Embed presentation
Downloaded 24 times















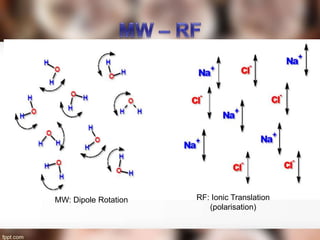

















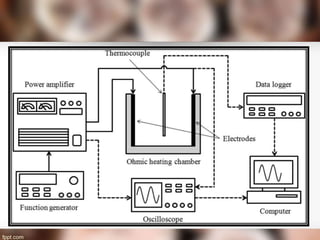






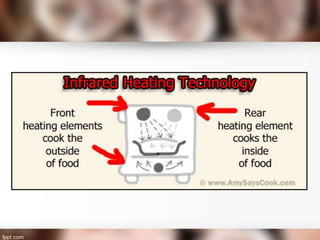


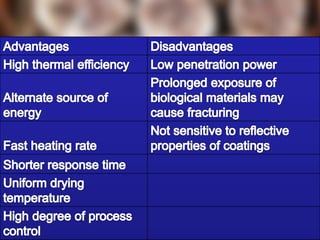

The document explains the processes of heat transfer, including conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs when heat is transferred from one particle to another, as seen when heating water in a pan or cooking an egg. Convection involves the movement of air masses to transfer heat, while radiation transfers energy through electromagnetic waves without requiring a medium.












































