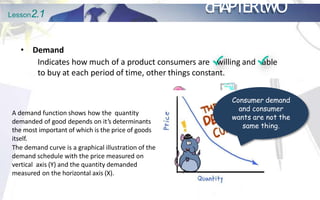
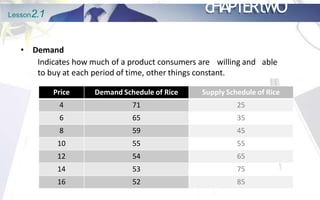
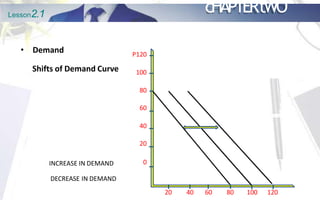
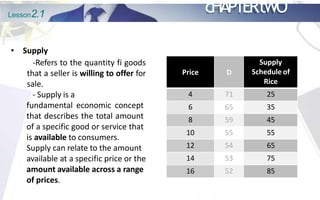
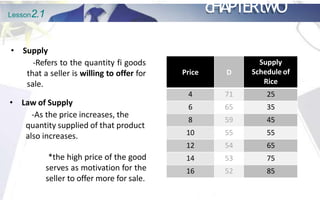
This document discusses the principles of demand and supply. It begins by outlining the chapter's objectives which are to explain the law of demand and supply, factors affecting demand and supply, analyze prices of commodities, and discuss market structures. The document then provides details on the basic principles of demand and supply, including definitions of demand, the law of demand, and factors that shift the demand curve. It also discusses the definition of supply, the law of supply, and factors that shift the supply curve. Finally, it explains the concept of market equilibrium.