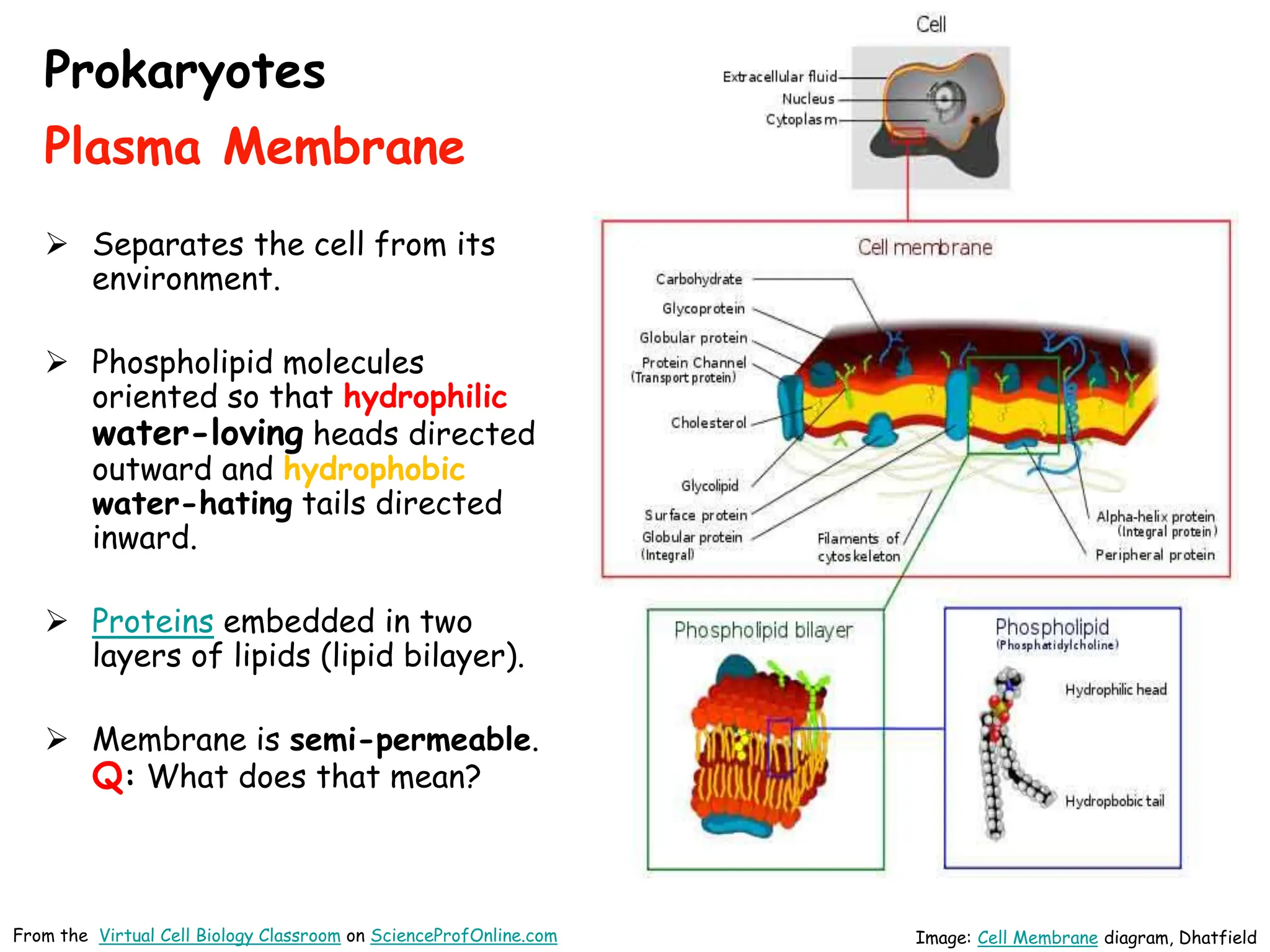
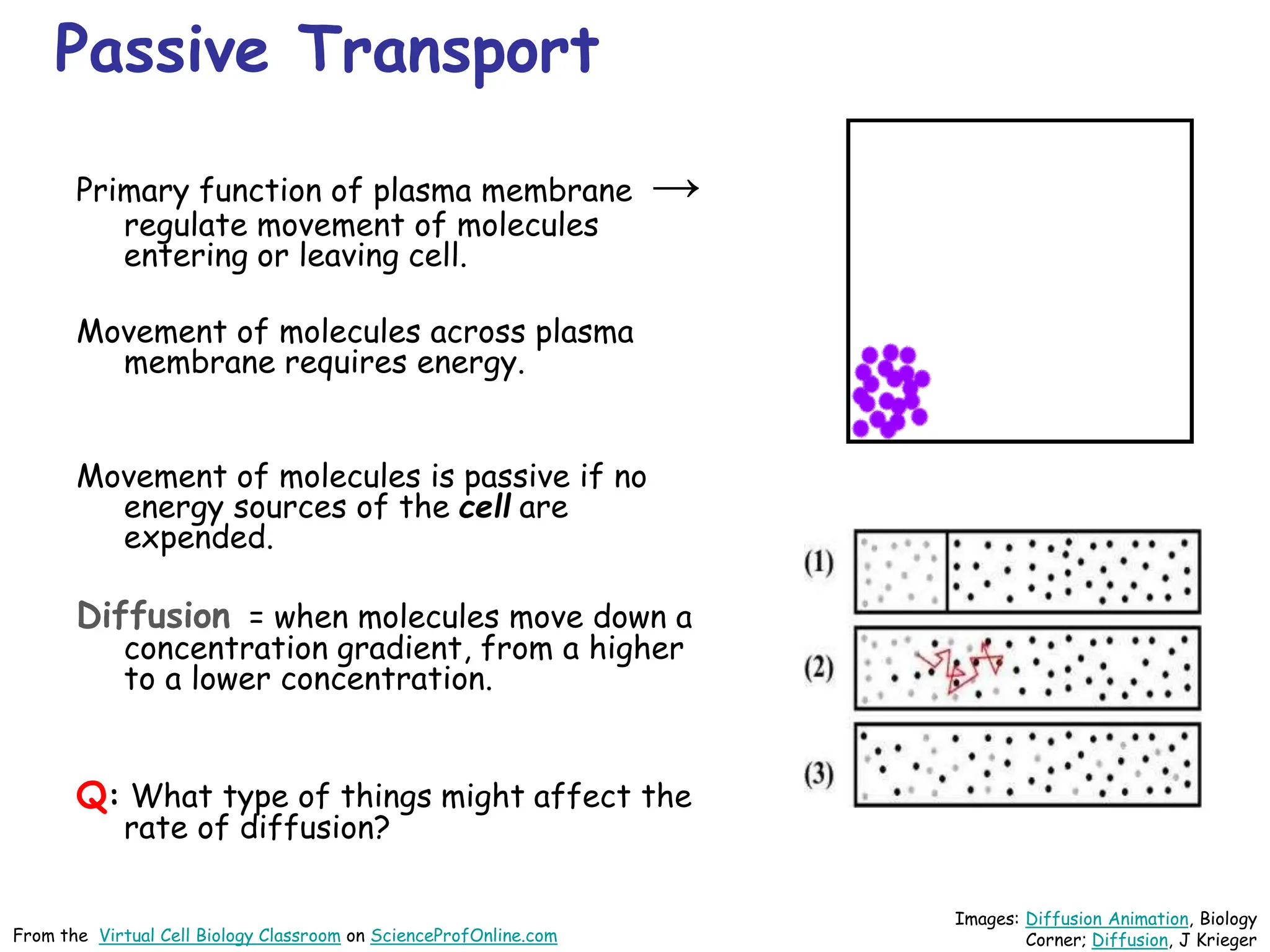
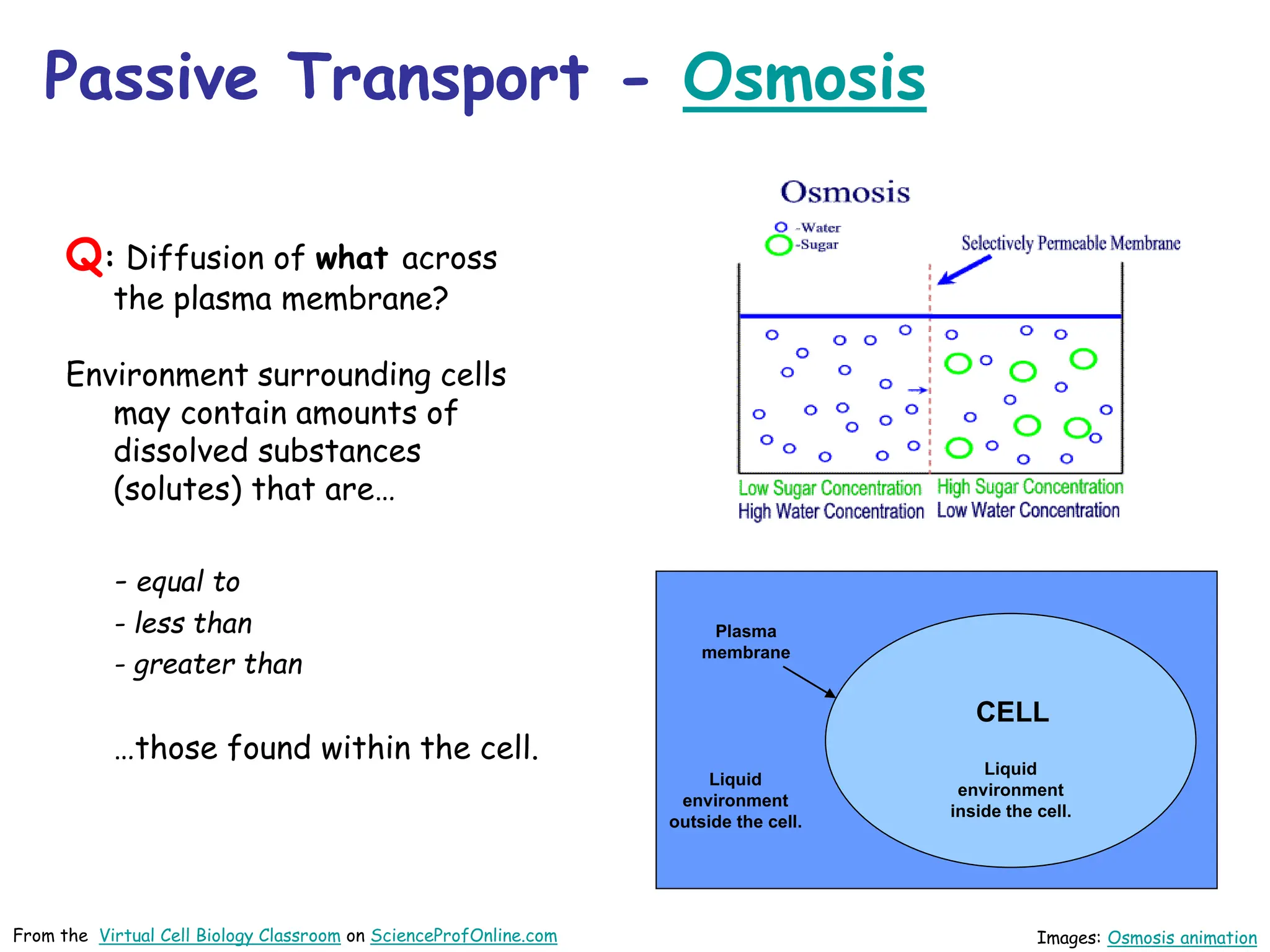
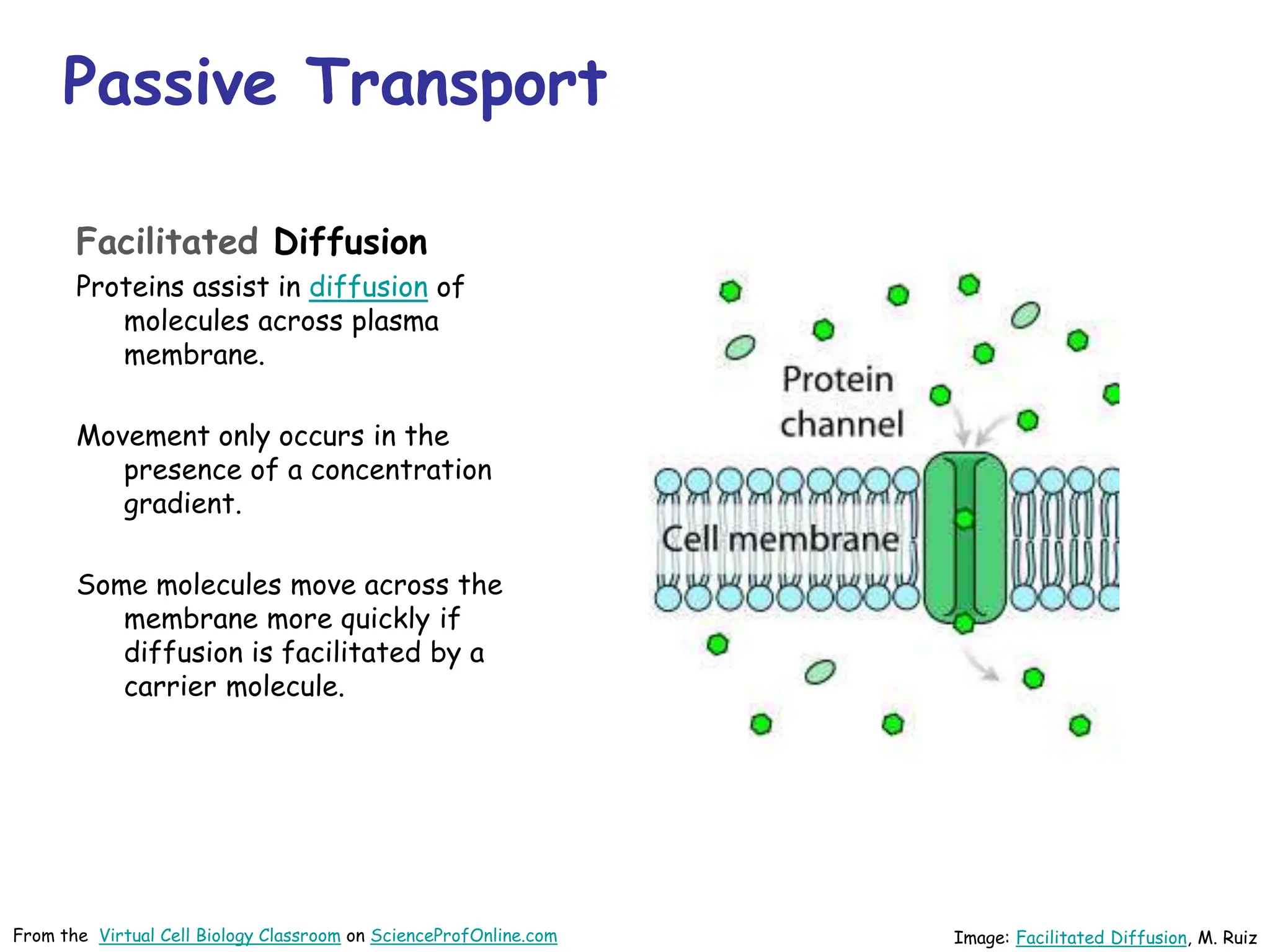
