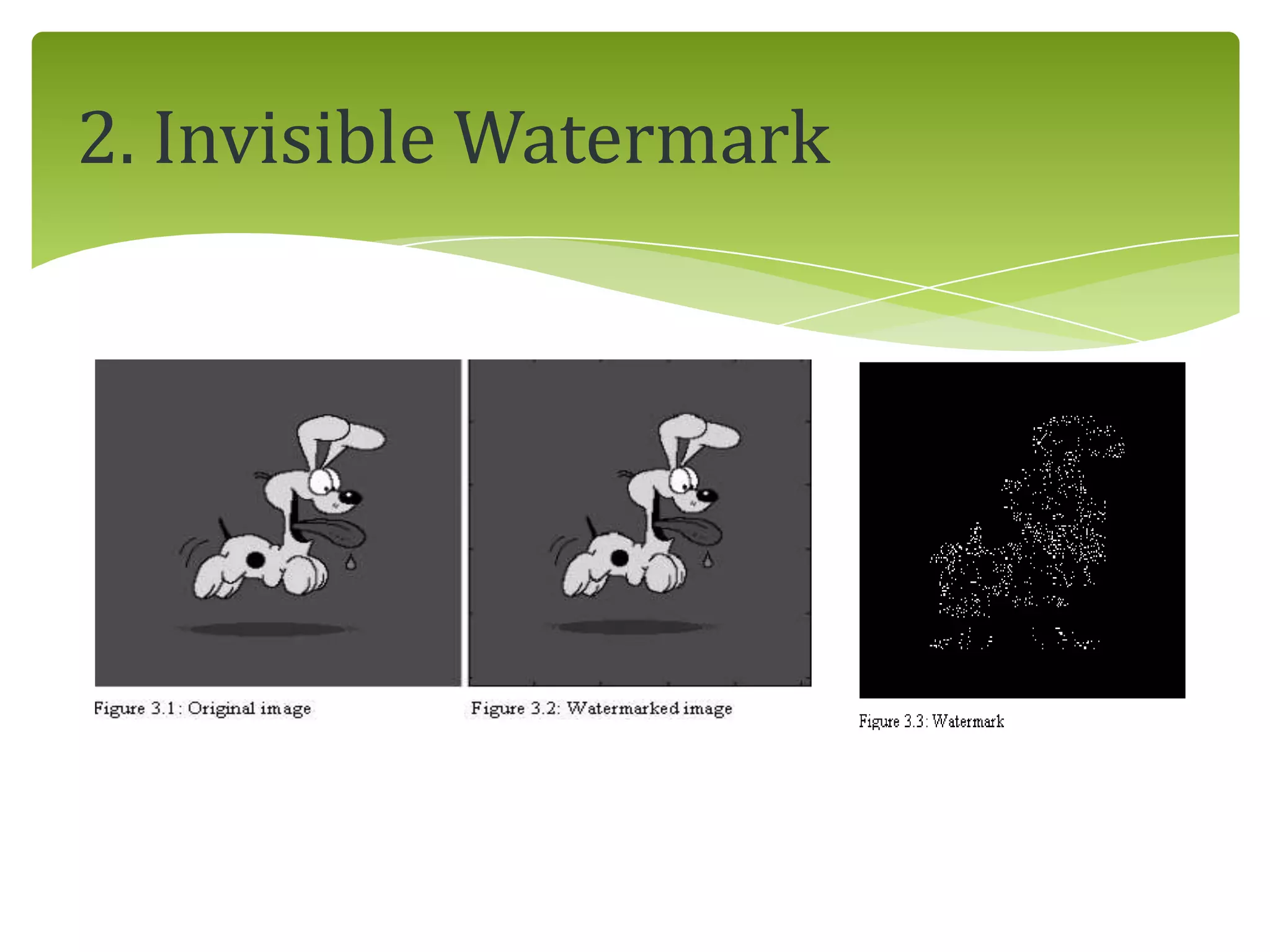
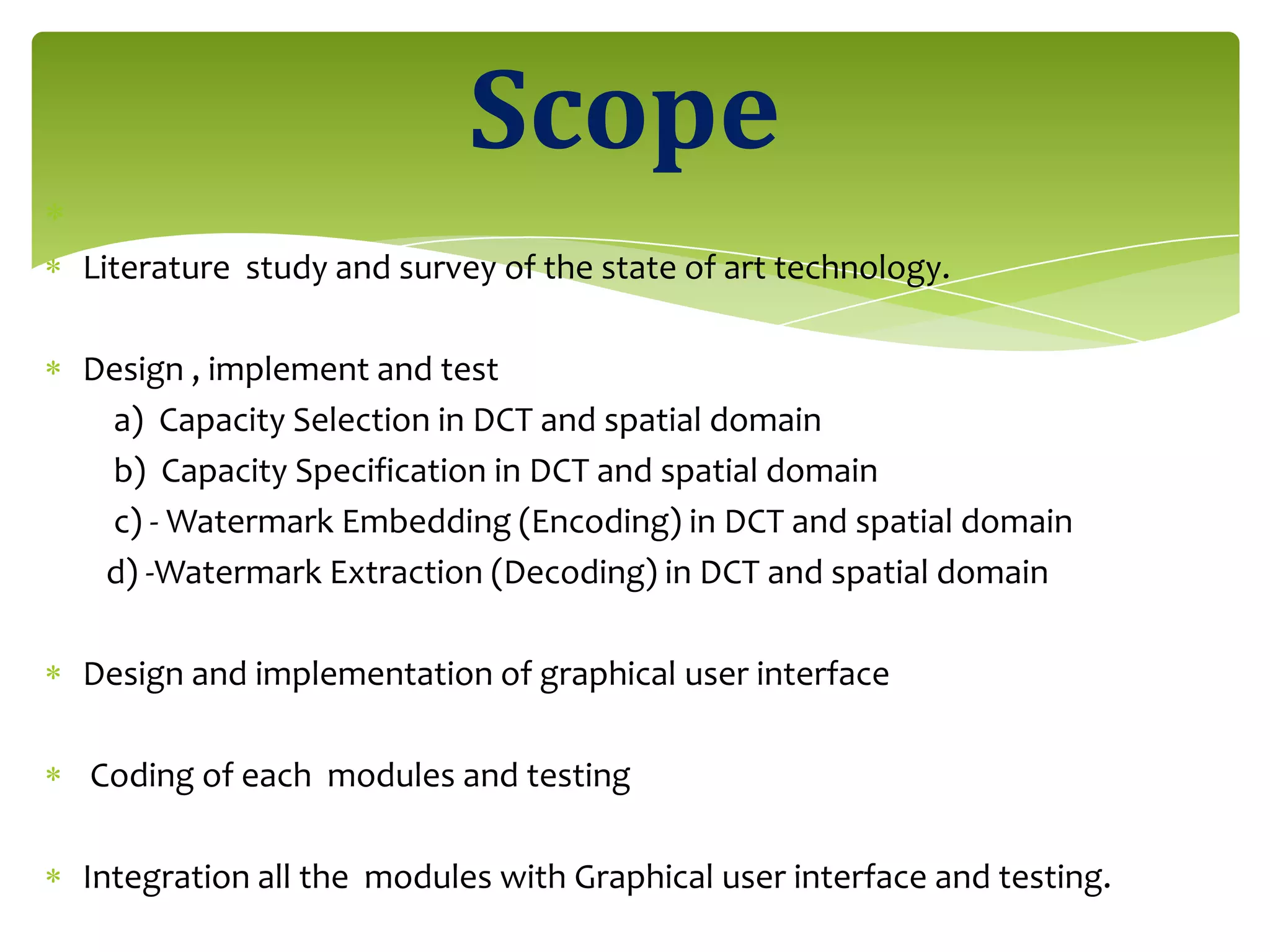
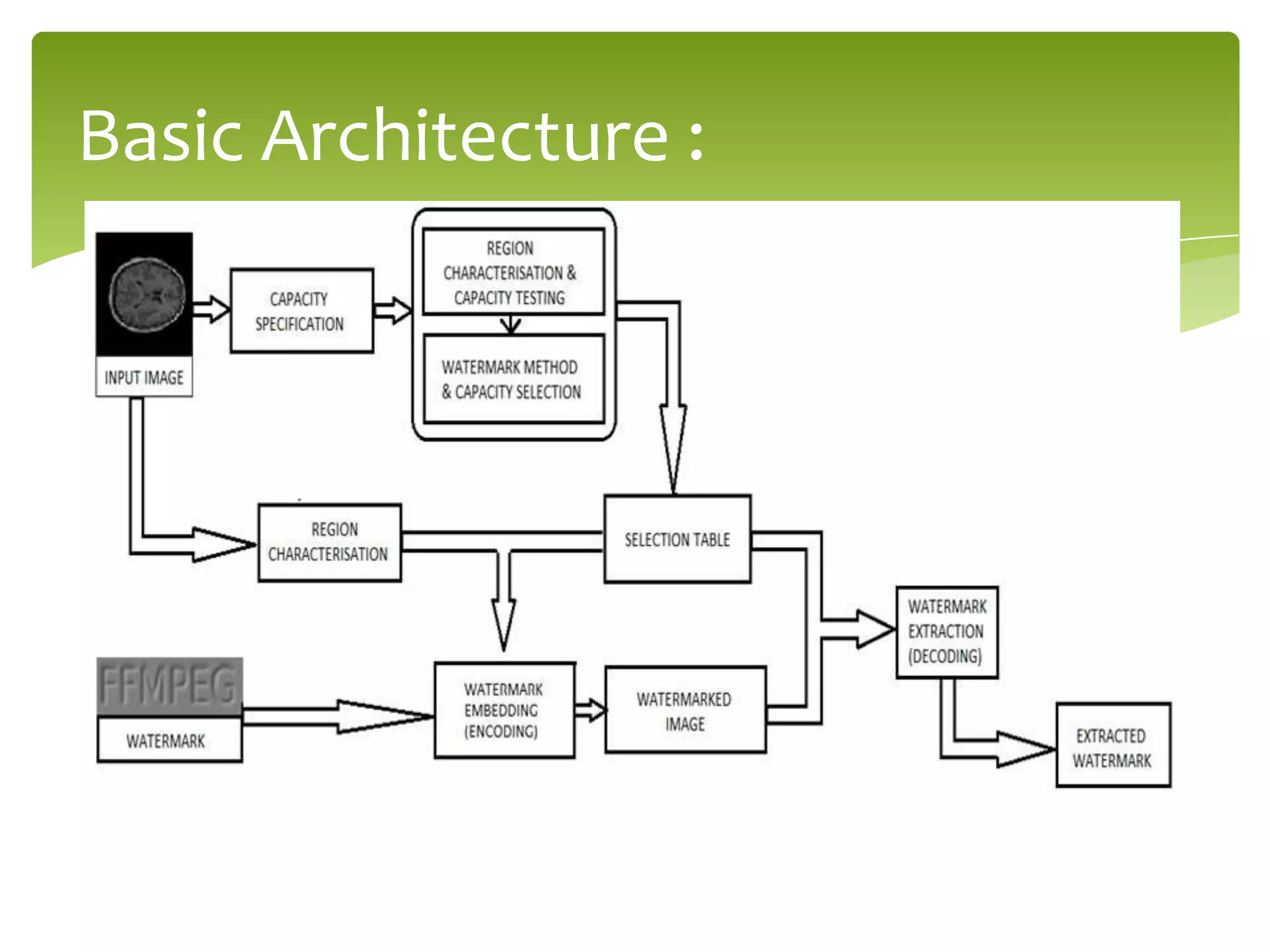
