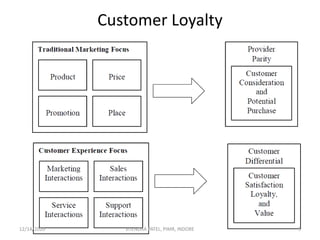
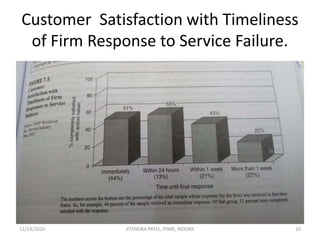
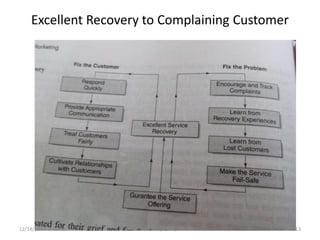
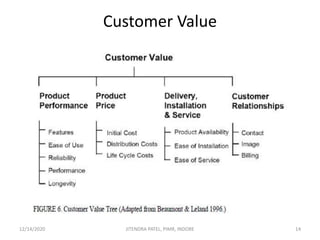
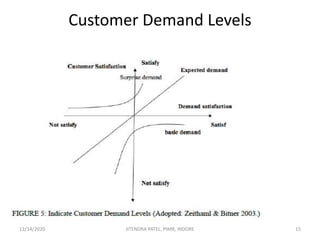
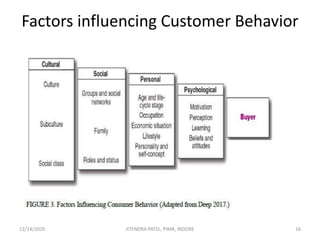
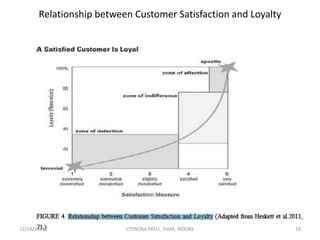
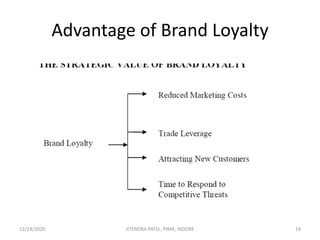
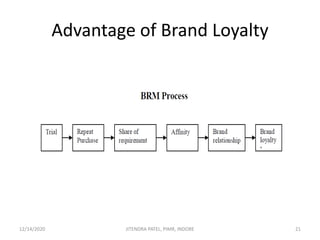
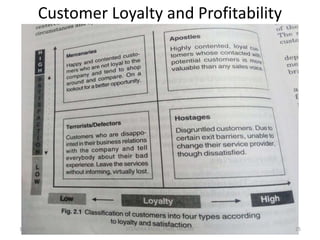
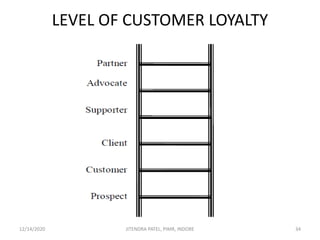
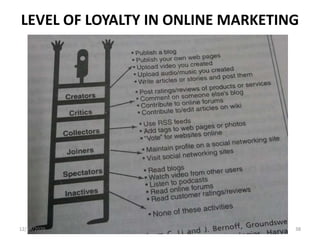
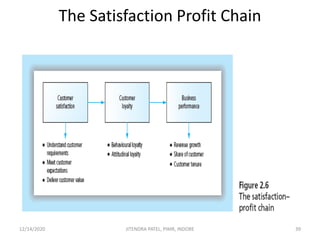
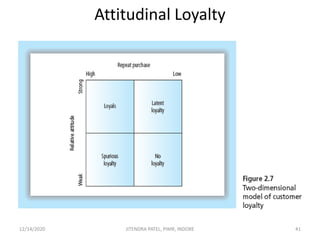
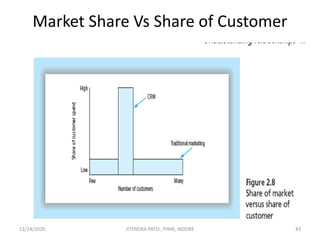
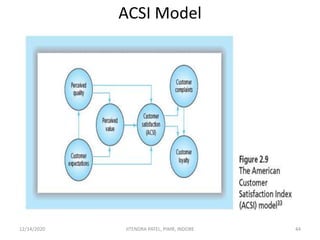
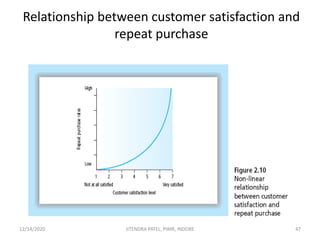
The document outlines a comprehensive CRM strategy focused on customer loyalty, satisfaction, and value. It discusses various aspects including types of customer loyalty, factors influencing customer behavior, and loyalty programs within different industries, emphasizing the importance of measuring customer satisfaction for retention and profitability. Additionally, it explores the relationship between profitability and customer loyalty, highlighting effective practices for maintaining long-term customer relationships.