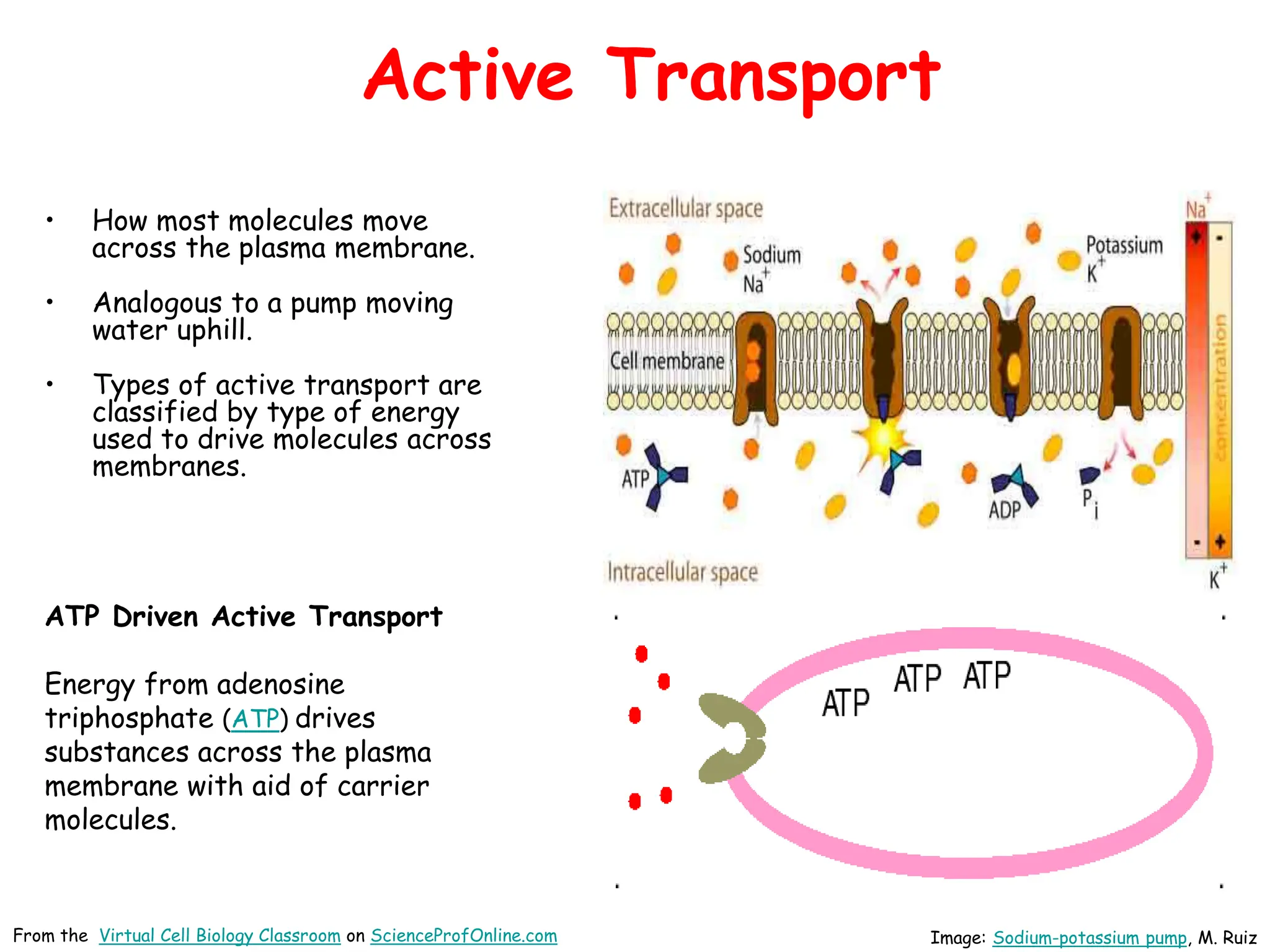
This document discusses different types of transport mechanisms across cell membranes, including diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. It defines diffusion as the passive movement of molecules down a concentration gradient. Osmosis is defined as the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane toward a higher solute concentration. The document describes cellular environments as being isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic depending on solute concentrations inside and outside the cell. Active transport mechanisms use energy like ATP to move molecules against a concentration gradient.