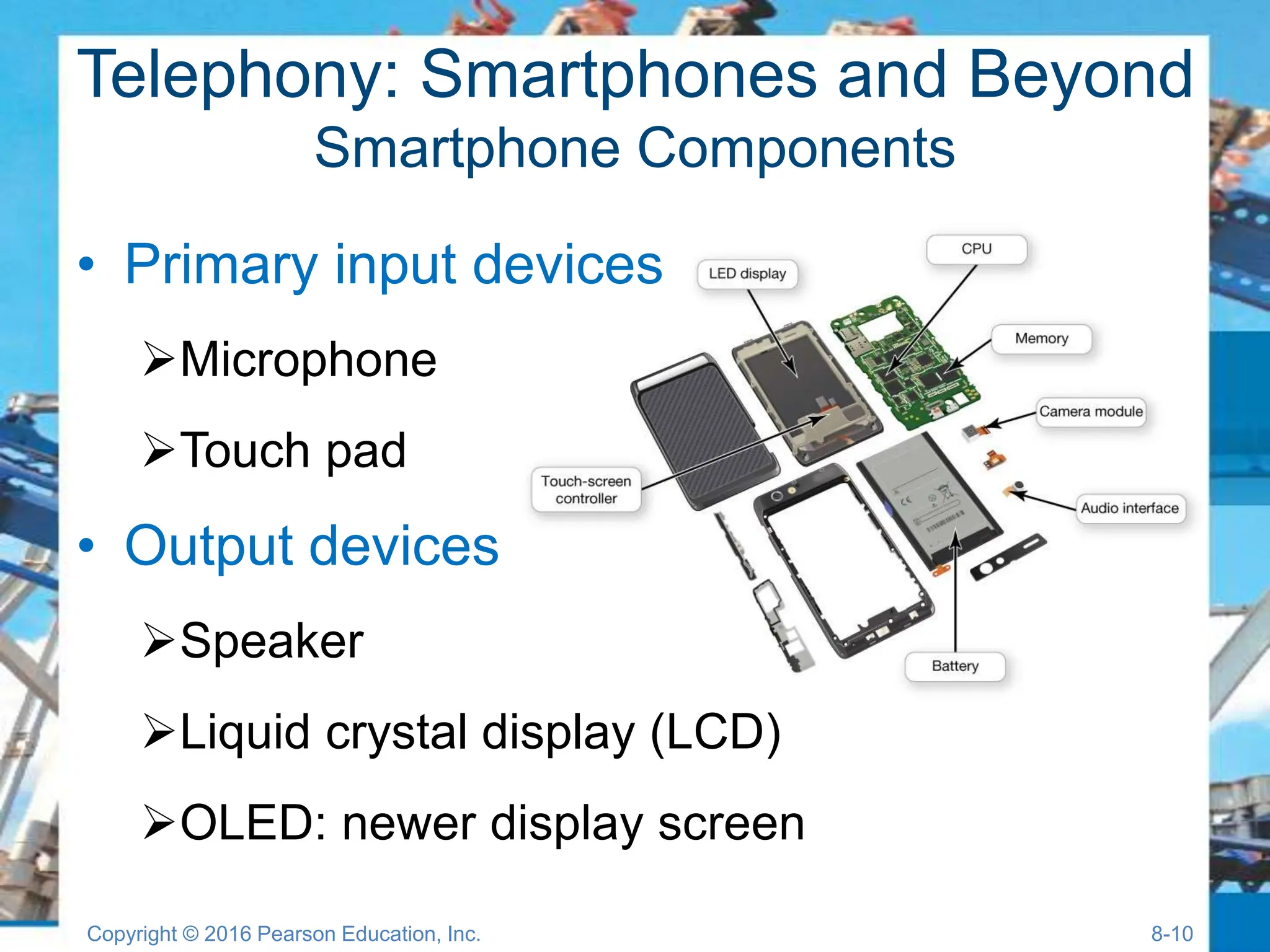
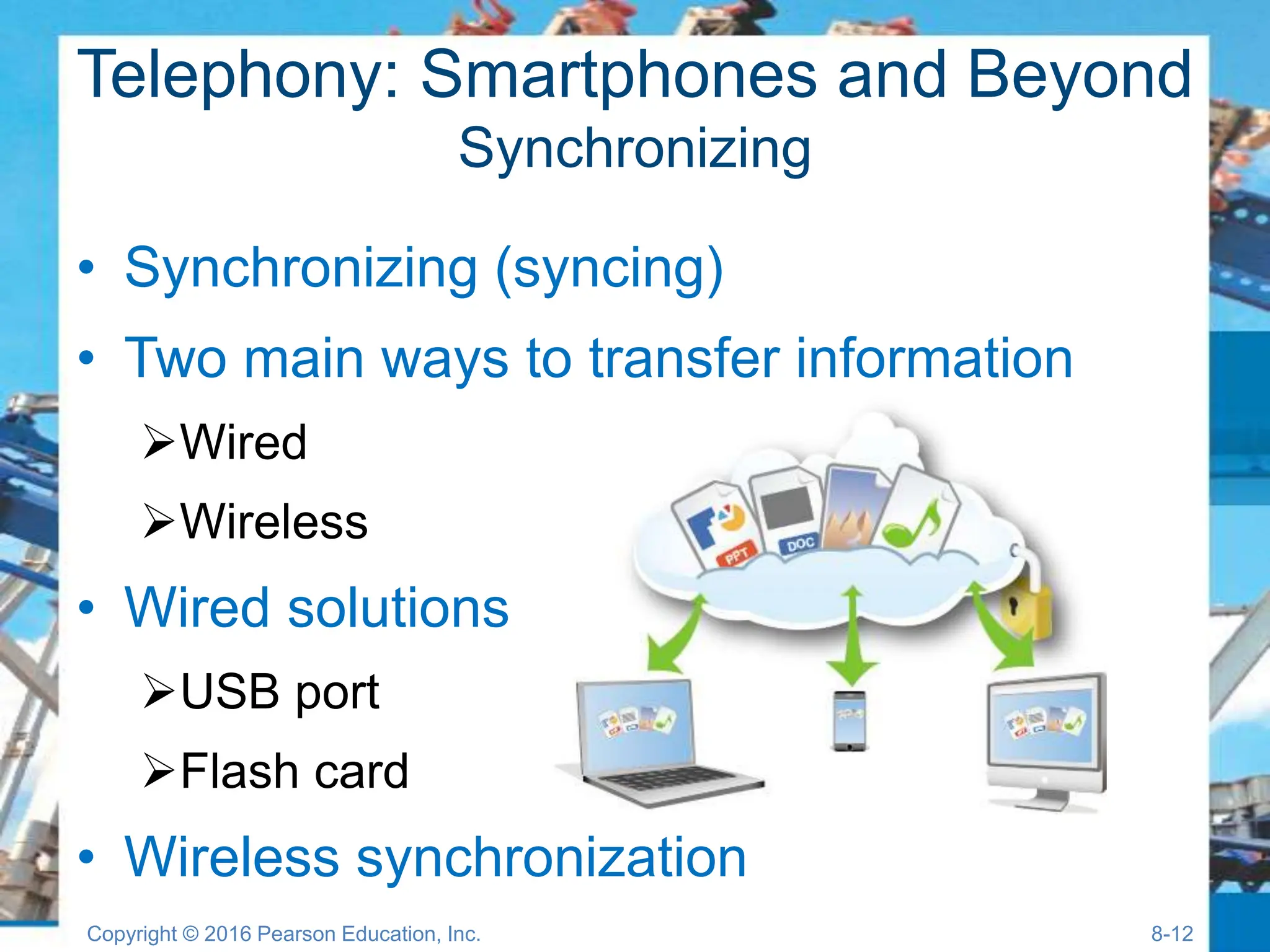
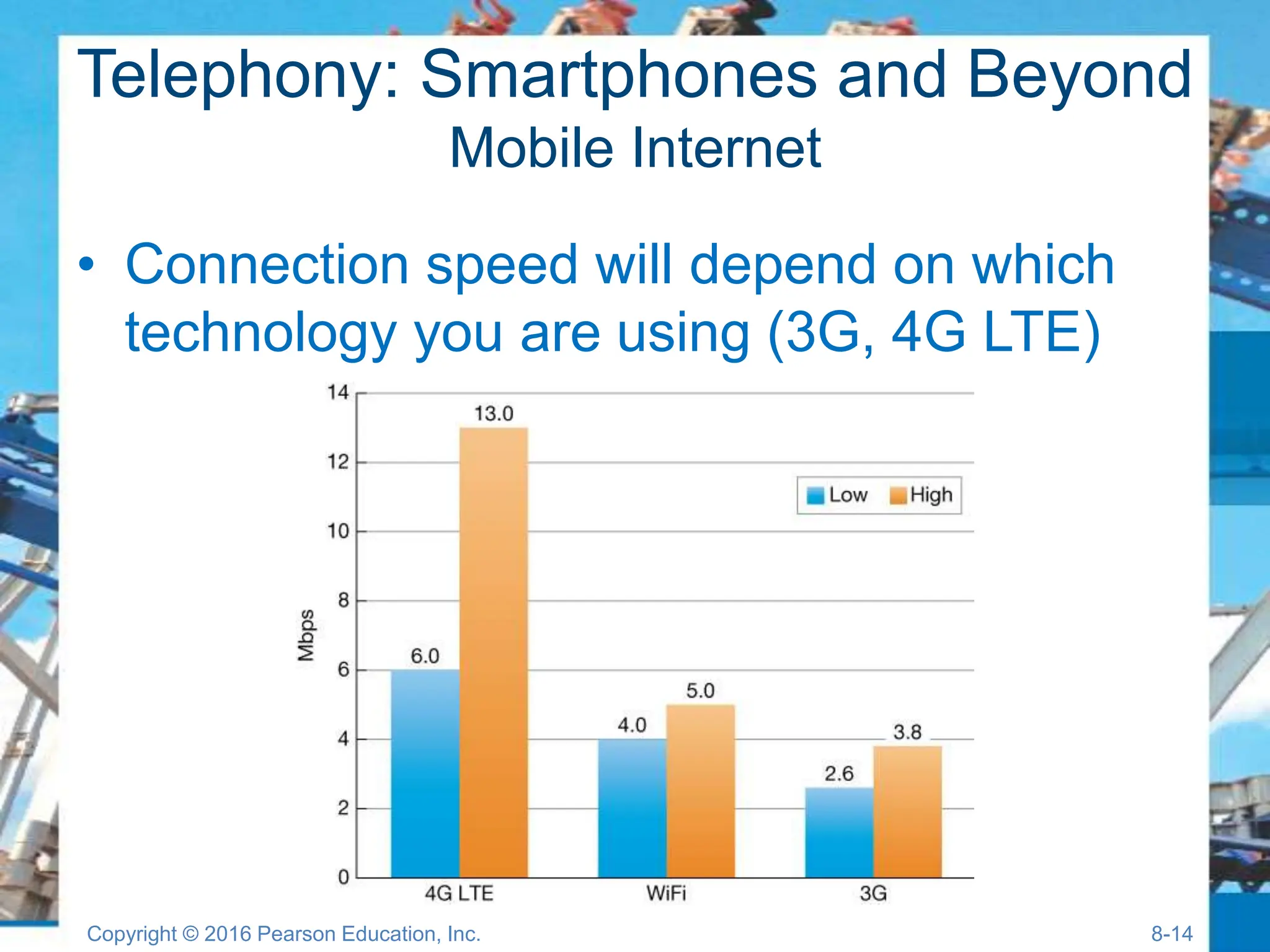
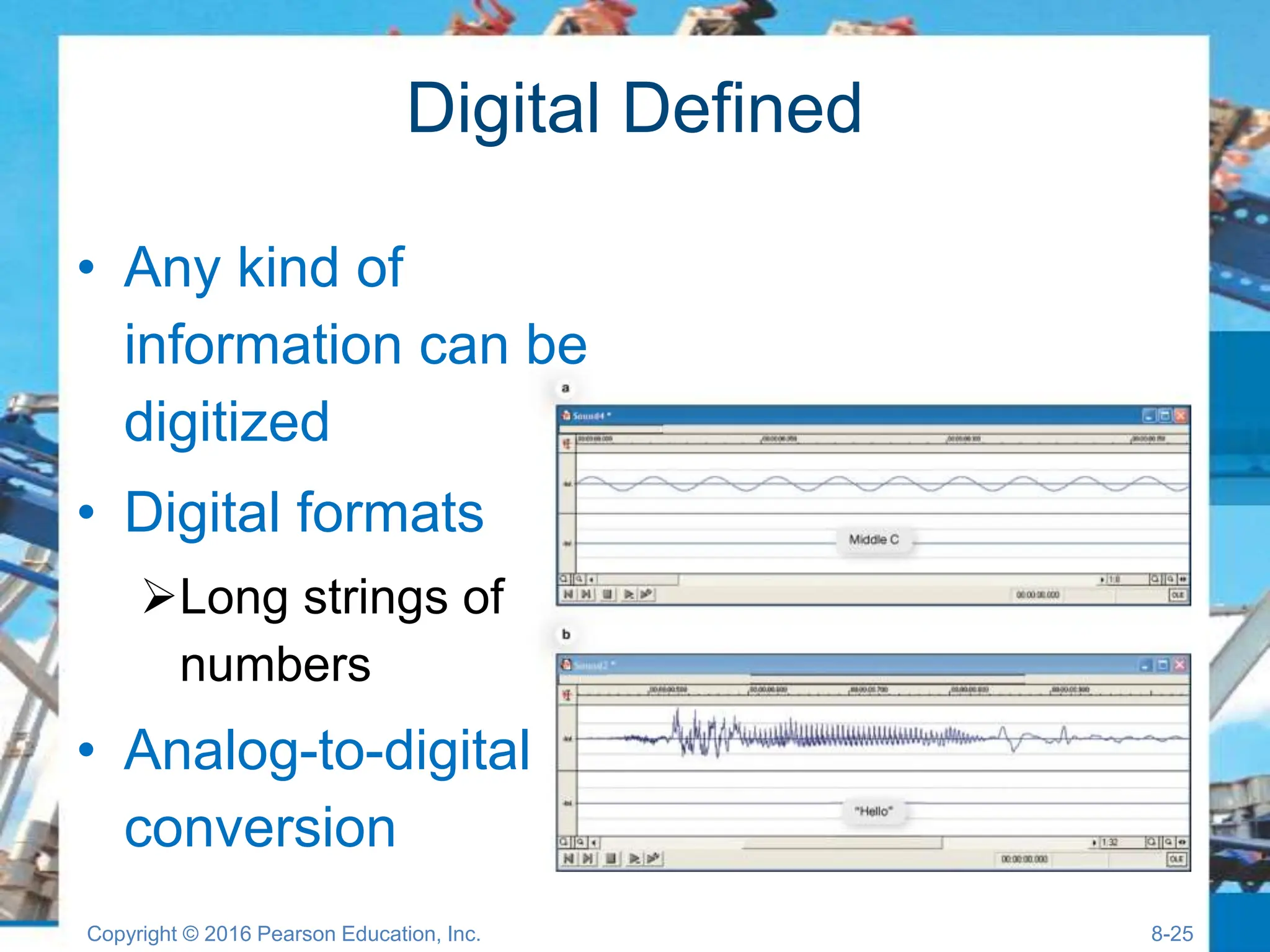
The document discusses digital devices and media, focusing on mobile technology, including smartphones, tablets, and ultrabooks. It covers topics such as digital convergence, telephony, synchronization, mobile internet, and digital media creation and distribution. Additionally, it provides insights into the advantages of digital formats over analog and the hardware and software components of various devices.