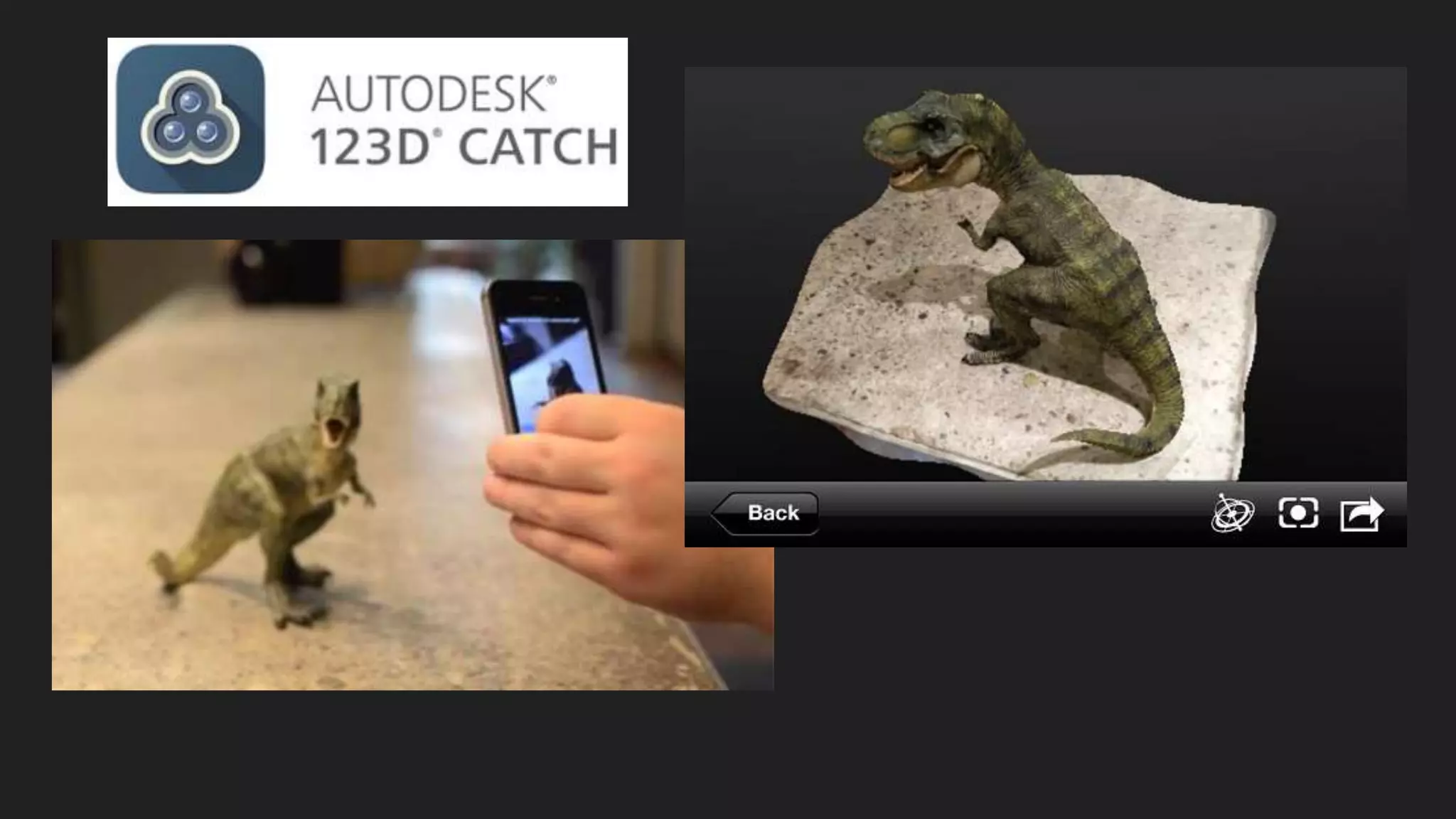
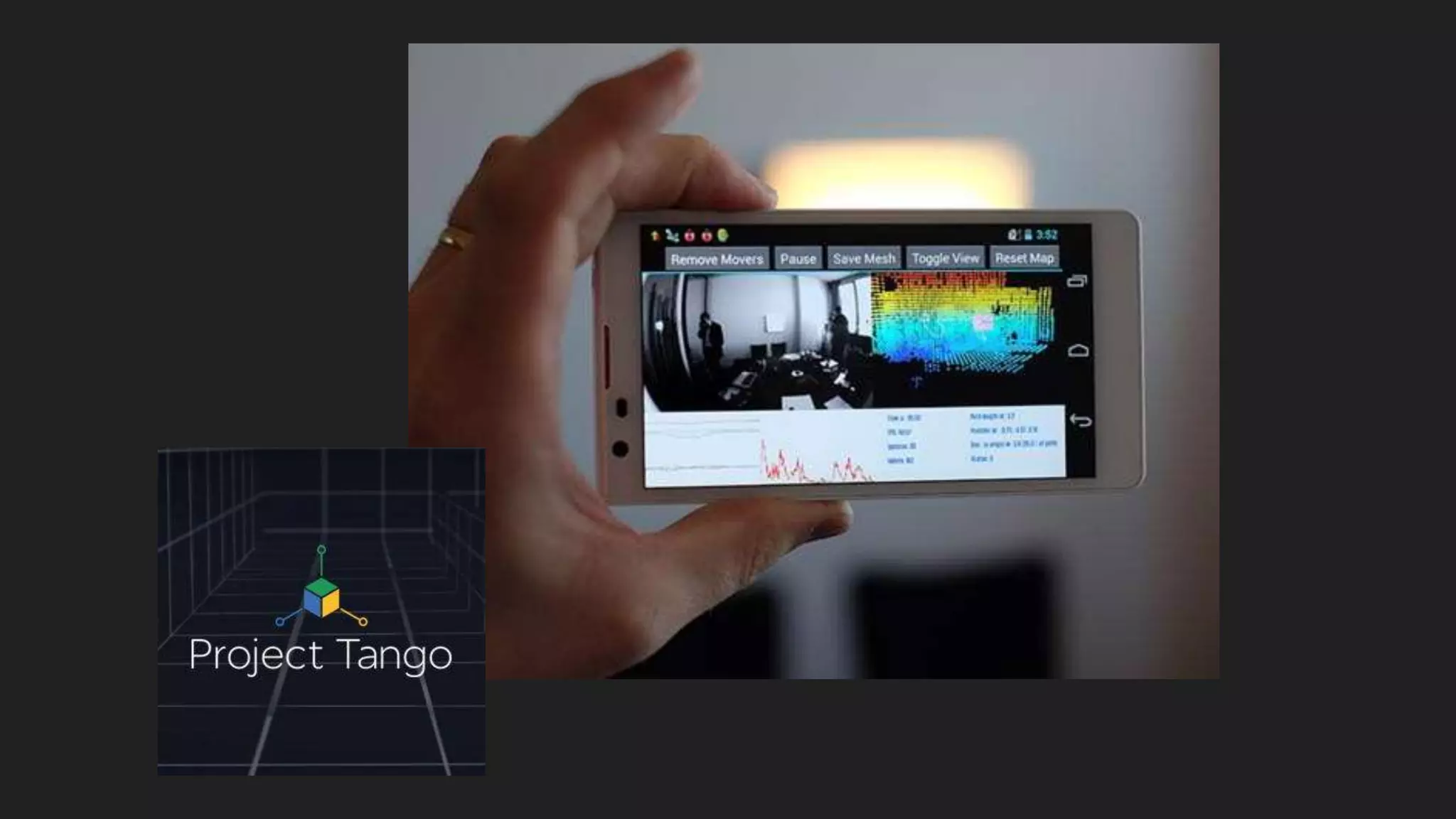
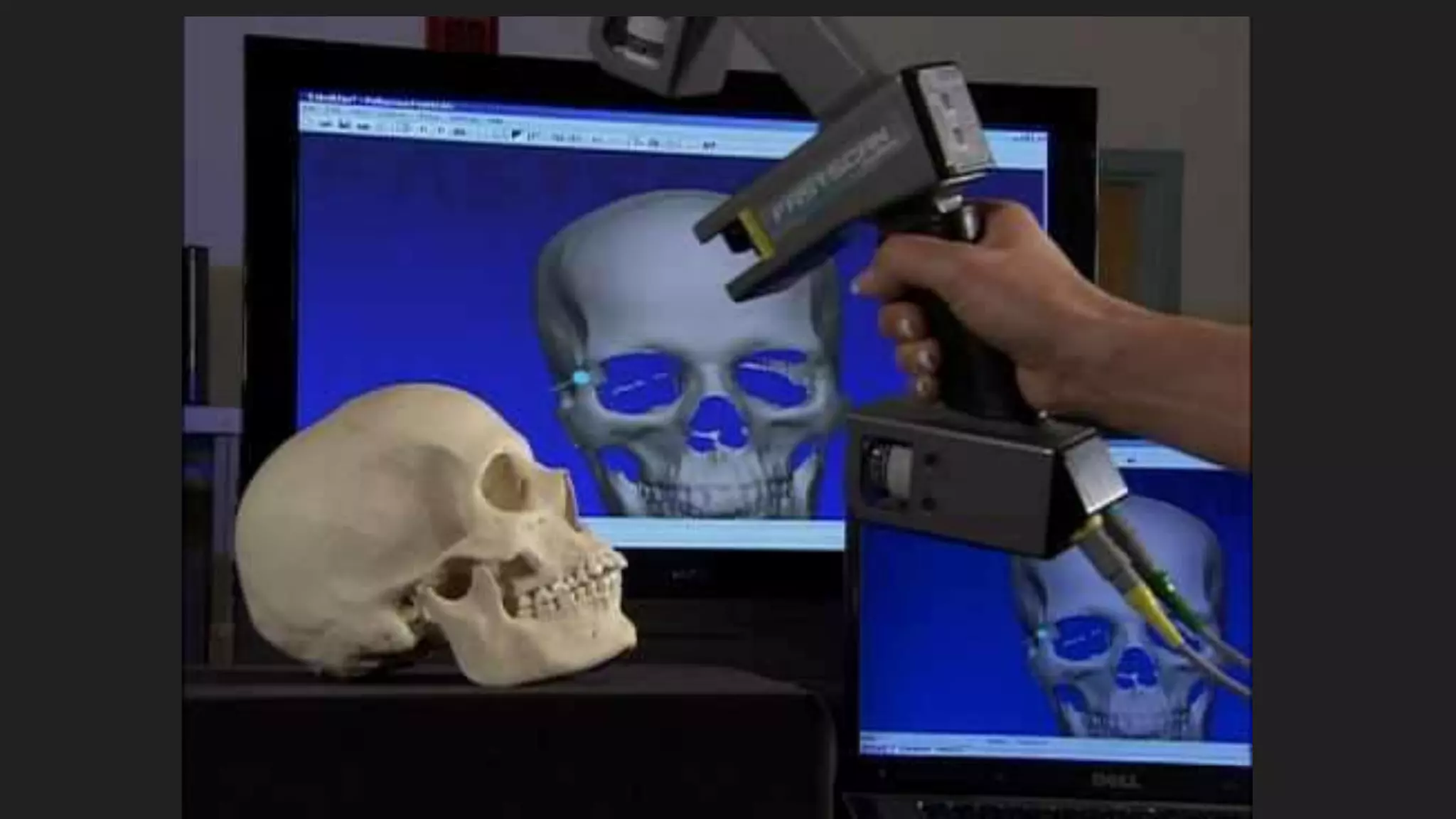
