This study aimed to identify current practices for detecting and managing depression in patients with low vision among eye health professionals and rehabilitation workers. A survey of 94 such professionals found that fewer than 40% attempted to identify depression in patients. Rehabilitation workers were more likely than eye health professionals to do so. Those who tried to identify depression reported greater confidence and fewer perceived barriers. The resources and management strategies available varied between settings, with rehabilitation agencies having the most support available. Overall, no consistent strategy for depression management was identified. The study concludes that training is needed to improve skills for addressing depression in patients with low vision.


![0.001]. Reminders had a substantial impact on the overall re-
sponse rate, with 34.0% of questionnaire returns coming after
the reminder.
Participants
Tables 1 and 2 describe the participants. The sample was largely
female aged between 23 and 69 years. The length of time the
participants had been in their current role, or eye care services in
general, ranged from less than a year to more than 35 years. Work
settings included public hospital, private practice, community set-
tings, or combinations of these and varied across professional
groups. The number of patients with vision impairment seen each
week ranged from 1 to 120, and the time spent with each patient
also varied considerably (1 to 200 min). Professional groups dif-
fered on the number of people with vision impairment reported to
be seen each week (F4,87 ϭ 7.612, p Ͻ 0.001) and the amount of
time spent with each patient (F4,87 ϭ 43.239, p Ͻ 0.001). Oph-
thalmic nurses and ophthalmologists saw significantly more pa-
tients with vision impairment than did optometrists or RWs (p Ͻ
0.05). However, RWs had significantly longer consultations with
patients than any other group (p Ͻ 0.001), and optometrists had
significantly longer consultations than ophthalmologists (p ϭ
0.005). Less than 20% (n ϭ 18) of participants reported having
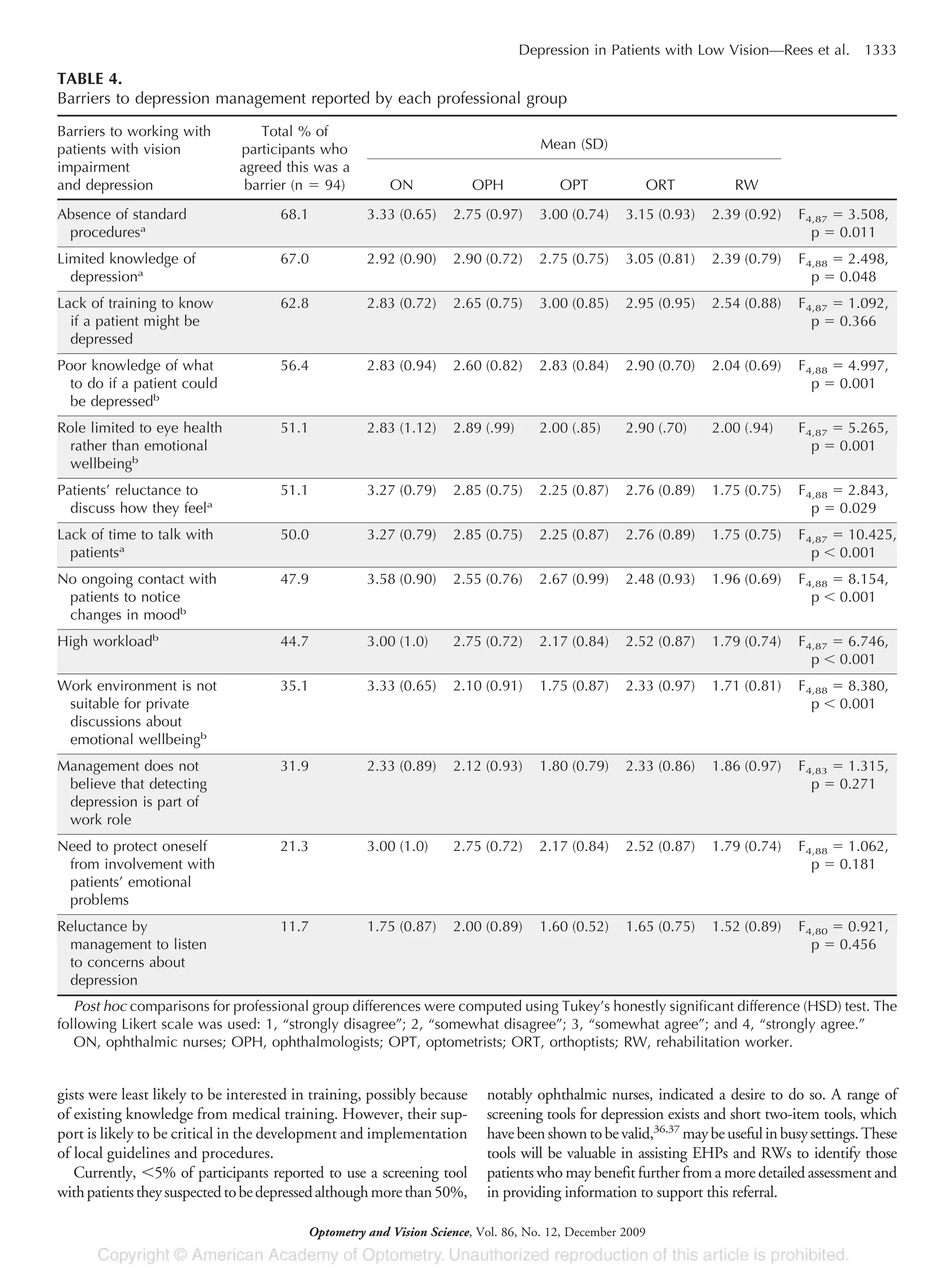
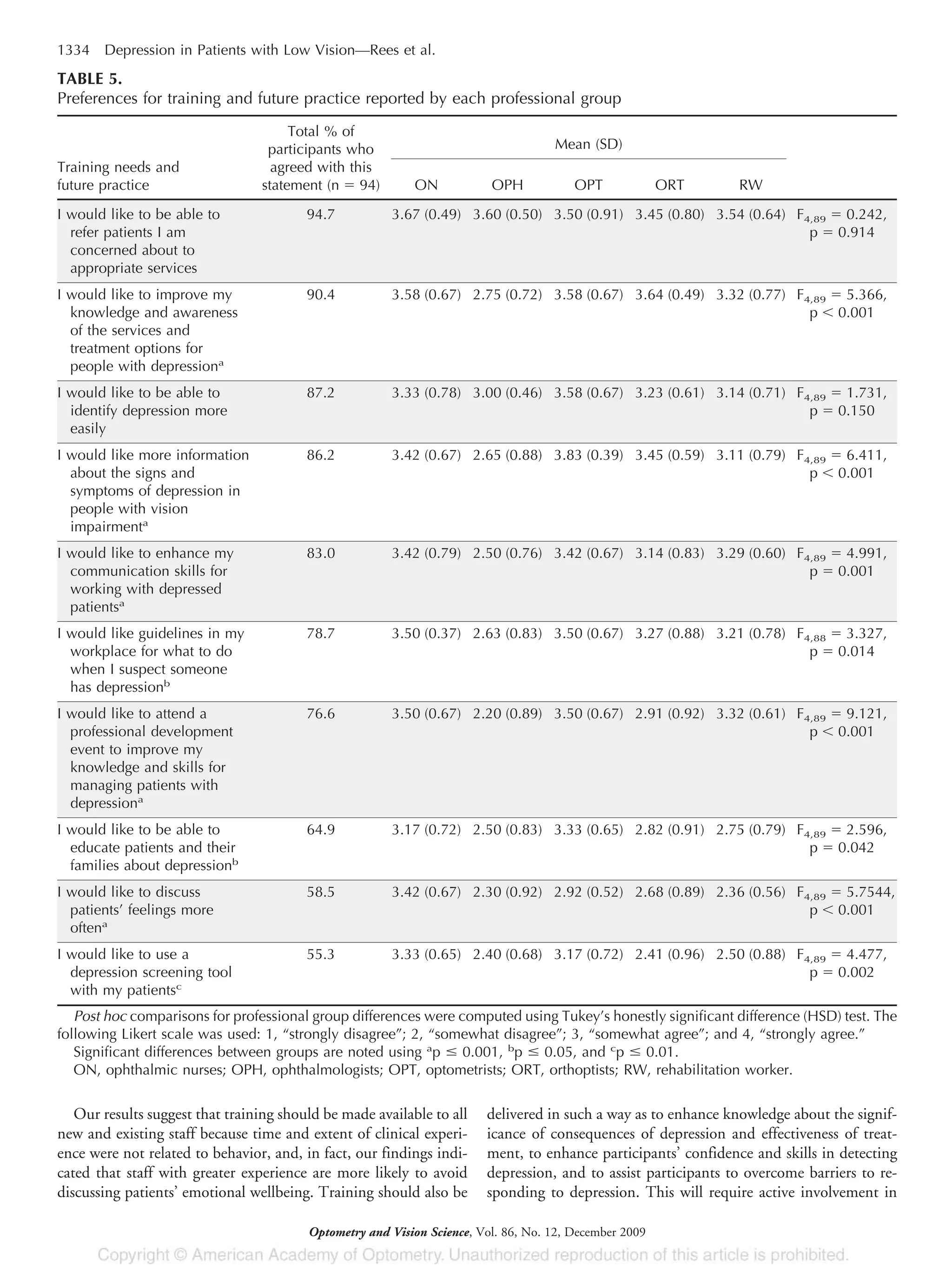
ever received any training in depression. Although few participants
(n ϭ 15, 16%) reported having personally experienced depression,
more than 70% reported knowing family or friends who had.
