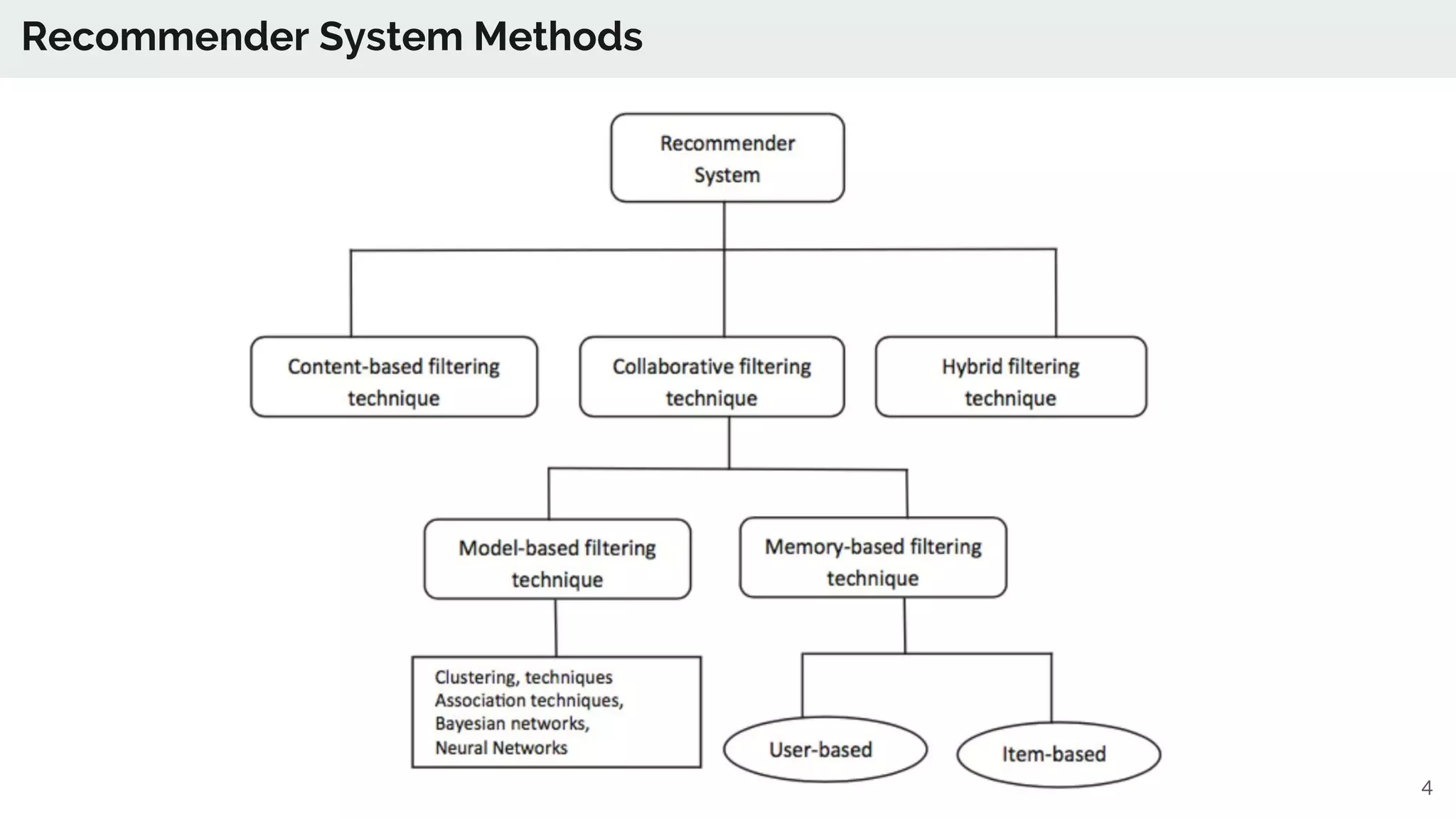
