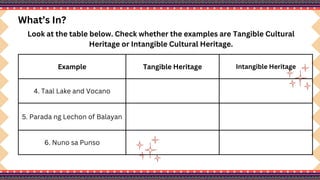
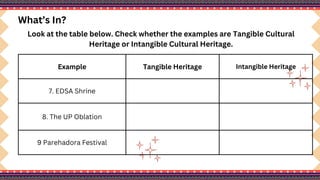
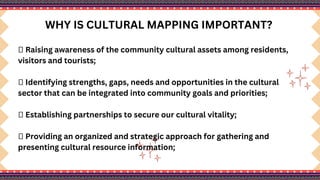
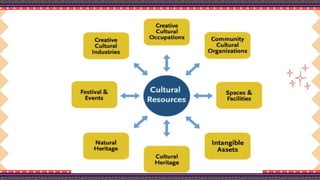
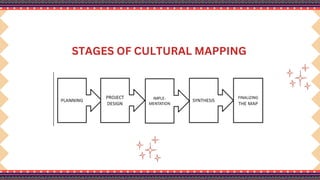
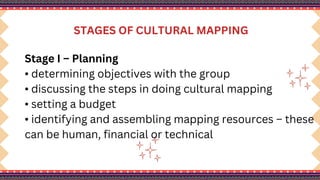
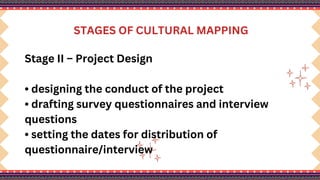
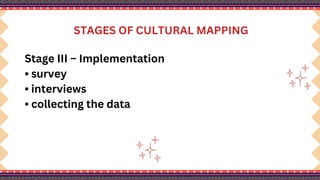
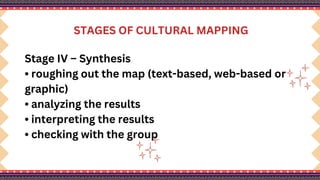
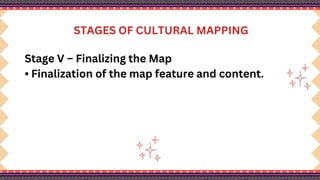
The document outlines a lesson plan on cultural mapping that has the objectives of discussing what cultural mapping is, explaining how to create a cultural map of one's community, creating a cultural map, and valuing one's cultural community; it discusses what cultural mapping is and why it is important; and it describes the stages of cultural mapping including planning, project design, implementation, synthesis, and finalizing the map.