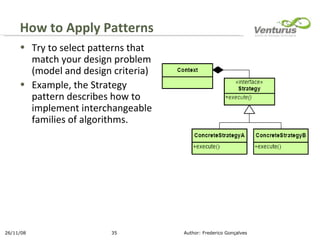
The document discusses object-oriented design patterns, outlining their definitions, principles, and applications, particularly within mobile development. It emphasizes the importance of patterns for creating flexible, reusable solutions to common design problems and introduces the Gang of Four (GoF) design patterns as foundational examples. Additionally, it provides guidance on applying these patterns effectively in design, while also recognizing the need for careful consideration when introducing new patterns.