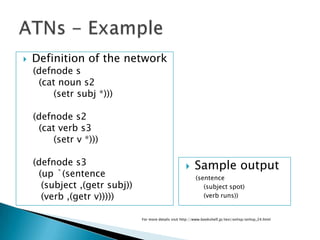
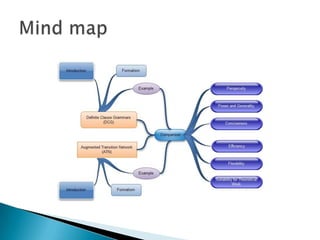
This document compares definite clause grammars (DCGs) and augmented transition networks (ATNs) for language analysis. DCGs extend context-free grammars by allowing non-terminals to be terms rather than just atoms, and allow procedure calls in rule right-hand sides. DCGs are more powerful, concise, efficient and flexible than ATNs, while also being well-suited for theoretical linguistic work.


![Extended from CFG specifying that:Non-terminals can be terms not only atomsnp(X,S) sentence(S)Procedure calls in the RHS of a rule enclosed within ‘{‘ and ‘}’noun(N) -> [W], {rootform(W,N), is_noun(N)}.DCGs - Formalism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/definiteclausegrammarsforlanguageanalysis-a-100311014212-phpapp02/85/Definite-Clause-Grammars-For-Language-Analysis-4-320.jpg)
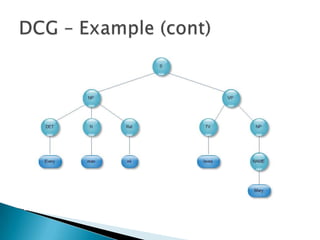
![sentence( s(NP, VP) ) ->noun_phrase(NP), verb_phrase(VP).noun_phrase(np(Det,Noun,Rel) )-> determiner(Det), nounI.Noun),rel_clause(Rel).noun_phrase(np(Name) ) -> name(Name).verb_phrase(vp(TV,NP) ) -> trans_verb(TV), noun_phrase(NP).verb_phrase(vp(IV) ) -> intrans_verb(IV).rel_clause(rel(that,VP) ) -> [that], verb_phrase(VP).rel_clause(rel(nil) ) -> [].determiner(det(W) ) -> [W], {is_determiner(W)}.noun(n(W) ) -> [W], {is_noun(W)}.name(name(W) ) -> [W], {is_name(W)}.trans_verb(tv(W) ) -> [W], {is_trans(W)}.intrans_verb(iv(W) ) -> [W], {is_intrans(W)}.DCG - Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/definiteclausegrammarsforlanguageanalysis-a-100311014212-phpapp02/85/Definite-Clause-Grammars-For-Language-Analysis-5-320.jpg)