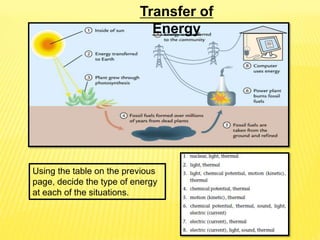
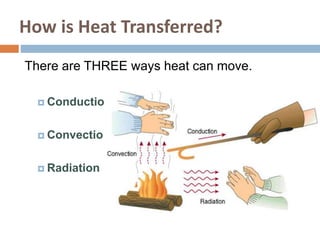
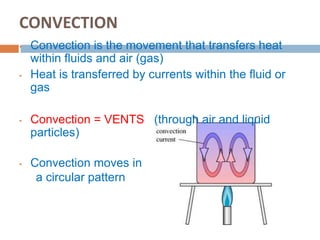
Thermal energy transfer occurs through three main mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the direct contact transfer of heat between objects through molecular collisions. Convection involves the transfer of heat by the circulation of fluids like air and water. Radiation involves the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves such as infrared and does not require direct contact between the objects. Examples provided include heat transfer through a metal spoon in water by conduction, heat transfer through air currents in a room by convection, and heat transfer from the sun by radiation.