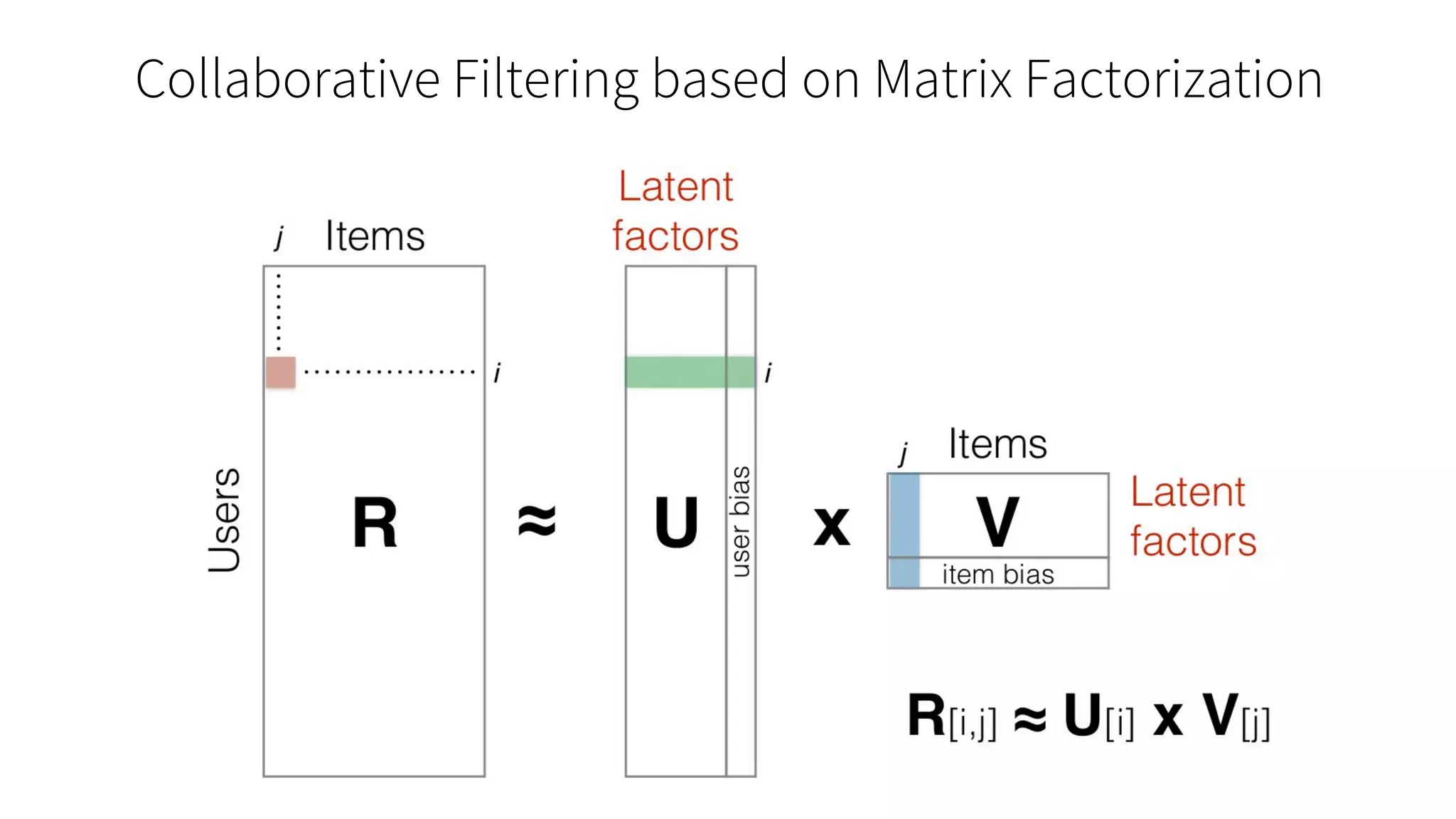
