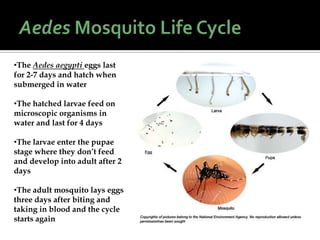
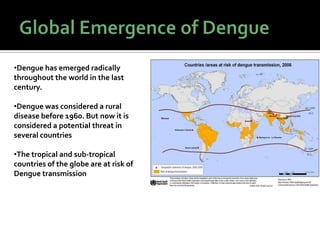
This document discusses dengue fever, which is transmitted by the Aedes aegypti mosquito. It describes the mosquito's life cycle and breeding habits. There are four types of dengue viruses that cause the disease. Symptoms include fever, headache, rash and joint pain. While historically a rural disease, dengue has emerged as a global threat present in tropical and subtropical regions. Prevention efforts include eliminating standing water and using protective clothing and repellents.