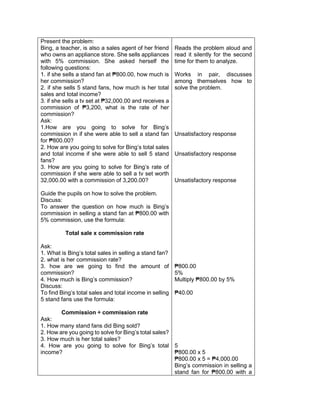
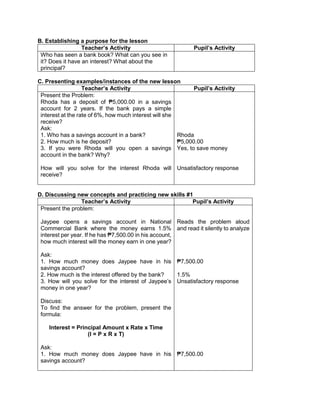
F. Developing Mastery (leads to formative assessment)
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
Activity 3: Group Activity
Bing asks her son to do his homework and looks
at his notebook. She finds the following:
Evaluate the expressions:
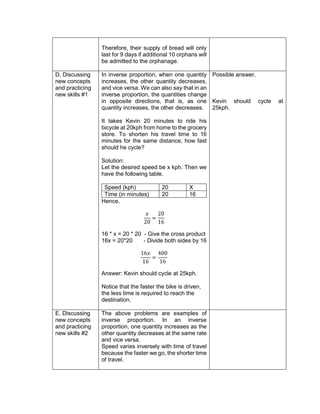
1) 6 + (2 x 7 + 52
)
2) 3 x (4 x 82) – 8
3) 5 x [24 2 x (10 – 8)2 10]
4) (15 – 6) + (4 – 1) x 23
5) 3 x [3 + 2 x (10 – 32)]
Ask each pair of pupils to answer the questions
below, let each group solve the given equations
on the board, allow them to explain their answers
in front of the class.
1) What are the facts given?
2) Which operation should be done first? second?
third? last? Why?
b) Have each pair of pupils evaluate the
expressions.
Actively participates in the
activity
Group reporting
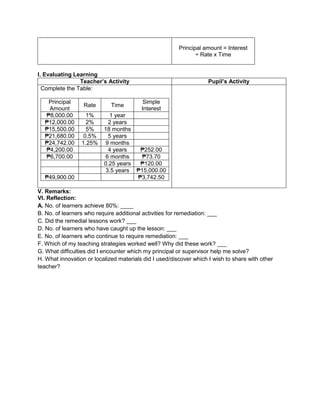
G. Finding Practical applications of concepts and skills in daily living
