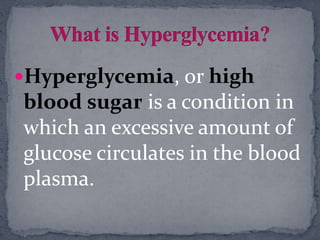
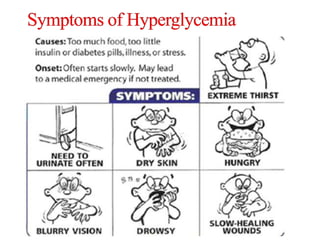
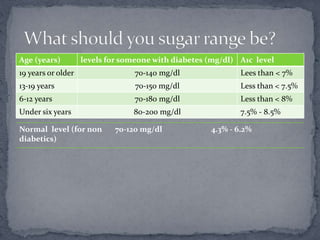
There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin and Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough. Hypoglycemia is low blood sugar below normal levels that should be treated with juice or glucose tablets. Hyperglycemia is high blood sugar above normal levels that should be managed by drinking sugar-free fluids, eating the right foods, more frequent blood sugar checks, and calling a doctor if ketones are present. Proper diabetes management involves being active, eating healthy, monitoring A1C and other health markers, and taking any needed medications.