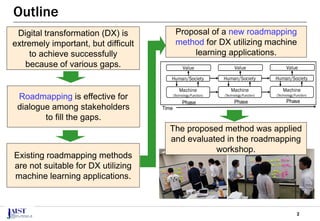
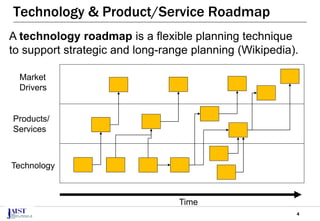
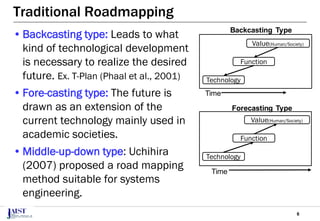
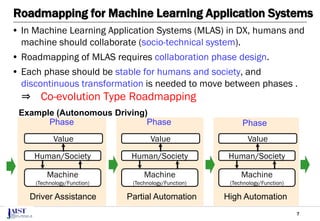
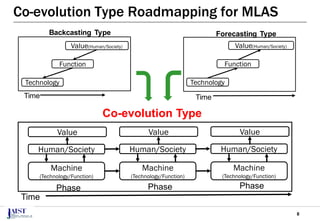
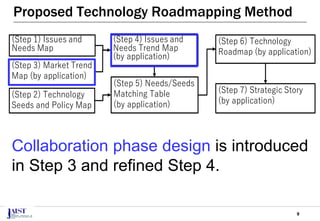
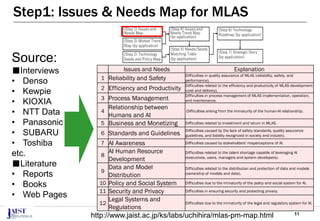
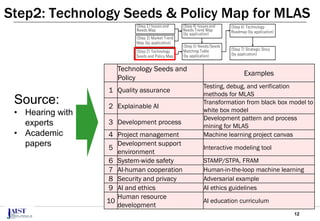
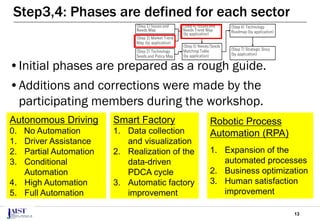
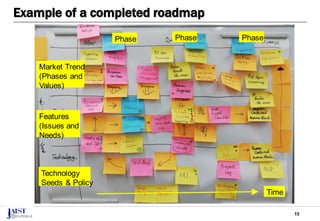
The document discusses the challenges of achieving successful digital transformation (DX) and presents a new roadmapping method tailored for machine learning applications to foster dialogue among stakeholders. It highlights the importance of addressing perception gaps caused by unclear goals and the need for closer human-machine collaboration. The proposed method was evaluated in a workshop, revealing the effectiveness of roadmapping as a tool for mutual understanding and planning in DX initiatives.