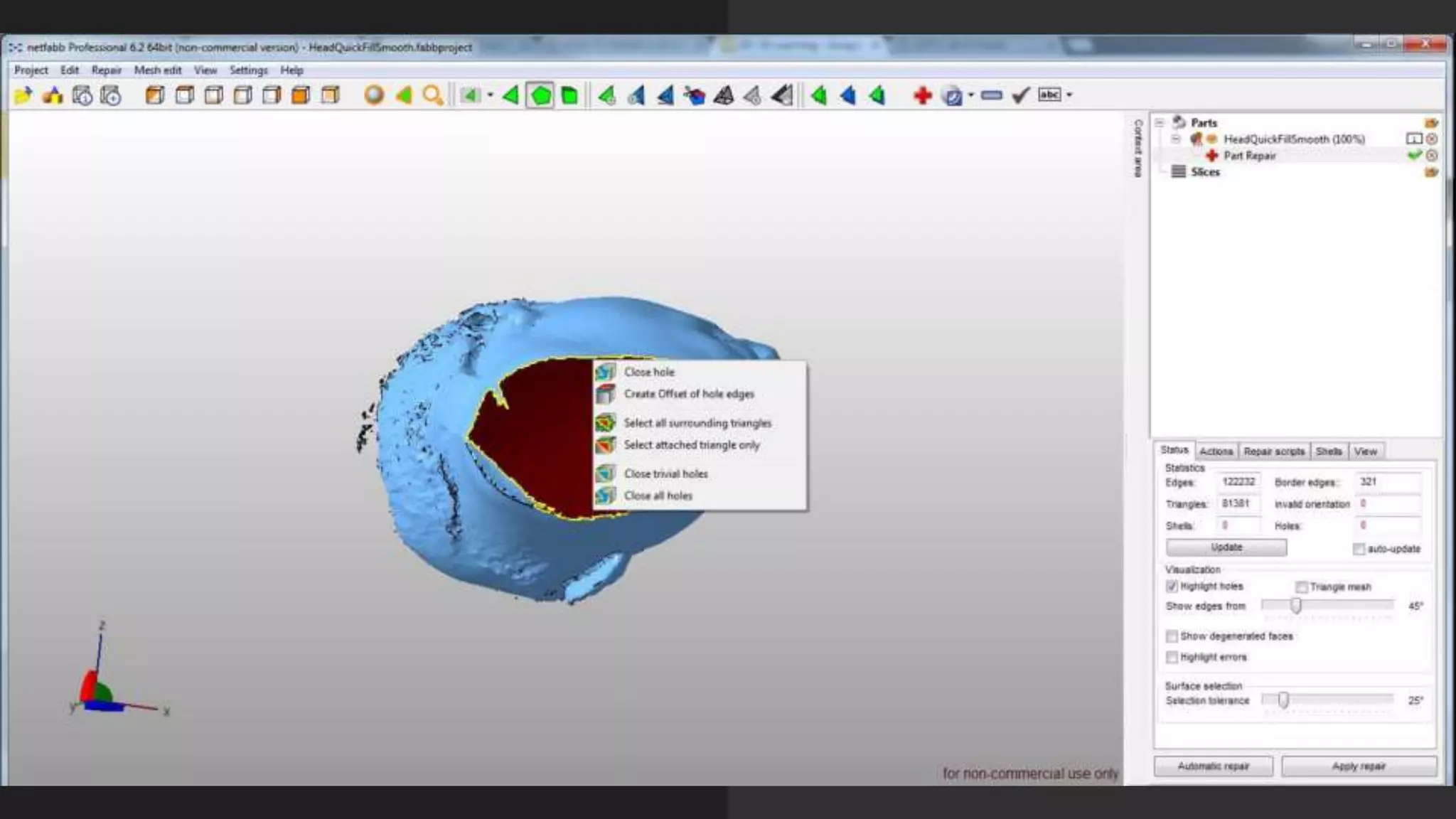
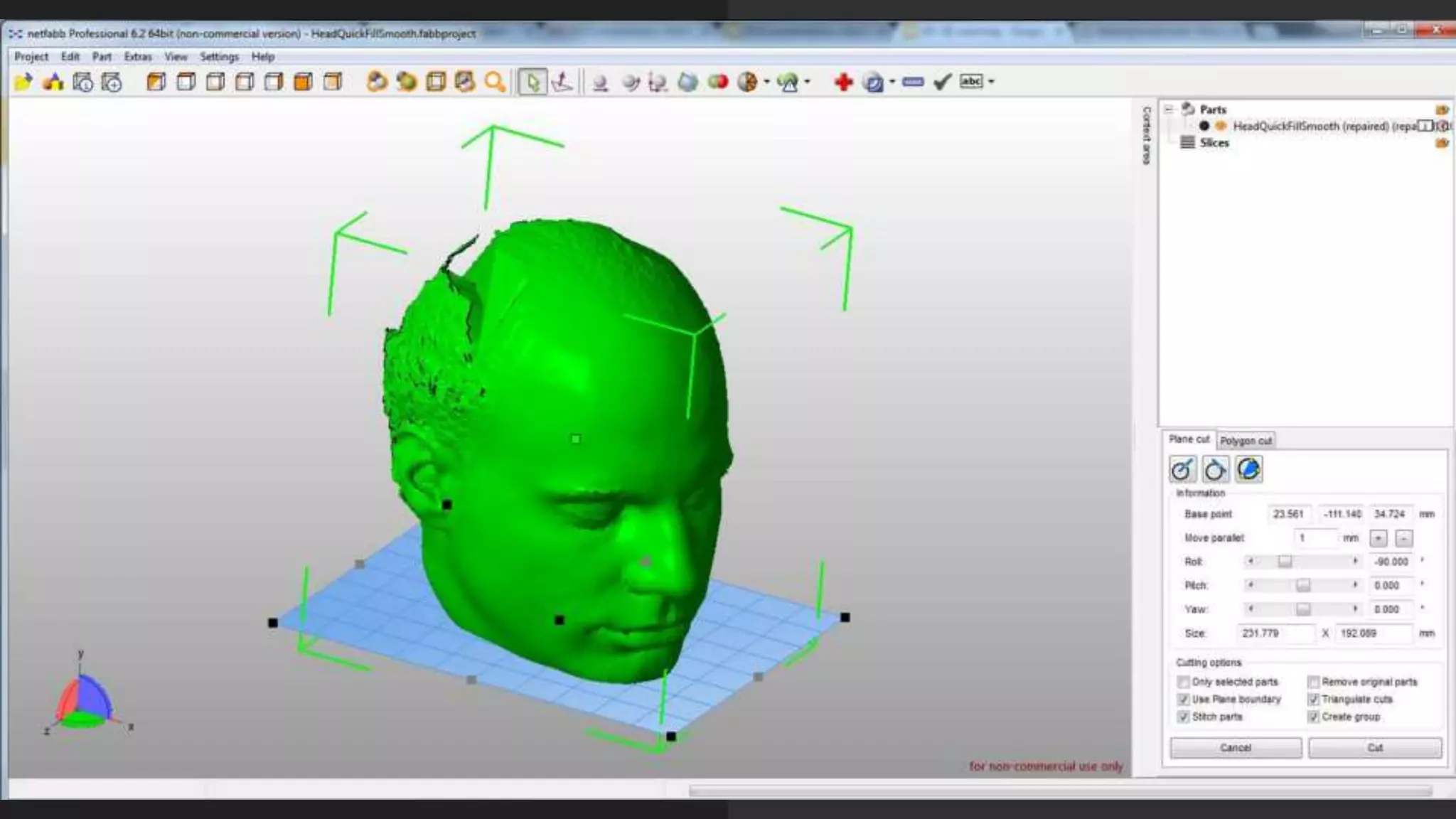
This document provides an overview of DIY 3D scanning techniques for 3D printing, including types of scanning methods and instructions for setting up Kinect and DAVID scanning. It also outlines the file preparation workflow needed to repair scanned files, including filling holes, smoothing, and fixing geometry issues, in order to produce a watertight STL file suitable for 3D printing.