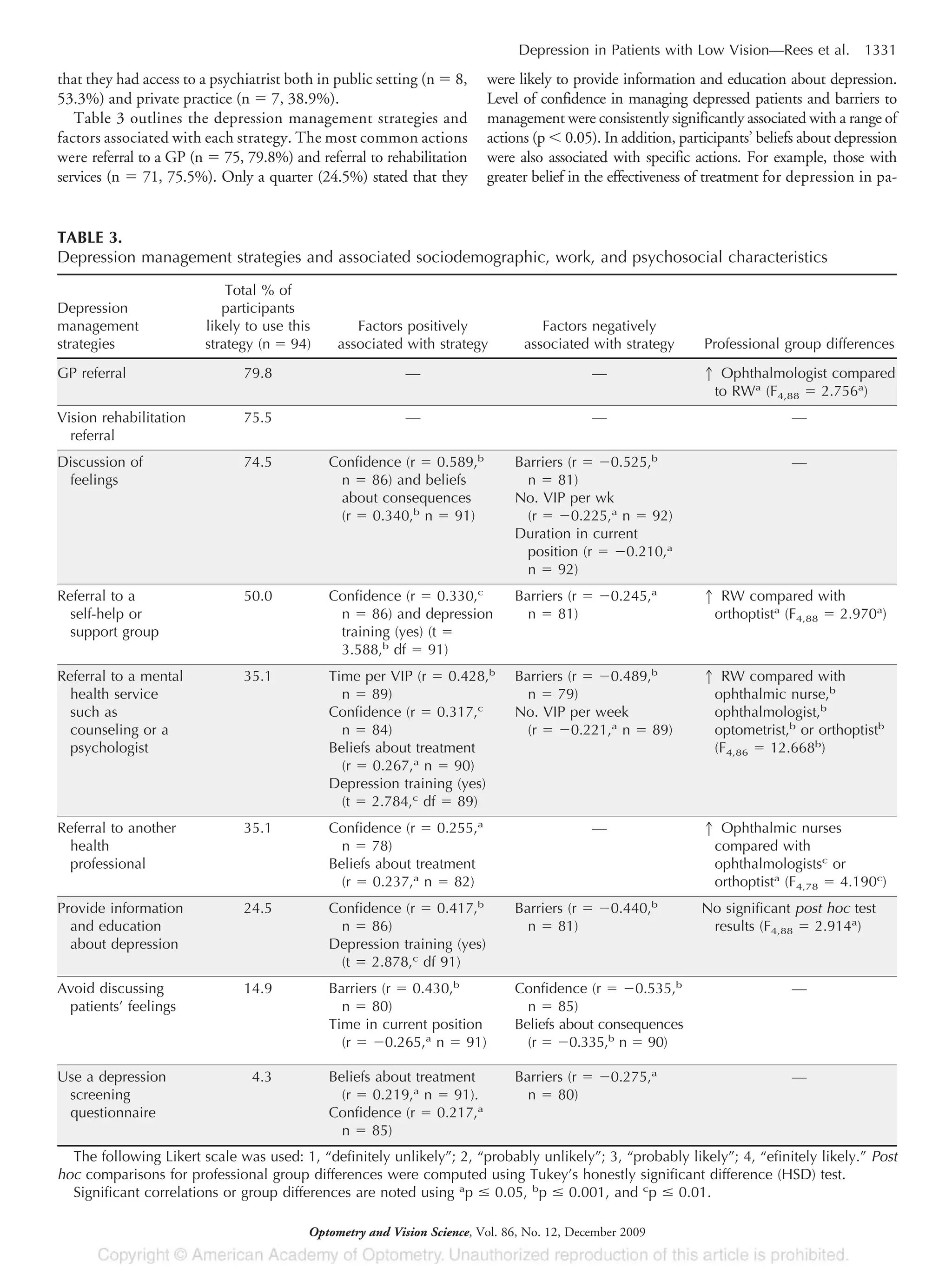
Current Practice
Identification of Depression
Overall, 39.8% (n ϭ 37) of participants stated that they at-
tempted to identify depression as part of patient management,
with RWs significantly more likely to do so (n ϭ 17, 60.7%) than
EHPs (n ϭ 20 30.8%) (2
ϭ 7.325, df ϭ 1, p ϭ 0.007). Socio-
demographic and work-related factors including duration in eye
care services and consultation times were not associated with in-
tention to identify depression, but confidence, barriers, and beliefs
about depression were associated (p Ͻ 0.05). Compared with those
who did not attempt to detect depression, participants who aimed
to identify depression were more confident (mean ϭ 37.89, SD
7.11 vs. mean ϭ 30.12, SD 7.66; t ϭ 4.772, df ϭ 85, p Ͻ 0.001),
reported fewer barriers (mean ϭ 27.09, SD 7.47 vs. mean ϭ
33.63, SD ϭ 7.05; t ϭ Ϫ4.034, df ϭ 80, p Ͻ 0.001), and believed
depression to hold greater consequences for a person with vision
impairment (mean ϭ 26.20, SD 2.92 vs. mean ϭ 24.59, SD 3.07;
t ϭ 2.48, df ϭ 89, p ϭ 0.015).
Management of Patients Who may be Depressed
The resources available to support patient management varied
according to work setting. The majority of participants working in
public hospitals stated that they had access to a social worker (n ϭ
29, 76.3%), RWs had access to a psychologist (n ϭ 18, 60%) and
counselor (n ϭ 16, 53.3%), and were more likely to refer to these
services than EHPs (2
ϭ 34.813, df ϭ 4, p Ͻ 0.000). Resources
available in private practice were limited, with more than a third
(n ϭ 16, 38.1%) of participants working in this setting reporting