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
Think-Pair-Share Activity:
Pupils are given the freedom to choose their
partners for the activity:
Evaluate the ff. expressions:
a) (114 – 4) x (12 ÷ 4)2 + 3
b) 16 + 82 ÷ (4 + 4)
c) (36 – 6) x (3 x 4)2 + 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlp-math-6-240207152821-44927f5c/85/DLP-MATH-6-docx-108-320.jpg)
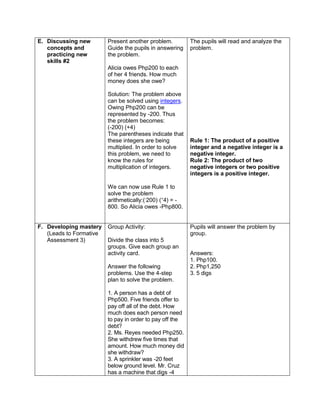
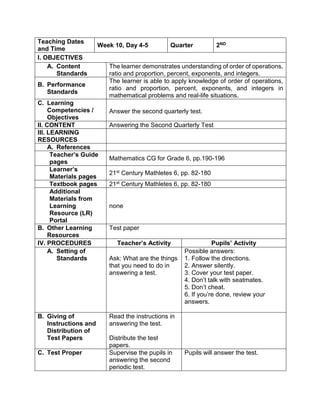
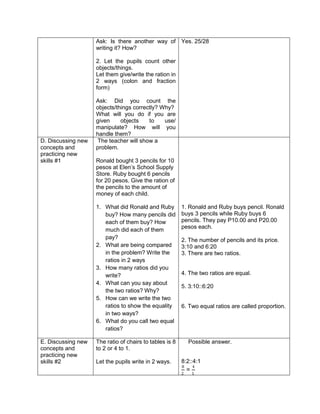
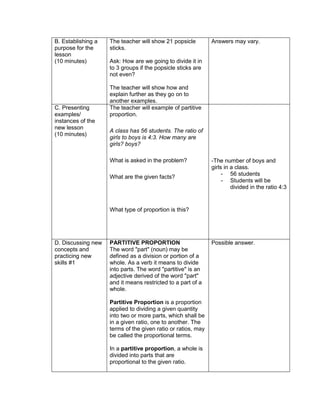
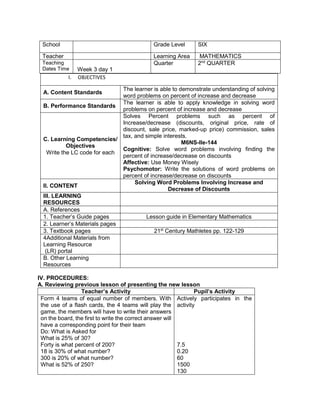
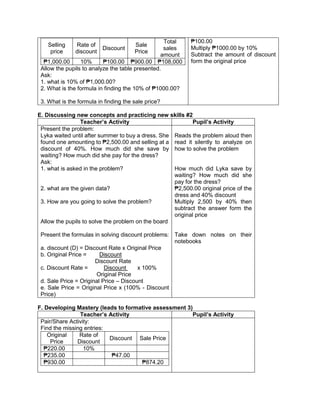
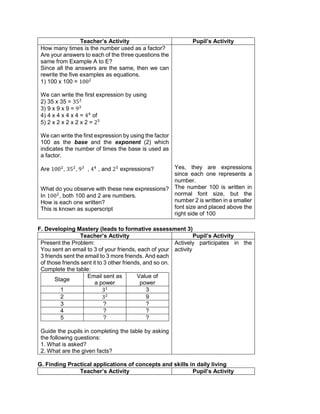
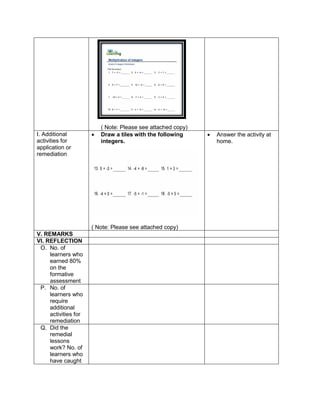
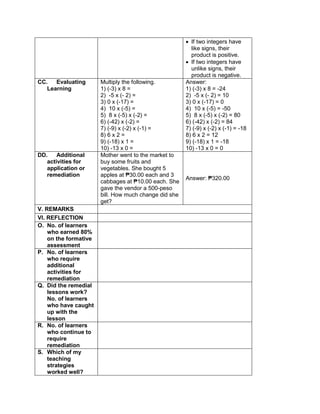
![d) 122 x 30 + (890 ÷ 2)
e) 62 x 23 + (400 ÷ 2)
H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
How do we evaluate an expression with more
than two operations with exponents and
parenthesis/grouping symbols?