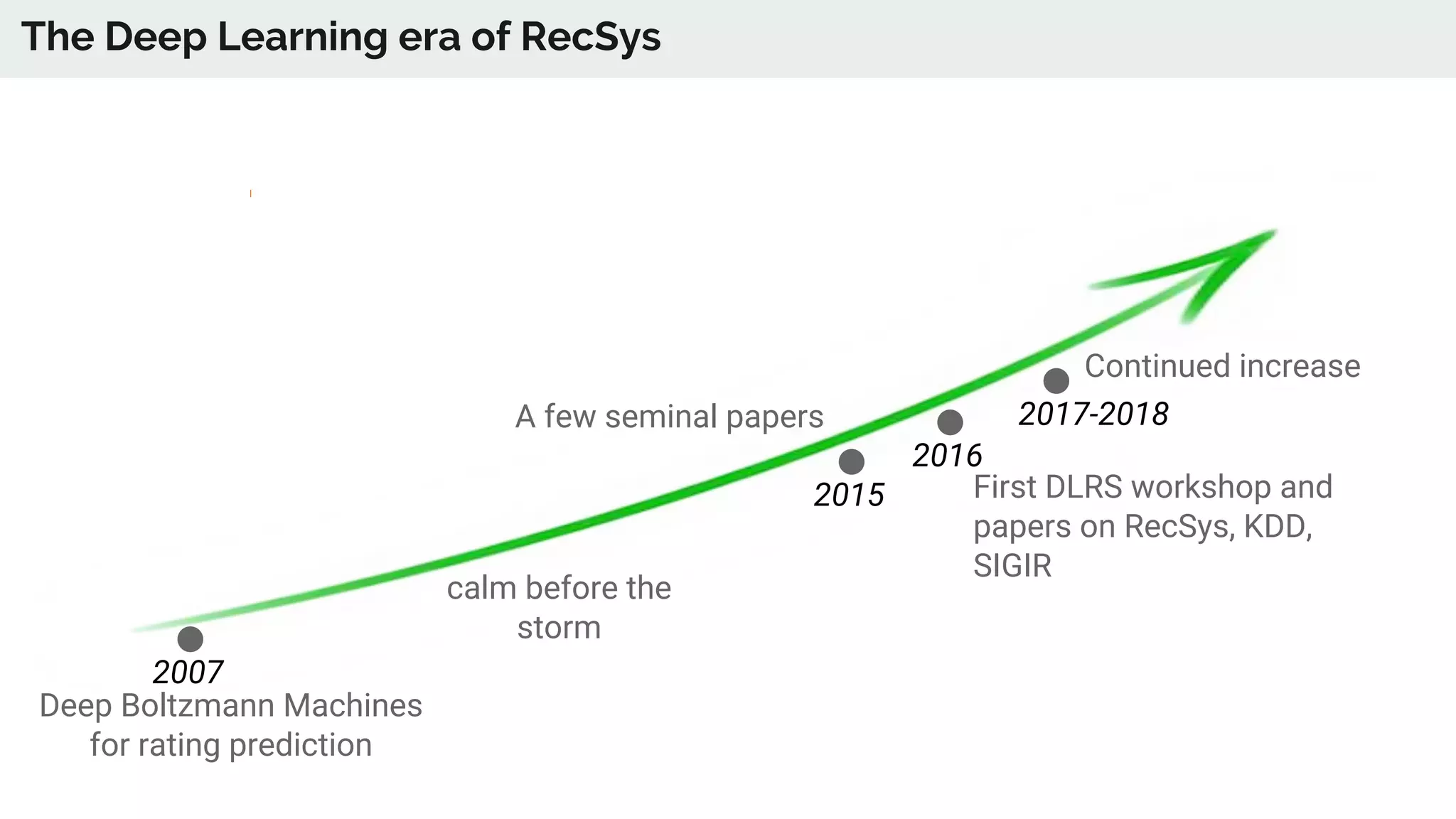
