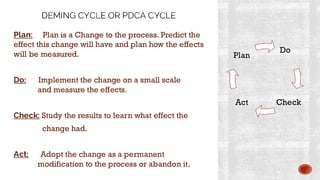
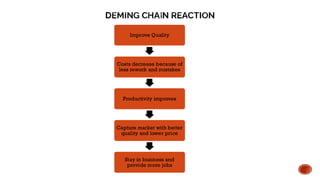
Dr. William Edwards Deming, an influential statistician and management consultant, introduced his quality improvement philosophy in his book "Out of the Crisis," significantly aiding Japan's post-war economy. His philosophy emphasizes the importance of total quality management, focusing on continuous improvement, leadership, and a systems thinking approach. Key principles include creating constancy of purpose, adopting a new philosophy, eliminating reliance on inspection, and fostering a collaborative environment among all employees.