Apply the GEMDAS RULE
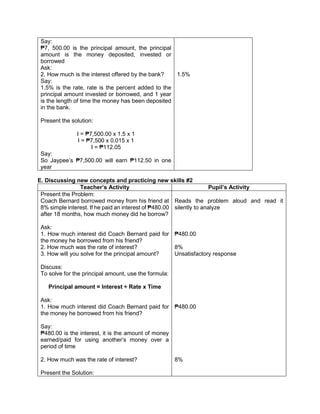
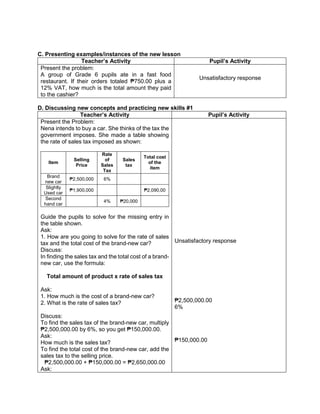
I. Evaluating Learning
Teacher’s Activity Pupil’s Activity
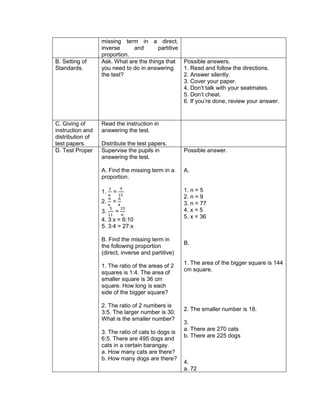
1.Evaluate the following expressions:
a) (9 – 2) + (32 x 21)
b) (18 + 14) ÷ (6 + 2)
c) 36 ÷ 22 + 4 x (4 – 2)
d) (36 – 6) + [(3 x 42) + 7]
e) (72 + 15) x 4 –
f) 4 x (15 – 32) + 16
g) (93 + 7) x 6 + 10
h) 12 x 30 + (890 ÷ 10)
i) [(144 ÷ 12)2 x 3] ÷ 3 x 6
j) (16 + 82) ÷ (4 + 4)
2.Evaluate the expression if: a) R = 2
1.[(6R + R x 8) ÷ 13] – 5 + R
2. S = 3 [(7S – S) x 6] + 6S – S x 5
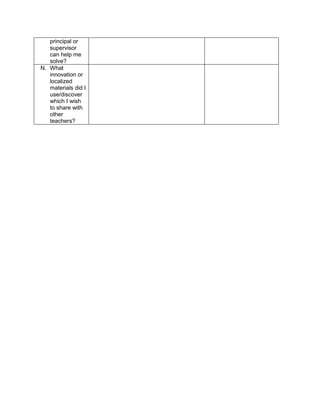
V. Remarks:
VI. Reflection:
A. No. of learners achieve 80%: ____
B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation: ___
C. Did the remedial lessons work? ___
D. No. of learners who have caught up the lesson: ___
E. No. of learners who continue to require remediation: ___
F. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? ___
G. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor help me solve?
H. What innovation or localized materials did I used/discover which I wish to share with other
teacher?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlp-math-6-240207152821-44927f5c/85/DLP-MATH-6-docx-109-320.jpg)




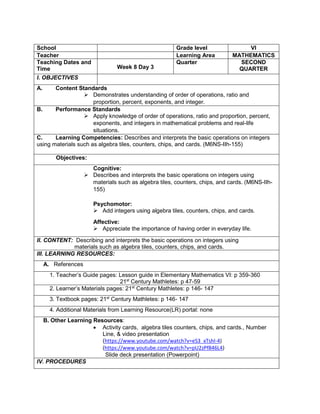
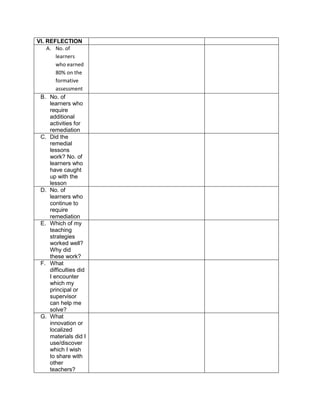









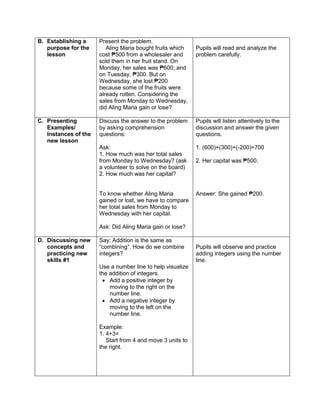

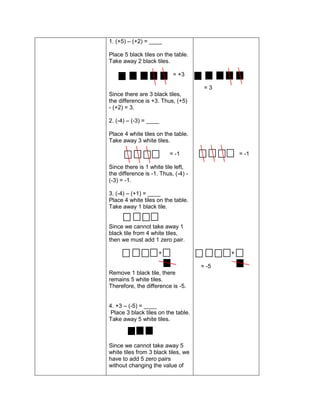




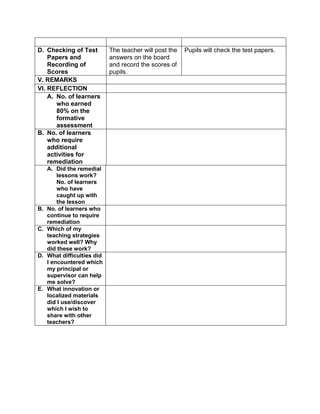
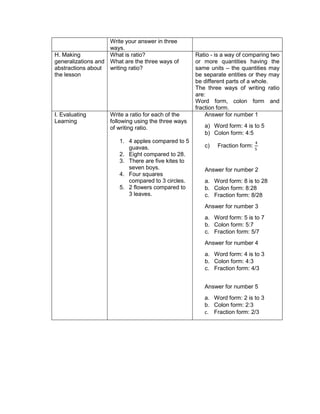
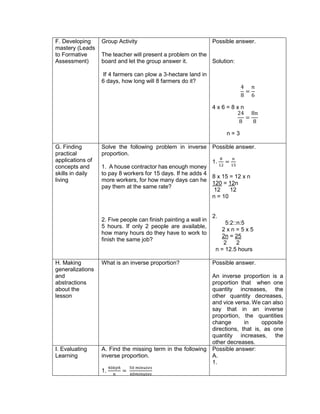
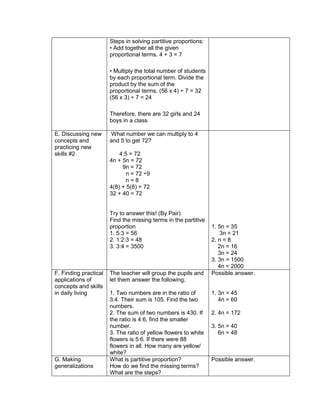
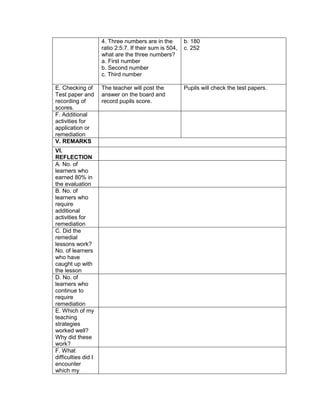
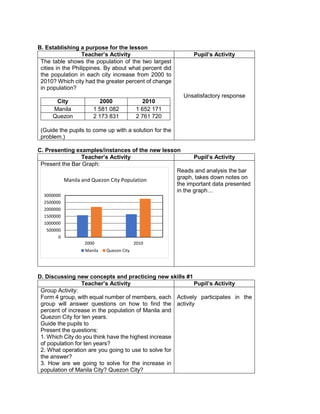
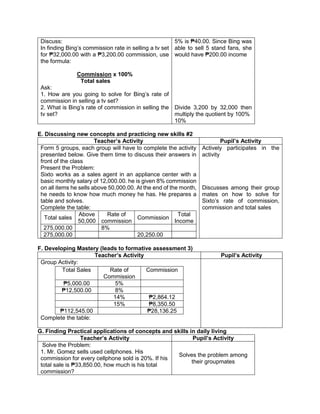
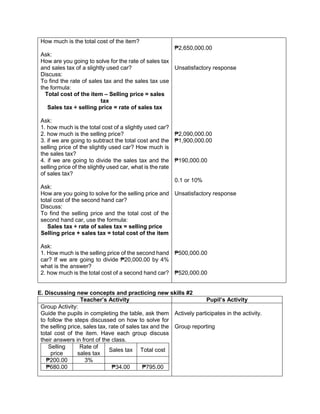
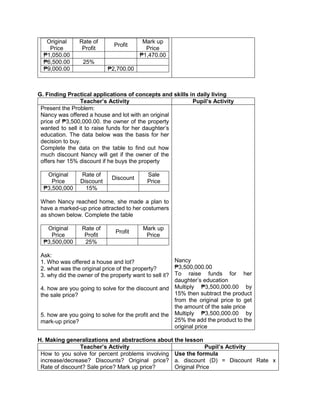
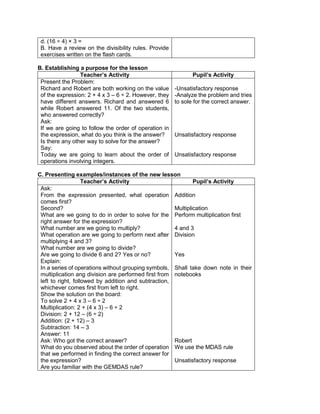
![The temperature in
Baguio City was 12°
Celsius in the morning.
