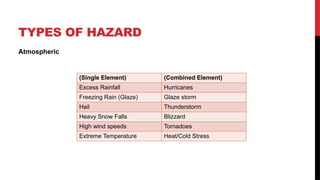
The document discusses the concept of hazards in disaster readiness and risk reduction, defining hazards as elements that can cause harm to people and their environment. It categorizes hazards into natural, quasi-natural, and technological, providing examples for each type and detailing long-term impacts on physical, psychological, socio-cultural, economic, environmental, and biological aspects. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of economic development in recovery and resilience from hazards.