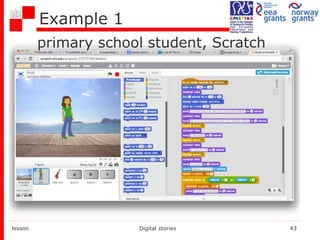
The document provides an extensive overview of digital storytelling, focusing on its definition, elements, pedagogical background, and tools for creating digital stories. It emphasizes the importance of digital competence in education and outlines various types of digital stories, along with guidelines and examples for effective storytelling. The conclusions highlight how digital storytelling enhances critical thinking and engagement among students.