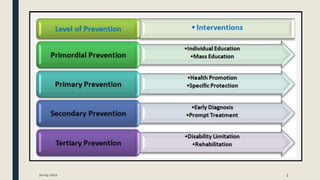
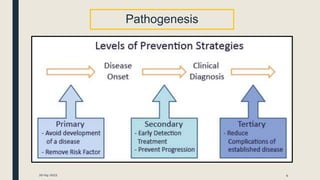
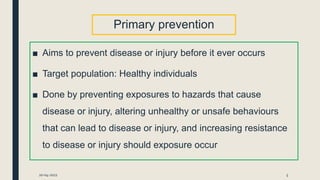
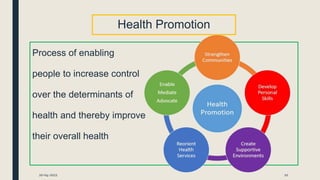
Primary prevention aims to prevent disease before it occurs by targeting healthy individuals. It involves preventing exposures to hazards, altering unhealthy behaviors, and increasing resistance to disease. Examples include legislation promoting safe practices, education on healthy habits like nutrition and exercise, and immunization. Primary prevention can be achieved through health promotion like education and lifestyle changes, or specific protection measures like immunization and chemoprophylaxis. The WHO recommends population and high-risk strategies, with population strategies targeting socioeconomic and lifestyle changes to benefit the whole population, and high-risk targeting at-risk individuals.