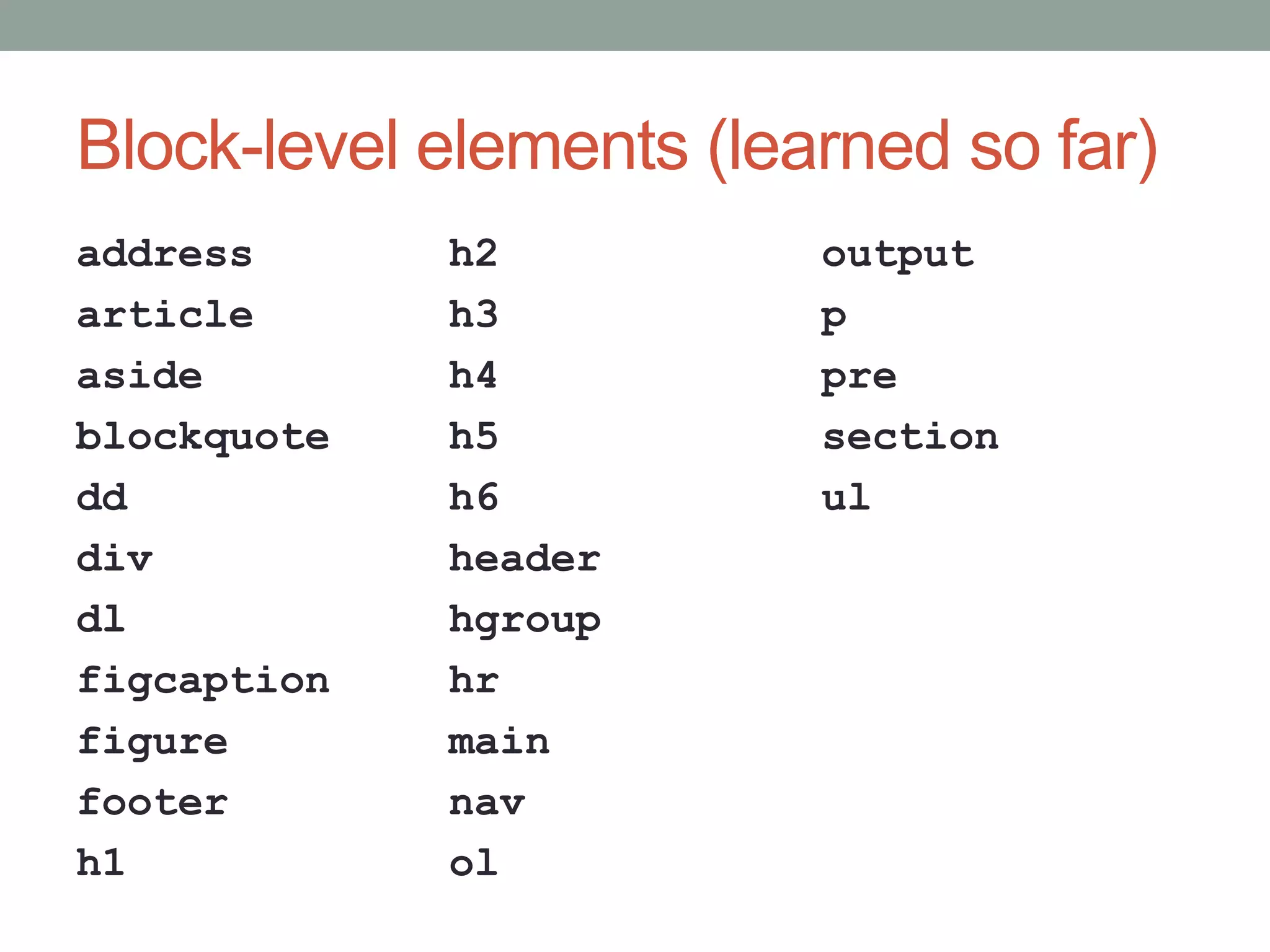
This document discusses block-level elements, inline elements, replaced elements, and the display, float, and clear CSS properties. It defines block-level elements as expanding to fill their container unless floated or positioned, and inline elements as flowing with text. The display property controls layout by setting element presentation type. Float pulls an element out of normal flow while clear prevents elements from moving up next to a floated element.