It dropped to 8° Celsius
in the evening. What is
the difference between
these temperatures?
C. Presenting
Examples/Instances
of the new lesson
Ask the following
questions.
1. What is asked?
2. What is the equation
representing this
situation?
3. What is the difference
between the
temperature of Baguio in
the morning and
evening?
To get the difference
between the two
temperatures, we need
to subtract 8° from 12°.
Answer:
12°- 8° = 4°
D. Discussing new
concepts and
practicing new skills #1
Present another
problem.
During summer, James
weighed 65 kg. When
he came back to school,
he realized that he lost 3
kg. He lost another 2 kg
in December. What was
his weight in December?
1. What is asked?
2. What are given?
3. What is the equation
representing the
situation?
4. What is the final
answer?
Answer:
1. What was his weight in
December?
2. 65 kg, 3kg, 2kg
3. 65-3-2=n
4. 65-3-2=n
=65+(-3)+(-2) [rule in subtracting
integer]
=60kg
E. Discussing new
concepts and
practicing new skills #2
Pair-share:
Answer the problem by
pair.
At sunrise, the outside
temperature was 1°
below zero. By lunch
time, the temperature
rose by 17° and then fell
by 4° by night. What
Pupils will find a partner and answer
the given problem together.
Solution:
The starting temperature is 1° below
zero, or -1°.
Later, the temperature rose, or went
up, by 17°.
Then, the temperature fell, or went
down, by 4°.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlp-math-6-240207152821-44927f5c/85/DLP-MATH-6-docx-193-320.jpg)
![was the temperature at
the end of the day? Equation:
-1° + 17° - 4°= -12°
F. Developing mastery
(Leads to Formative
Assessment 3)
Group Activity:
The teacher will divide
the class into 5 groups
and give the activity
card.
Solve the problem.
1. The highest point in
Asia is Mount Everest at
8850 meters. The shore
of the Dead Sea, the
lowest point in Asia, is
about 410 meters below
sea level. What is the
difference between
these elevations?
2. In Fairfield, Montana,
on December 24, 1924,
the air temperature
dropped a record
amount. At noon, the
temperature was 63°F.
Twelve hours later, the
temperature was 21°F.
What was the change in
temperature?
Pupils will answer the problem by
group and report their answer to the
class.
Solution:
Use integers to represent the two
elevations.
Mount Everest: +8850m
Dead Sea: -410 m
Find the difference of 8850 and 410
meters.
8850 -(- 410)
=8850 + 410 [Rule for subtracting
integers]
=9260
ANSWER: The difference between
the elevations is 9260 meters.
2. Solution:
Change in temperature = end
temperature - start temperature
=21 - 63 (Substitute values.)
= 21 + (-63) [Rule for subtracting
integers]
= -42
ANSWER:
The change in temperature was -42,
so the temperature dropped 42°F.
G. Finding practical
applications of
concepts and skills in
daily living
Individual Activity
Solve the problem.
1. In the Sahara Desert
one day it was 136°F.
In the Gobi Desert a
temperature of -50°F
was recorded. What is
the difference between
these two
temperatures?
Answer:
136° - (-50°)=n
136° + (50°) = 186°
The difference between the two
temperature is 186°F.
H. Making generalizations
and abstractions about
the lesson
Ask: How do you solve
routine and non-routine
problems involving
subtraction of integers
using appropriate
strategies and tools?
To solve routine and non-routine
problems involving subtraction of
integers, know what is asked and
given, formulate the equation to
represent the problem, solve the
equation and check your answer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlp-math-6-240207152821-44927f5c/85/DLP-MATH-6-docx-194-320.jpg)