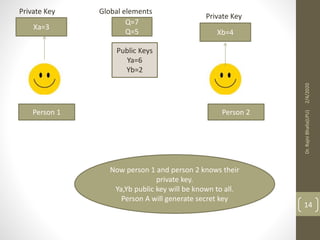
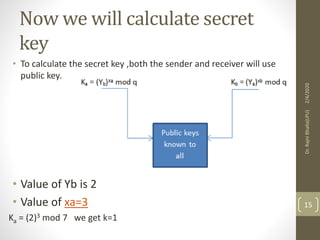
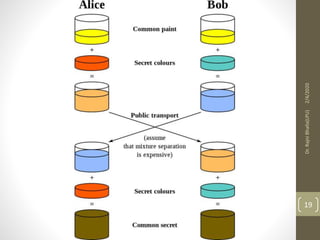
The Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm allows two users to securely exchange cryptographic keys over a public channel without directly sending the keys. The process involves selecting a prime number and a primitive root, with each user calculating their public key based on their private key. Both parties then compute a shared secret key using their private keys and the other's public key, ensuring that the keys remain secure despite being transmitted over a potentially insecure channel.