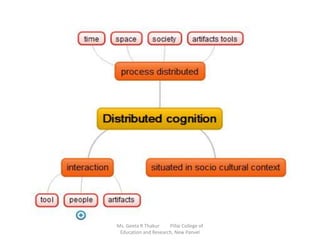
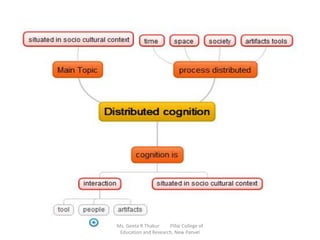
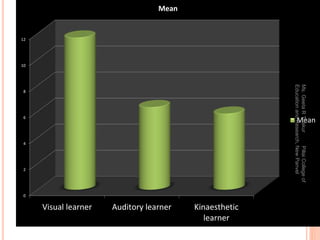
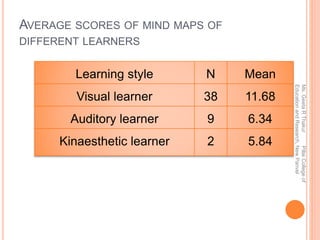
This document discusses using digital mind mapping tools for collaborative knowledge construction. It begins by explaining mind maps and their key features, such as starting with a central idea and using branches, colors and images to connect ideas. It then discusses using the digital mind mapping tool MindMaple to orient students to mind mapping and have them collaboratively develop digital mind maps. Students were then evaluated on individual mind maps based on a rubric. Results showed that visual learners scored highest on the mind maps on average, followed by auditory learners, with kinesthetic learners scoring lowest. The document concludes by advocating the use of mind maps to help students differentiate between what they know and don't know.