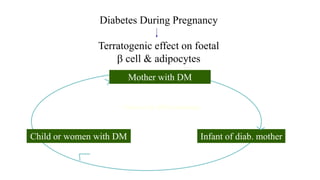
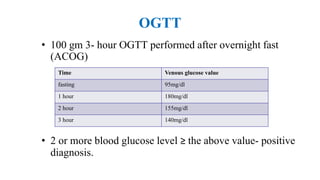
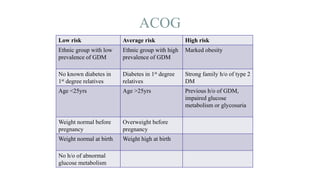
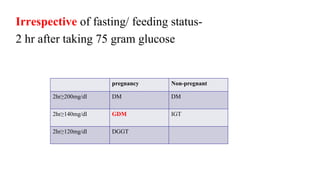
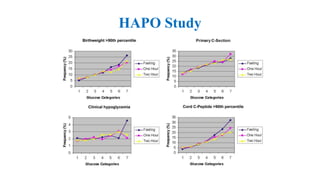
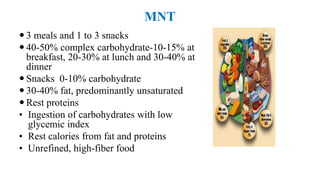
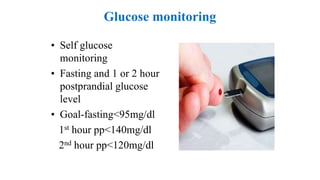
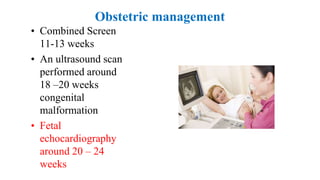
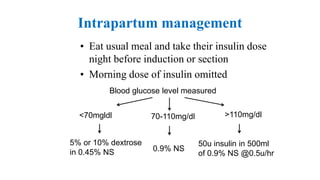
The document outlines guidelines for managing gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), emphasizing the importance of screening, diagnosis, and treatment protocols. It provides specific recommendations for dietary management, exercise, glucose monitoring, and obstetric management, as well as postpartum care and follow-up strategies. The guidelines highlight the need for a multidisciplinary approach and the role of healthcare providers in ensuring proper care for pregnant women with diabetes.