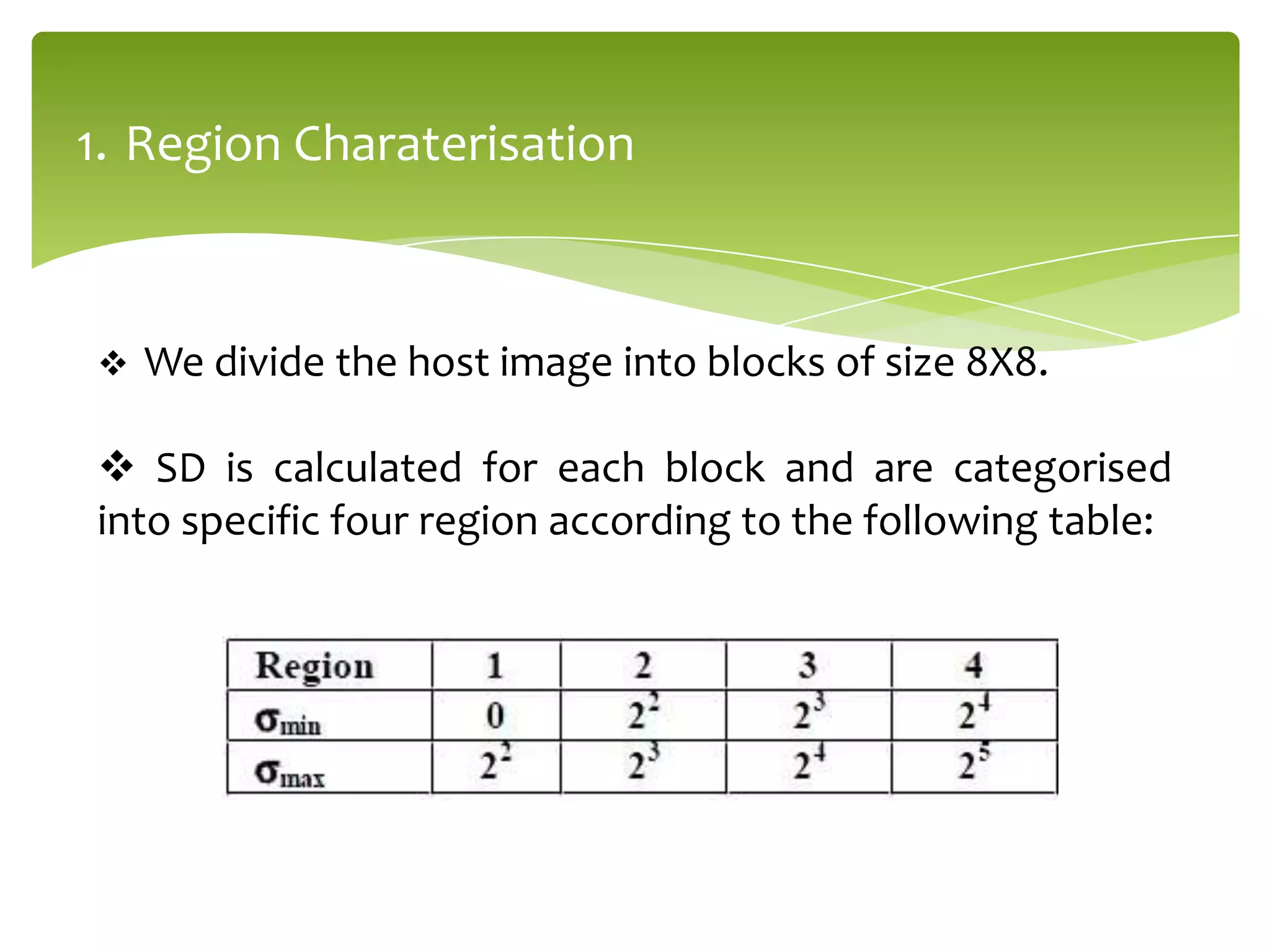
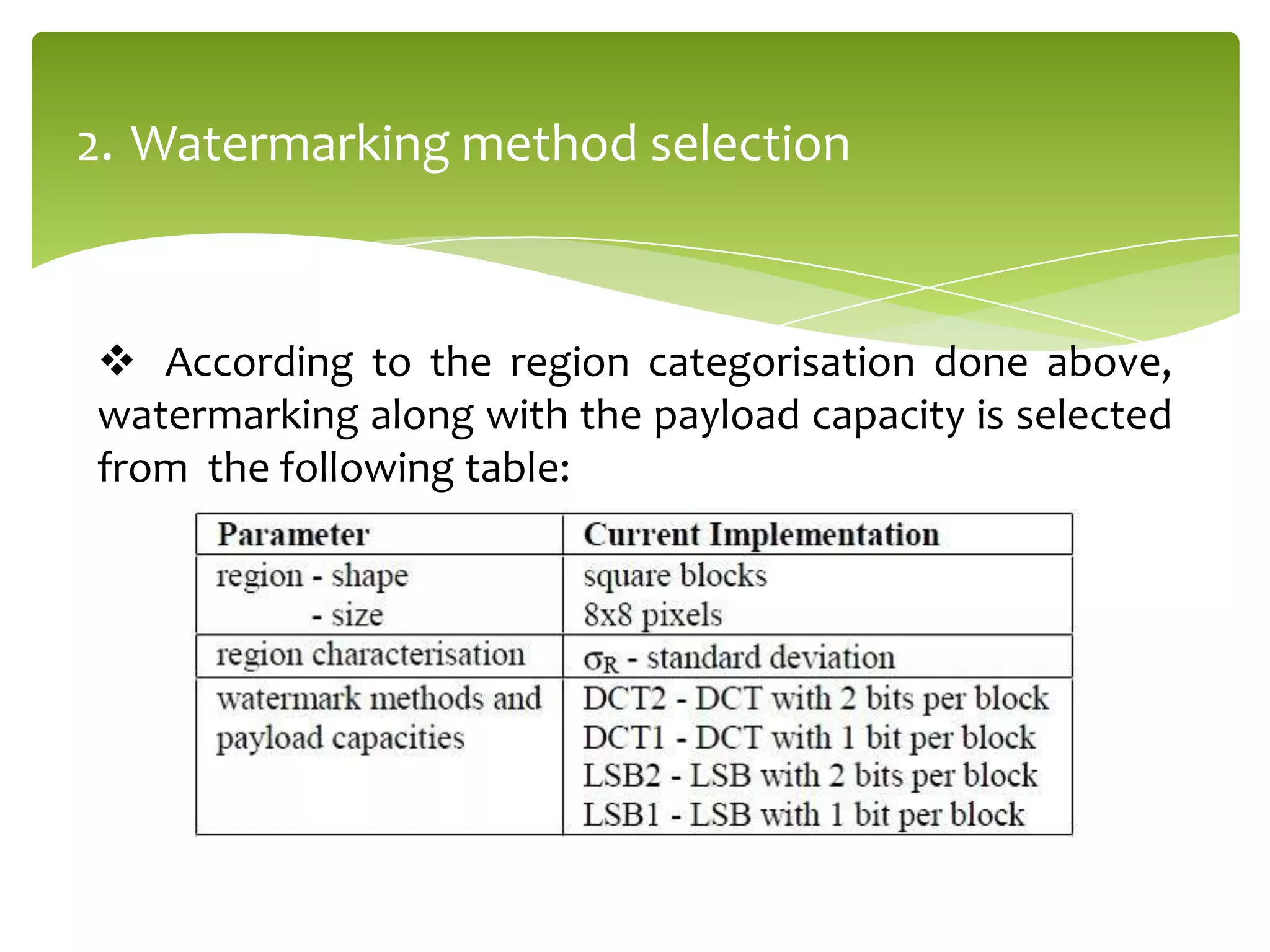
