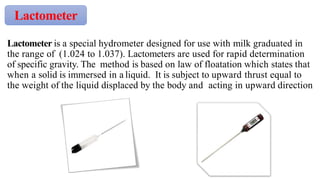
This document discusses determining the specific gravity of milk. Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of milk to water at the same temperature. The specific gravity of whole cow's milk ranges from 1.028 to 1.034 gm/ml on average. A lactometer, which is a hydrometer designed for milk, is used to rapidly determine specific gravity by measuring how far the instrument sinks into a milk sample. Partial skimming increases specific gravity while water adulteration lowers it.