no onsite resources. Ophthalmologists were most likely to report
TABLE 1.
Sociodemographic, work, and personal characteristics of
the 94 participants
Age (yr)
Mean 42.1
Range 23.3–69.4
Sex, n (%)
Female 71 (75.5)
Male 23 (24.5)
Time in current role (yr)
Mean 8.5
Range 0.4–37
Time in eye care services (yr)
Mean 14.6
Range 0.4–42
Previous depression training, n (%)
Yes 18 (19.1)
No 76 (80.9)
Personal experience of depression,a
n (%)
Yes 15 (16.0)
No 65 (69.1)
Family or friends’ experience of depression,a
n (%)
Yes 66 (70.2)
No 27 (28.7)
a
Percentage does not total 100 due to missing data.
TABLE 2.
Work setting and number and duration of consultations with patients with vision impairment for each professional group
Professional group Most common work setting
No. patients with vision
impairment seen each
week, mean (SD)
Average time spent
with each patient
(min), mean (SD)
Ophthalmic nurse (n ϭ 12) Public hospital (n ϭ 11, 91.7%) 29.7 (32.3) 20.5 (34.05)
Optometrist (n ϭ 12) Private practice (n ϭ 7, 58.3%) 5.08 (8.9) 46.4 (15.6)
Ophthalmologist (consultant)
(n ϭ 20)
Combination of private practice and
public hospital (n ϭ 13, 65%)
37.9 (33.8) 13.0 (3.6)
Orthoptist (n ϭ 22) Private practice (n ϭ 8, 36.4%) 20.2 (17.7) 23.6 (26.7)
Rehabilitation worker (n ϭ 28) Rehabilitation agency (n ϭ 27, 96.7%) 8.3 (4.3) 98.2 (32.6)
1330 Depression in Patients with Low Vision—Rees et al.
Optometry and Vision Science, Vol. 86, No. 12, December 2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/detectionofdepressioninpatientswithlow-130709120030-phpapp01/75/Detection-of-depression_in_patients_with_low-4-3-2048.jpg)