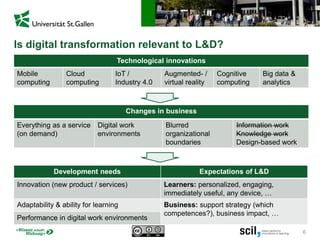
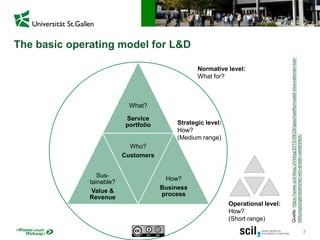
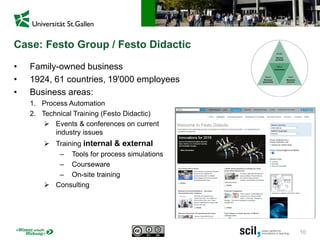
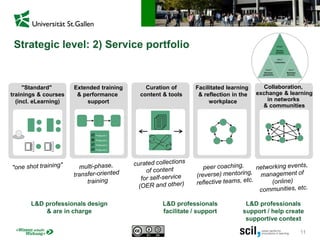
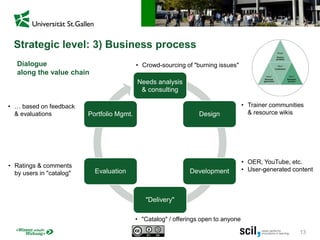
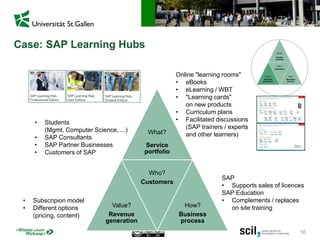
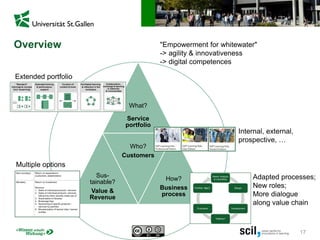
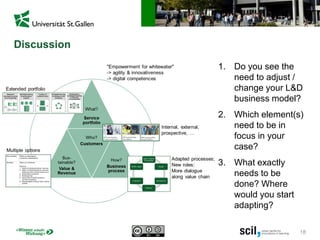
This document discusses the implications of digital transformation for learning and development (L&D). It outlines how technological innovations like mobile computing, cloud computing, the internet of things, and cognitive computing are changing business needs and learner expectations. Learners now want personalized, engaging learning that is immediately useful on any device. Businesses want L&D support for their strategies and measurable business impact. The document presents a framework for how L&D organizations can adapt, including adjusting their service portfolios, business processes, customers, and revenue models to focus on agility, innovation, and developing digital competencies. It provides examples from companies like Festo Group, scil academy, Centre for Young Professionals, and SAP Learning H