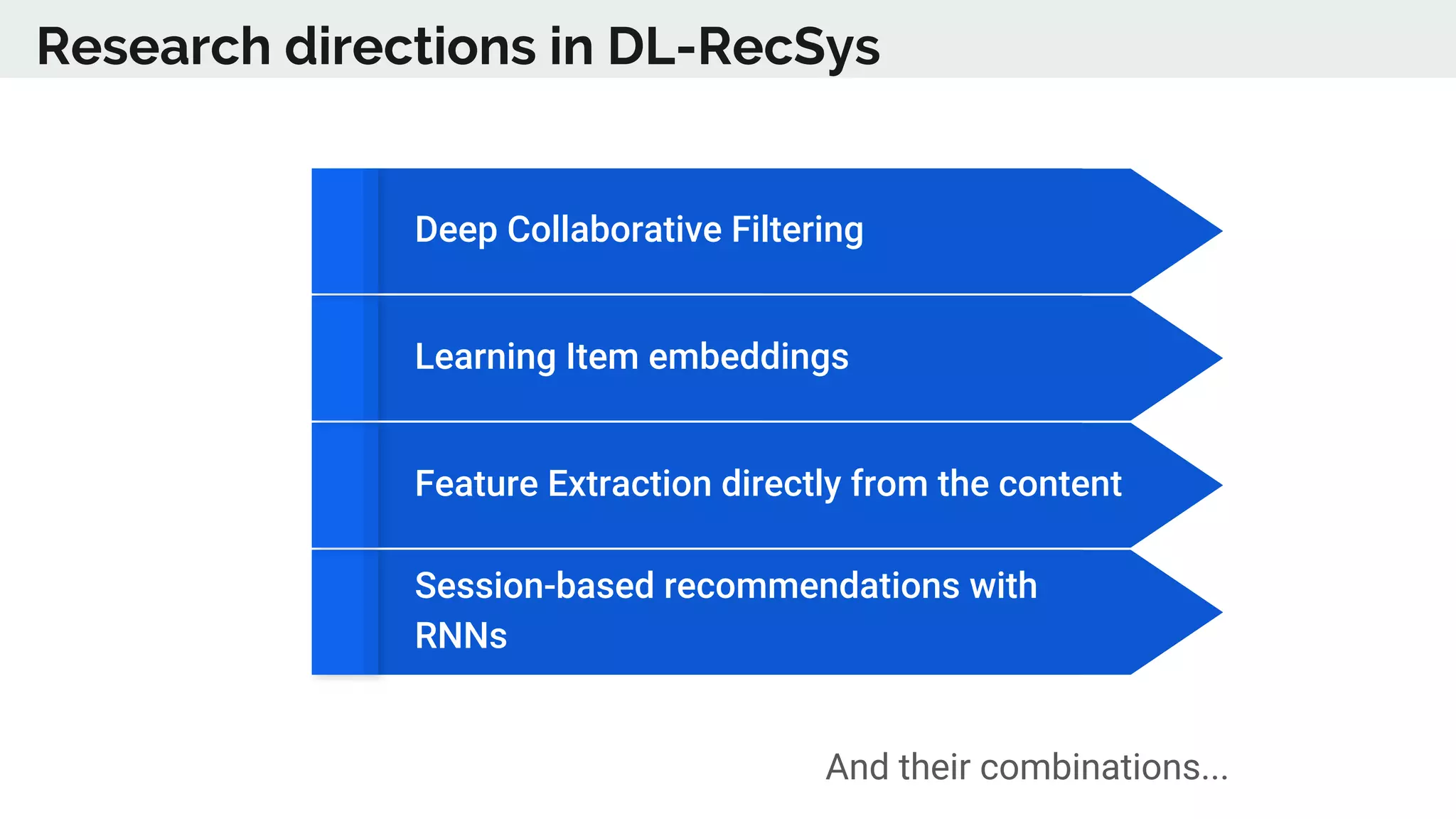
