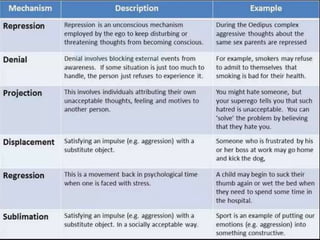
This document discusses various psychological defense mechanisms. It defines defense mechanisms as unconscious strategies used to protect from anxiety arising from unacceptable thoughts or feelings. It then explains several common defense mechanisms, including repression, projection, displacement, sublimation, denial, intellectualization, rationalization, and regression. For each defense mechanism, it provides a definition and example to illustrate how that mechanism might operate. The overall document aims to help readers understand different unconscious strategies the mind uses to reduce anxiety and protect the ego.