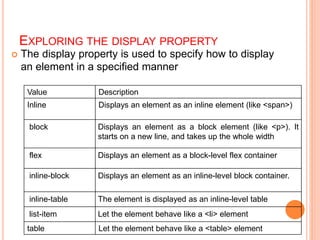
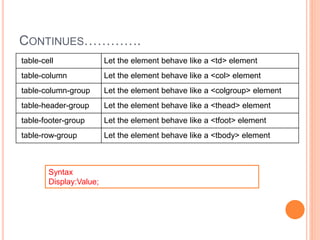
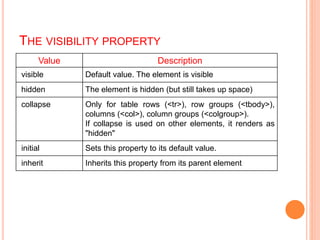
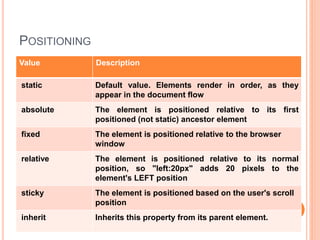
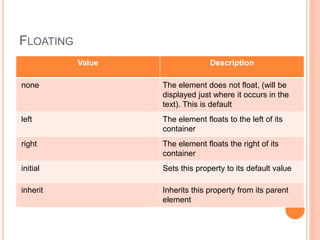
This document discusses controlling the display, positioning, and floating of elements using CSS. It covers the display property for controlling element visibility, the position property for positioning elements relative to the page or other elements, and the float property for floating elements left or right. Specific values for these properties are defined, such as "inline" or "block" for display, "absolute" or "relative" for position, and "left" or "right" for float. Syntax examples are also provided.