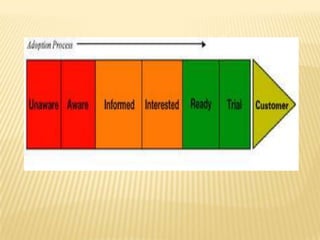
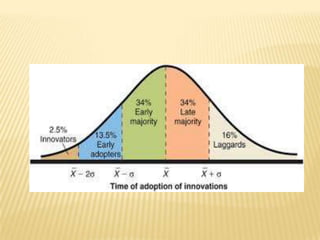
The document discusses the consumer adoption process, also known as the diffusion of innovations. It describes the six main stages consumers go through when adopting a new product or service: 1) Awareness, where consumers first learn about the product's existence; 2) Interest, when consumers search for more information; 3) Evaluation, where consumers assess the product's benefits and compare alternatives; 4) Trial, when consumers experience the product; 5) Adoption or rejection decision, when consumers decide whether to continue using the product; and 6) Different categories of adopters, from innovators to laggards, who adopt the product at different points in its lifecycle.