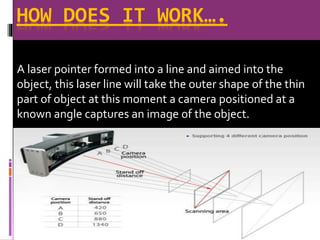
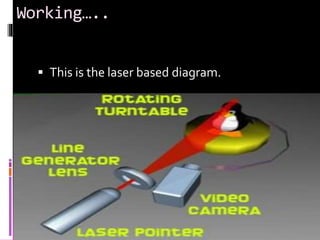
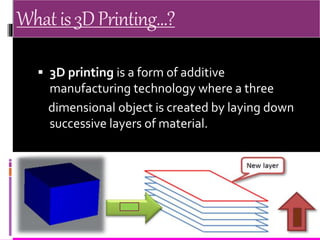
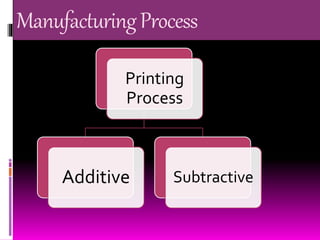
3D scanning involves analyzing and collecting data about a real object's shape and appearance to build a digital 3D model. It works by using a laser line and camera to capture images of an object's surface from different angles. The images are then combined to form point clouds depicting the object's geometric features. 3D scanning has applications in reverse engineering, entertainment, cultural artifact documentation, and face scanning. 3D printing involves layer-by-layer deposition of material according to a digital 3D model to physically create an object. It has uses in manufacturing, medical procedures, research, product prototyping, construction, and more. The presenter proposes integrating 3D scanning and printing further, such as by adding a touchscreen to