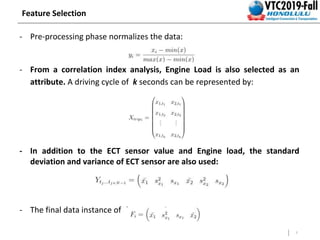
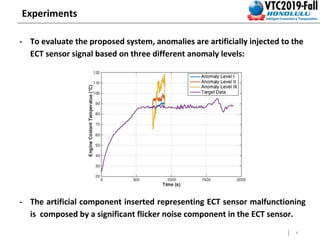
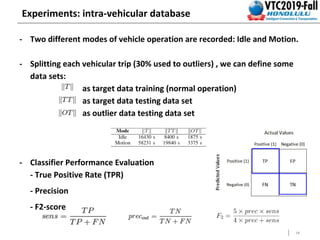
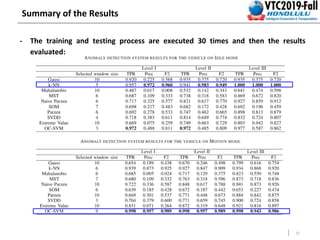
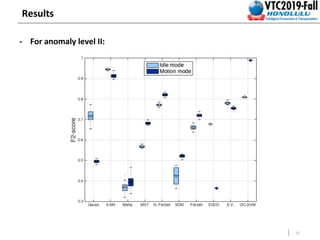
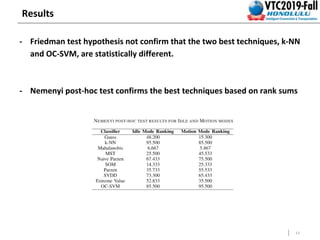
This document summarizes a study that detects anomalies in engine coolant temperature sensors using one-class classifiers. It describes how data is acquired from vehicle sensors and preprocessed, features like temperature, load, and their statistics are extracted. Different one-class classifiers like k-NN, OC-SVM, and Gaussian methods are evaluated on normal and artificially injected anomalous data. The results show k-NN and OC-SVM perform best for idle and motion modes respectively, demonstrating these techniques can detect sensor malfunctions of different severity levels.