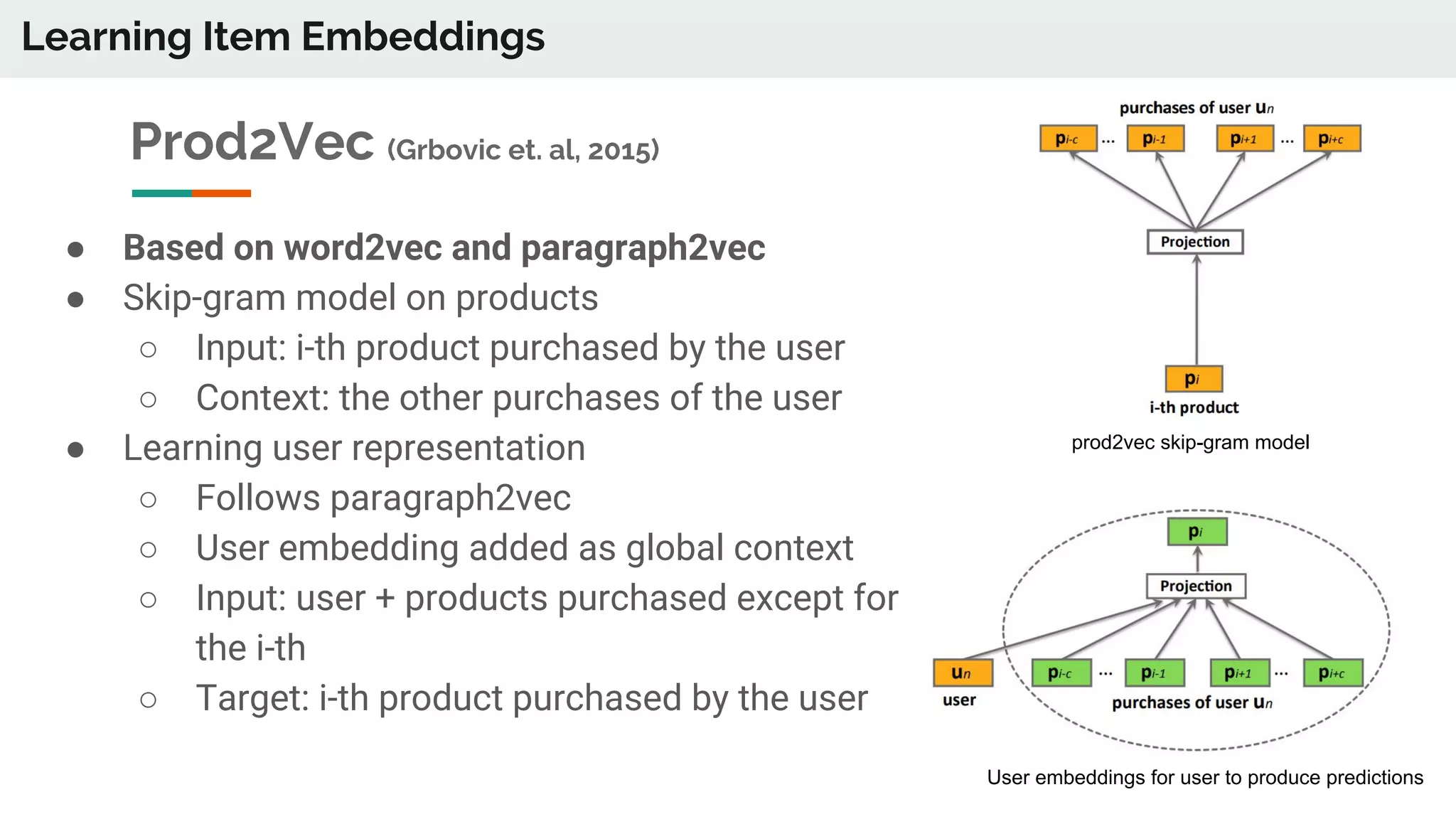