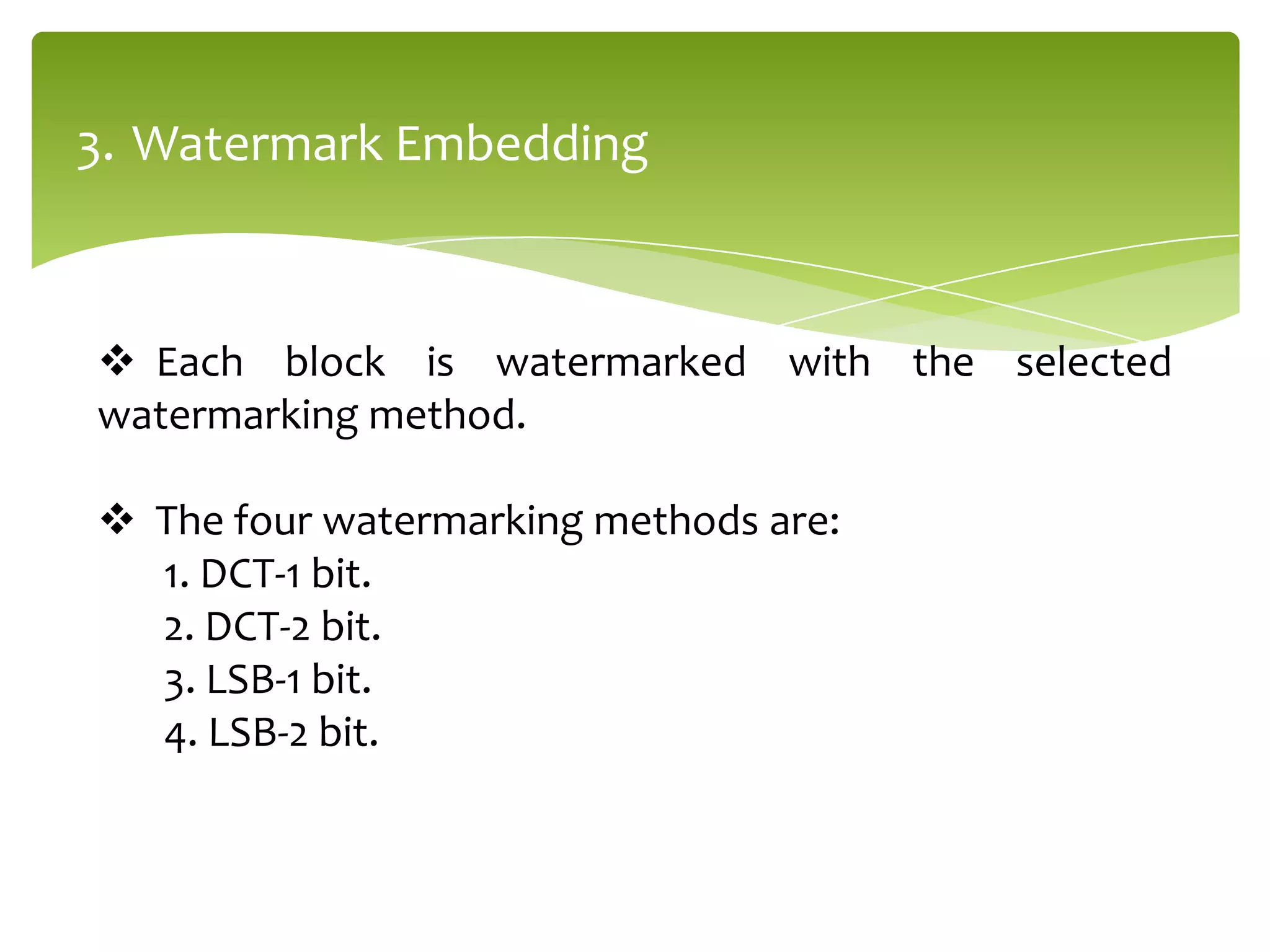
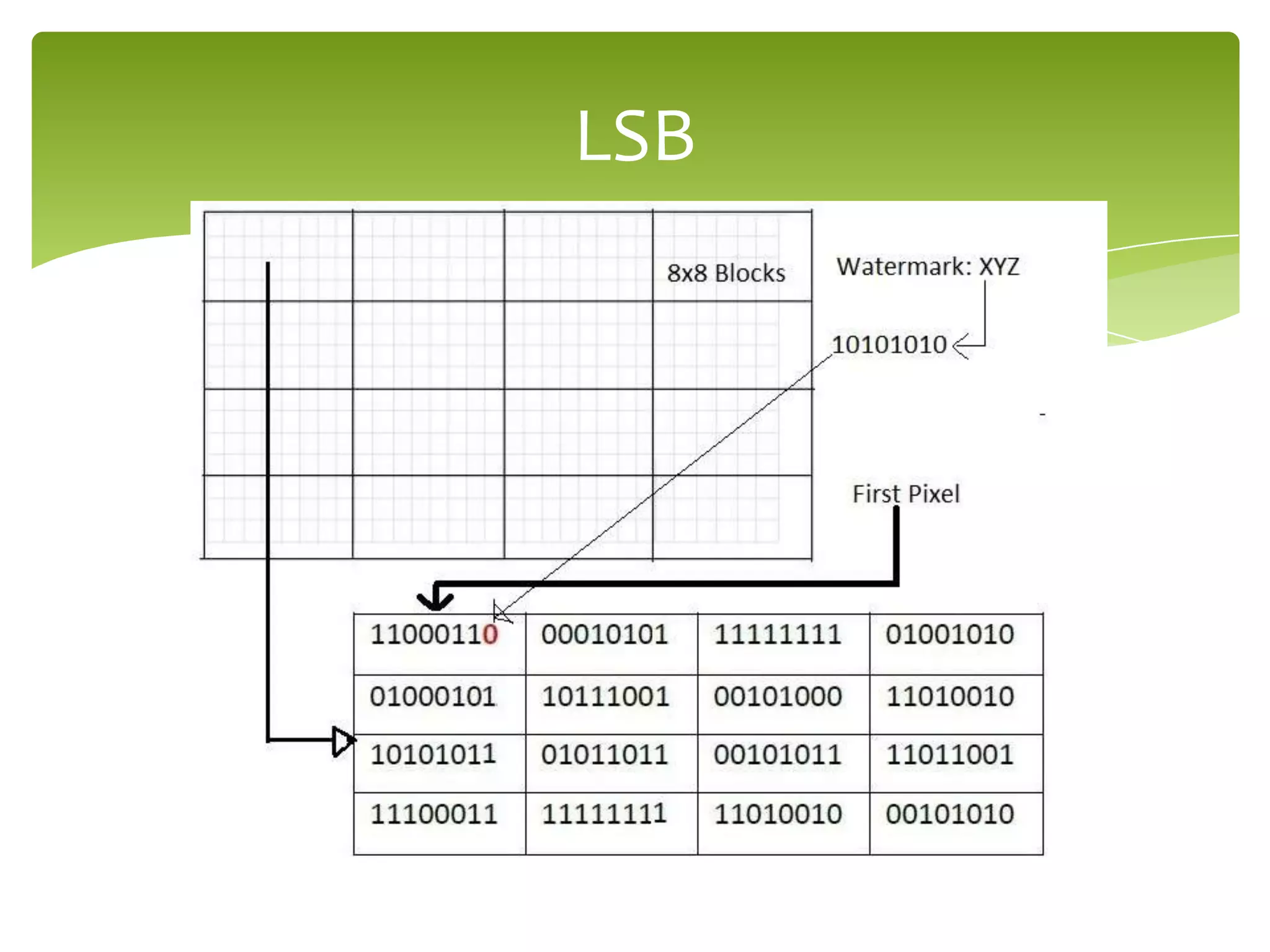
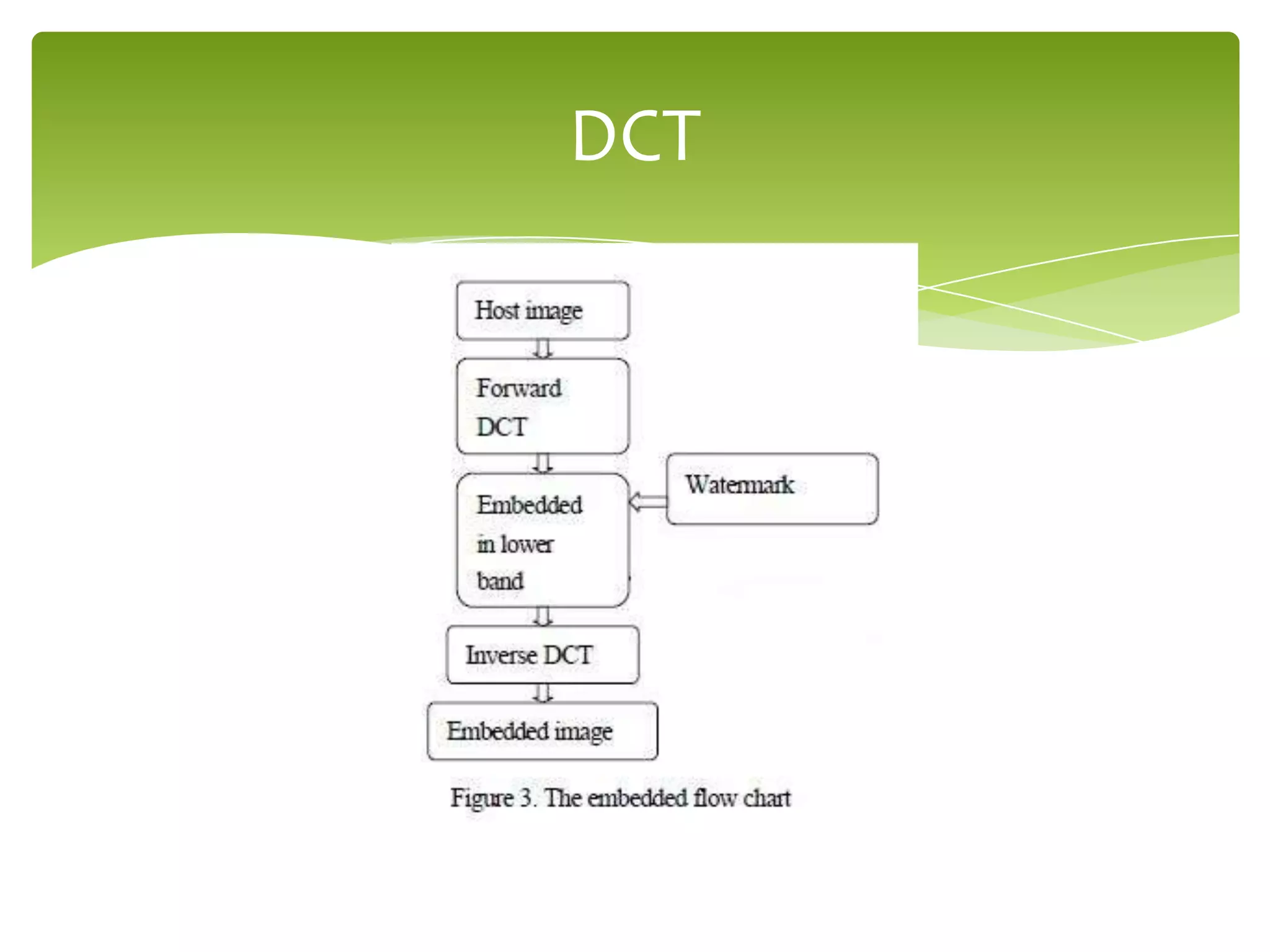
