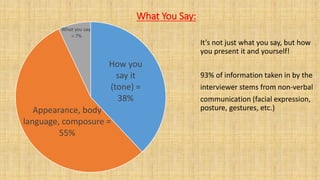
Here are 3 tips for Abdullah on how he should have prepared for the interview:
1. He should have read the application form carefully to understand the requirements for the role and what information the interviewer would ask about.
2. He should have prepared answers to common interview questions related to his skills, qualifications, and experience and how they meet the job requirements.
3. He should not have let his sister complete the application form for him. He needed to provide truthful answers himself so he could discuss his own background knowledgeably in the interview.