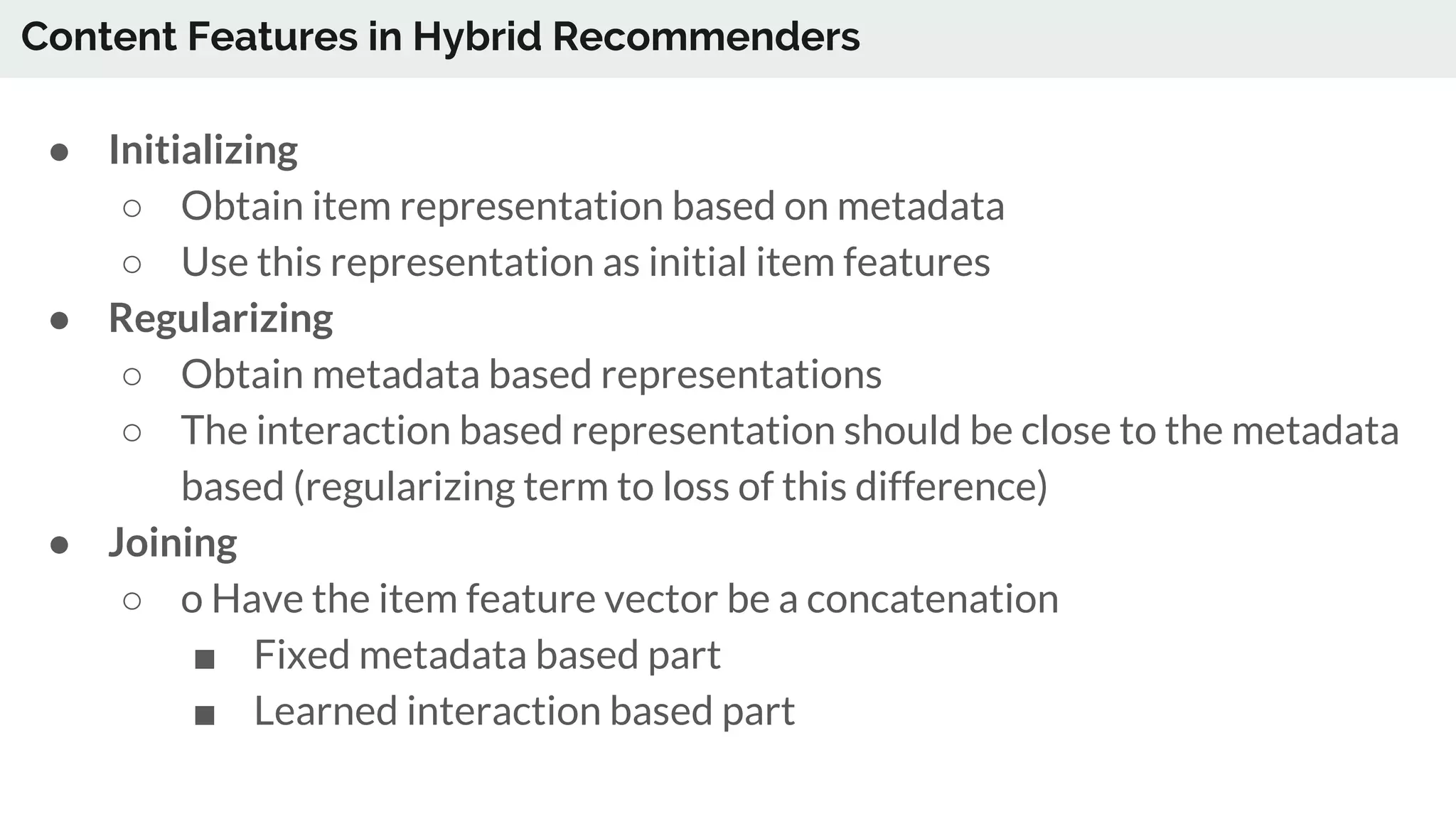
