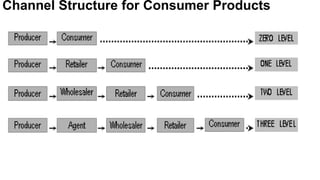
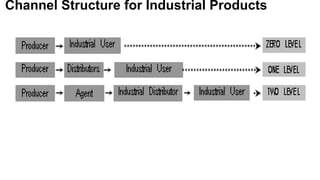
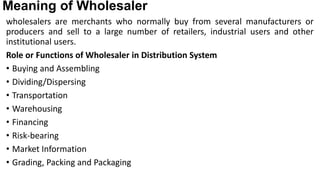
The document discusses the concept of distribution, highlighting its two main components: channels of distribution and physical distribution. It covers the roles of wholesalers and retailers, factors influencing channel selection, channel conflicts and their resolutions, as well as the objectives and functions of marketing logistics. Additionally, it details logistics functions such as transportation, warehousing, order processing, inventory management, and material handling to maximize customer satisfaction and efficiency in distribution.