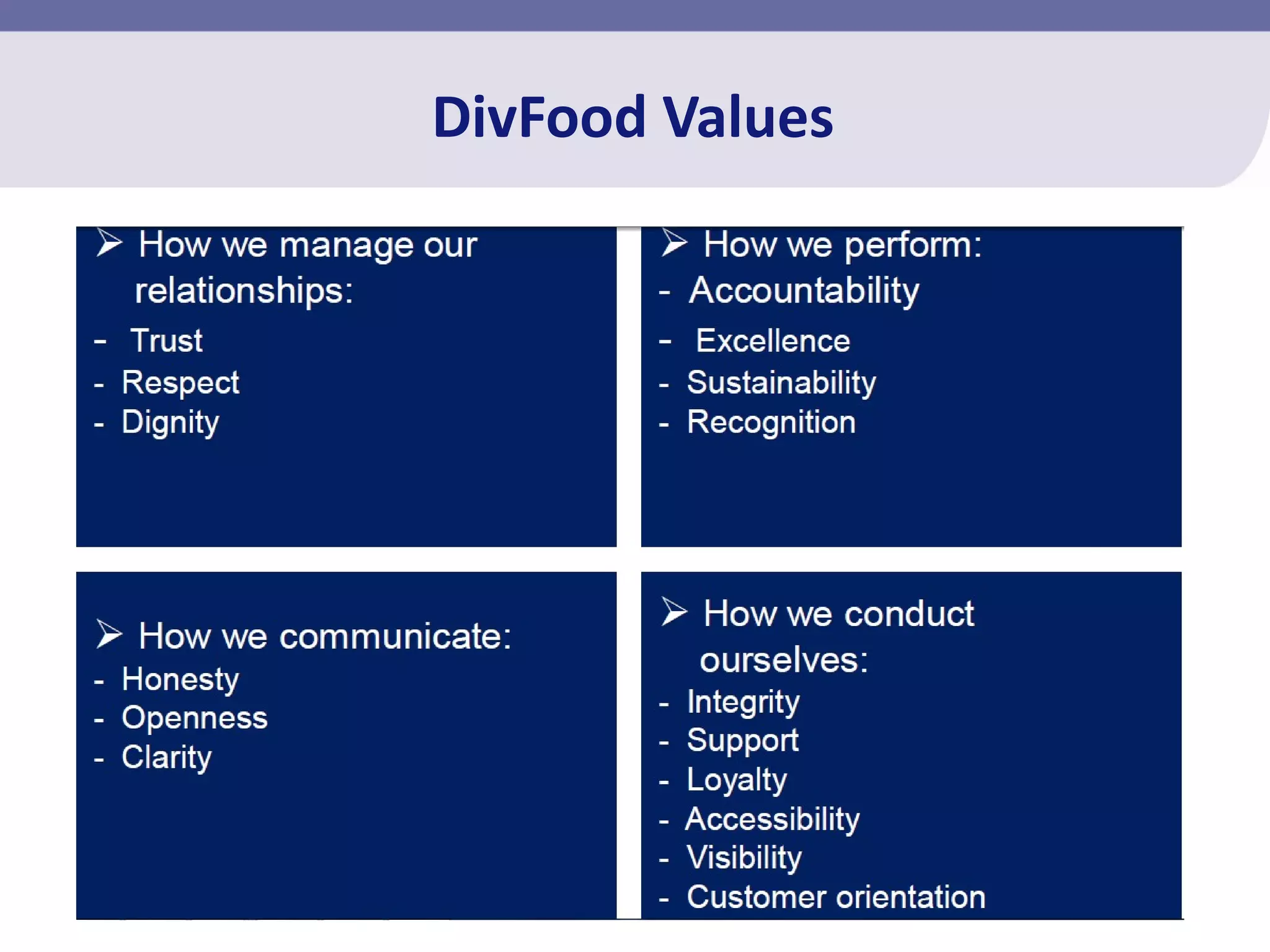
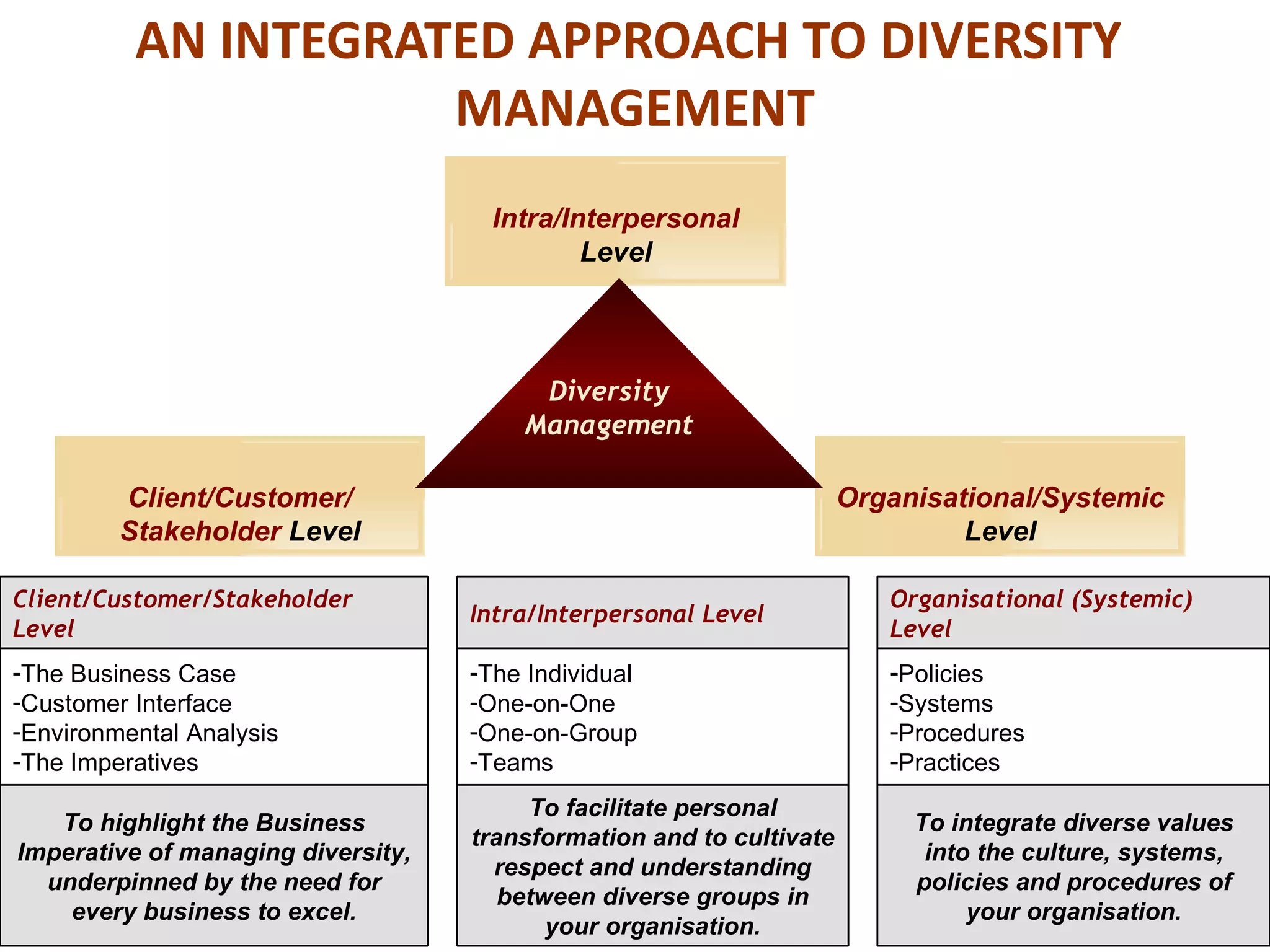
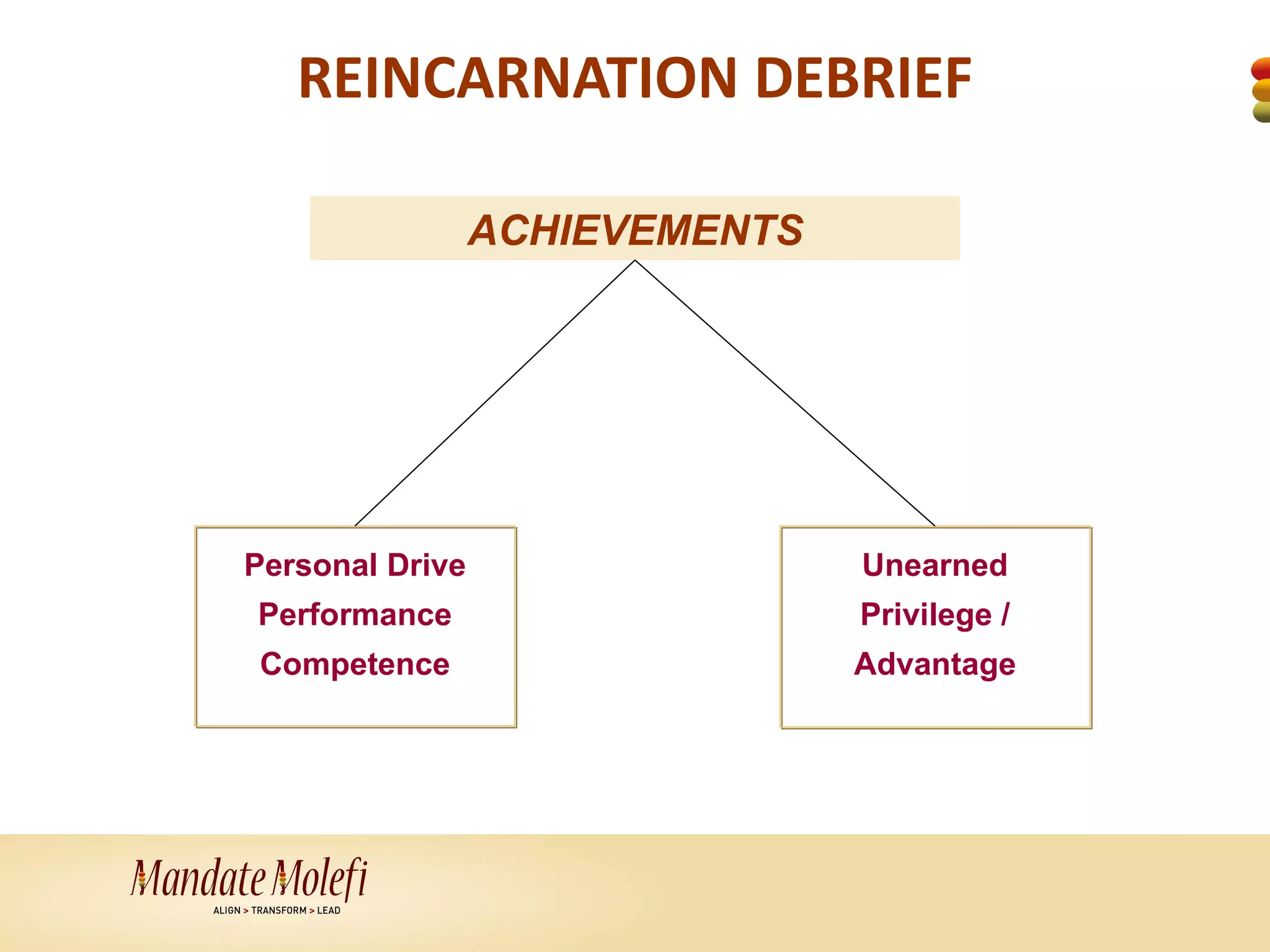
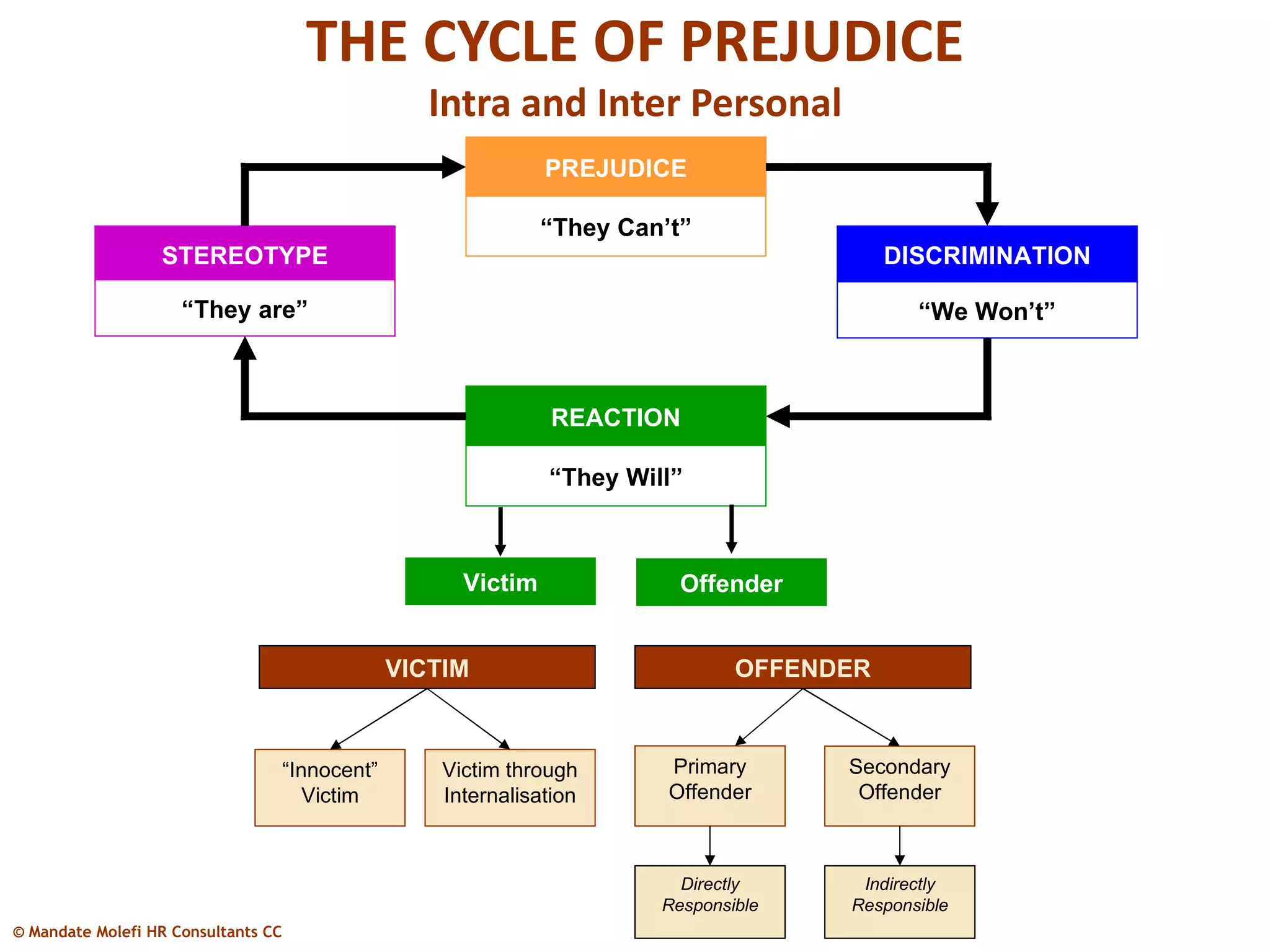
This document summarizes a diversity management workshop. The objectives of the workshop are to:
1) Cultivate respect and understanding between diverse individuals within the company.
2) Provide a platform for participants to engage in crucial diversity conversations.
3) Share knowledge on diversity and its impact on society, demographics, legislation, and the workplace.
The workshop covers definitions of diversity, global and South African diversity perspectives, limiting values within the company's culture, and the Employment Equity Act. Interactive exercises are used to facilitate personal transformation and understanding between diverse groups within the organization.