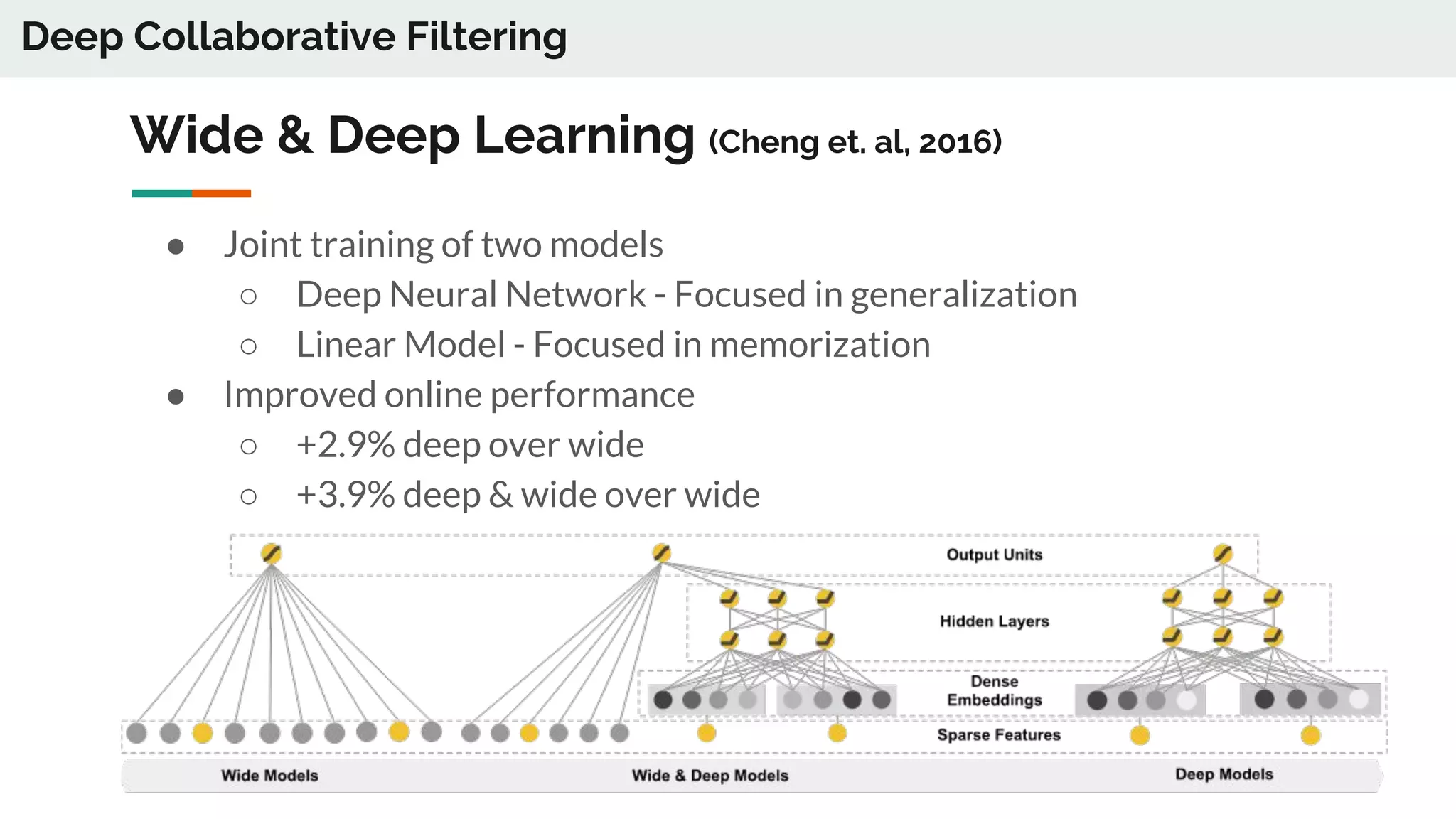