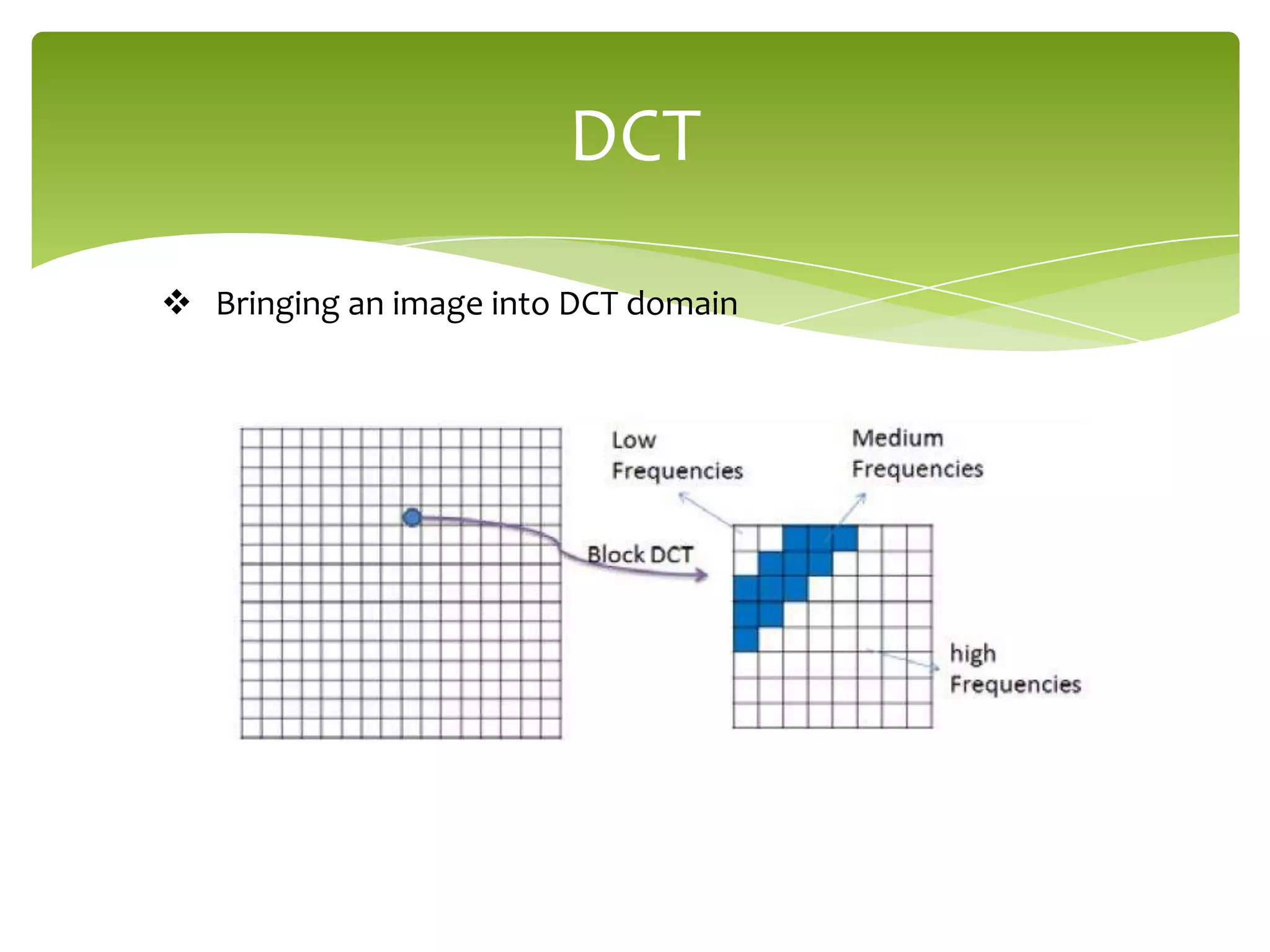
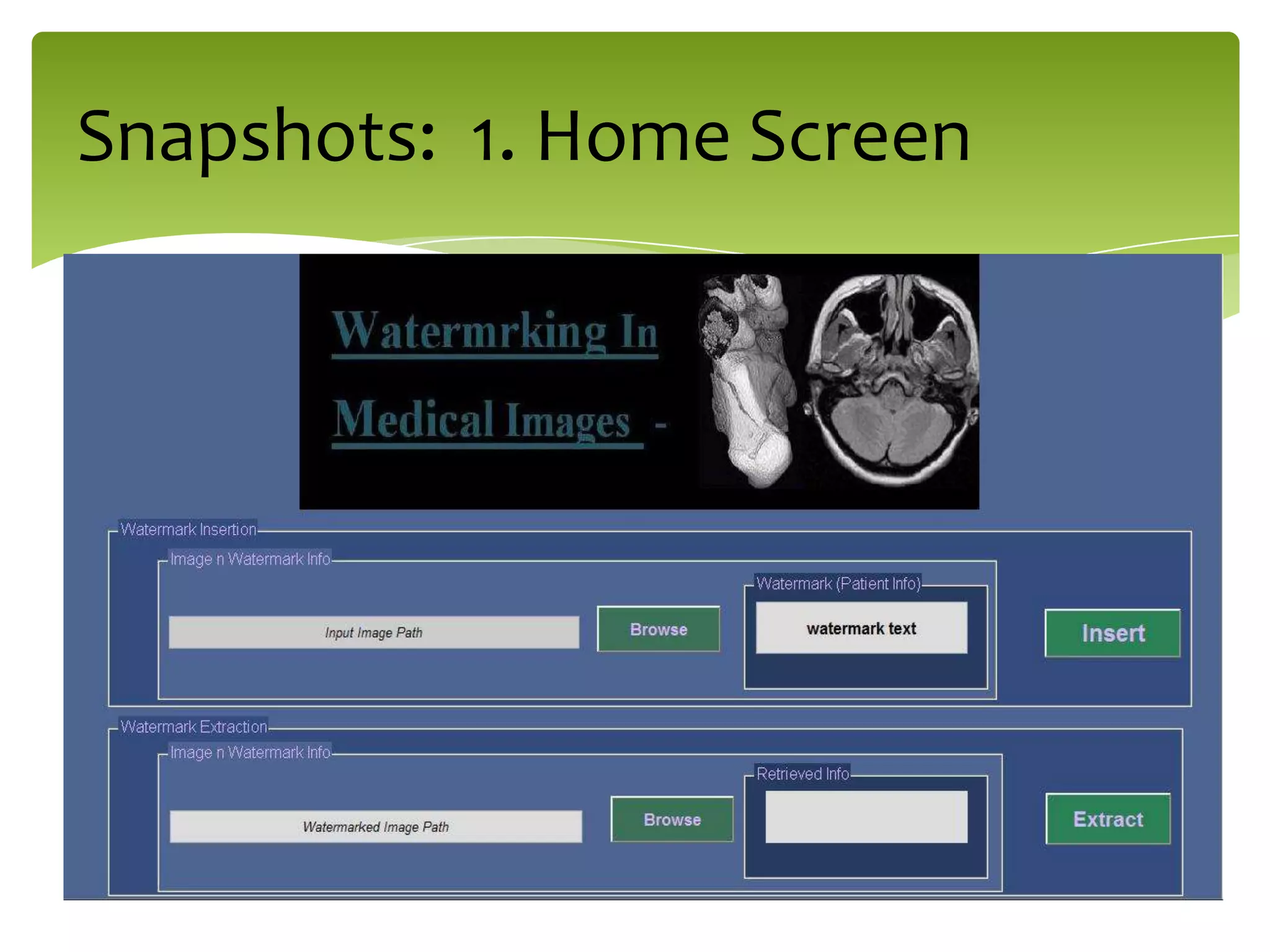
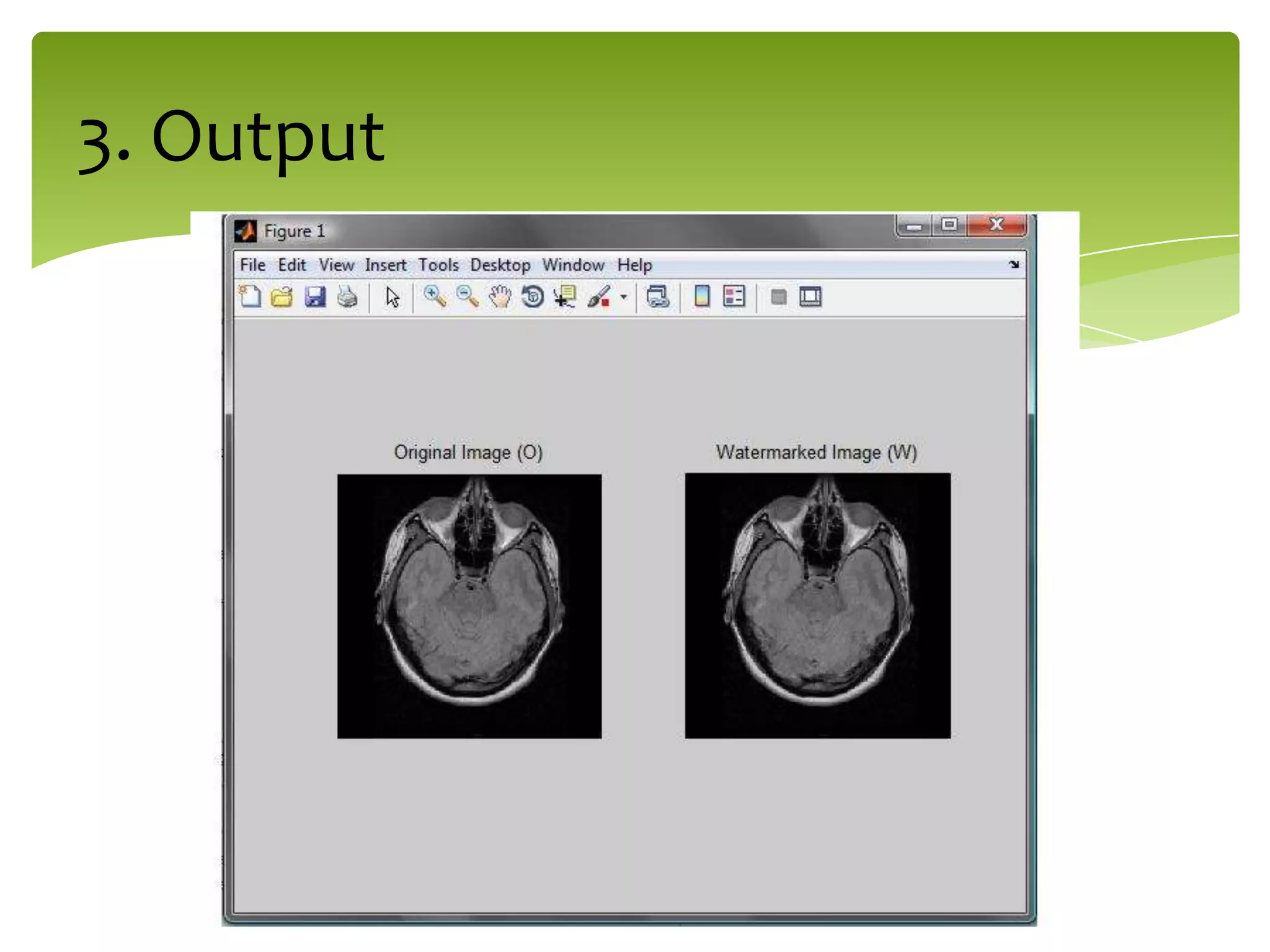
The document outlines a project on digital watermarking for medical images, emphasizing its importance for secure electronic transfer of sensitive data. It discusses techniques for watermark embedding and extraction without data loss, focusing on maintaining image integrity and providing secure access to authorized users. Future directions include enhancing hiding capacity and robustness of the watermarking method.