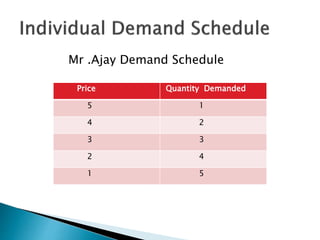
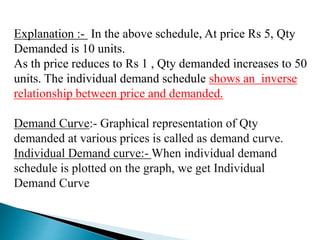
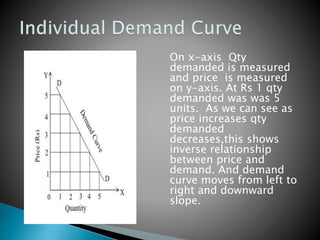
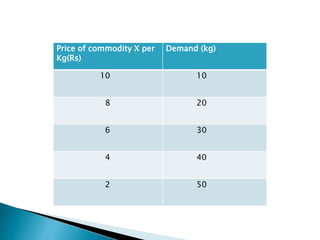
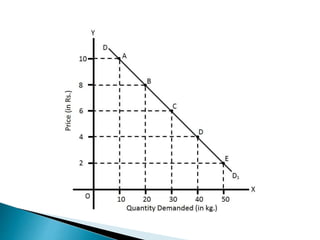
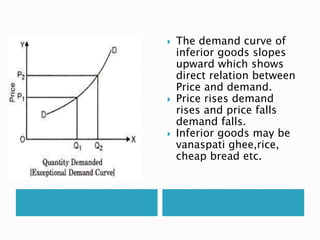
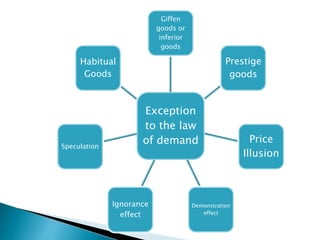
The document discusses the law of demand and its exceptions. It defines demand and explains the three necessary conditions for demand - desire, ability to pay, and willingness to pay. The law of demand states that, assuming all other factors are held constant, quantity demanded and price are inversely related - as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa. The law is presented through sample demand schedules and graphs. Exceptions to the law include Giffen goods, prestige goods, price illusion, demonstration effect, ignorance effect, speculation, and habitual goods.