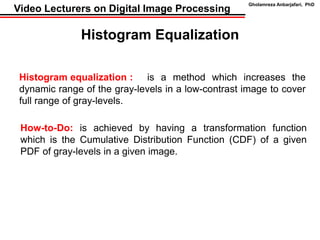
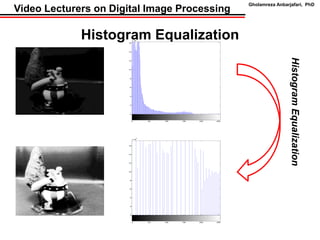
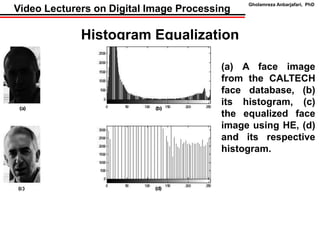
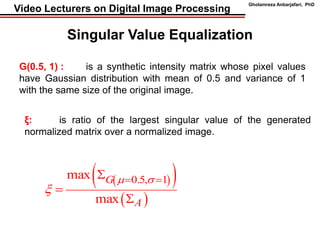
This document discusses techniques for contrast enhancement in digital images, including histogram equalization and singular value equalization. Histogram equalization increases contrast by transforming pixel values to evenly distribute them across the full intensity range. Singular value equalization also enhances contrast by modifying the largest singular value obtained from singular value decomposition of the image matrix, effectively changing the overall luminance. Examples are provided to demonstrate the effects of these methods on image histograms and visual appearance.

![Gholamreza Anbarjafari, PhD
Video Lecturers on Digital Image Processing
Histogram Processing
Histogram : is the discrete function h(rk)=nk , where rk is the kth
gray level in the range of [0, L-1] and nk is the number of pixels
having gray level rk.
Normalized histogram : is p(rk)=nk/n, for k=0,1,…,L-1 and p(rk)
can be considered to give an estimate of the probability of
occurrence of ray level rk.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vidlecture06fin-220414192808/85/DIGITAL-IMAGE-PROCESSING-2-320.jpg)