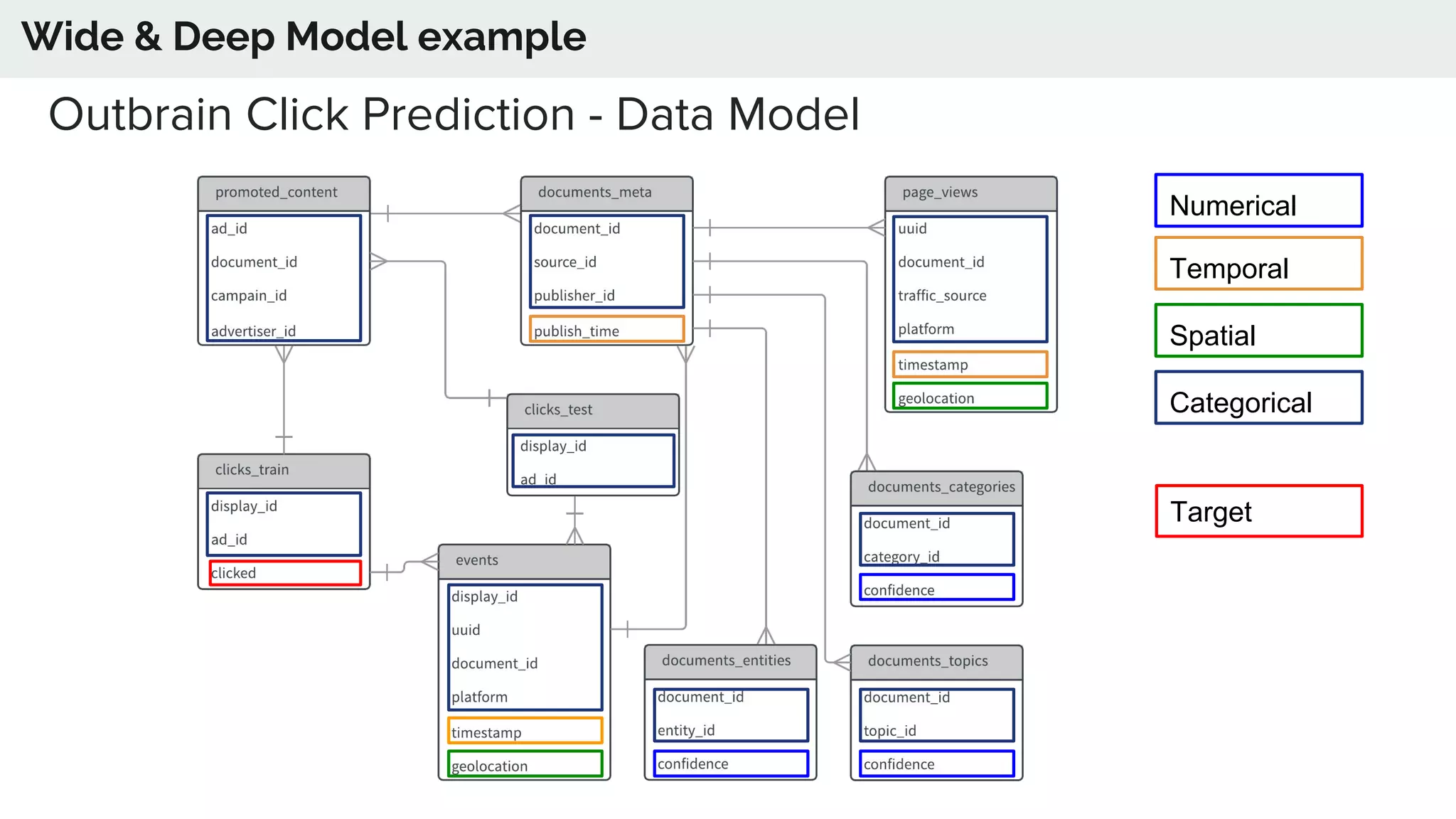
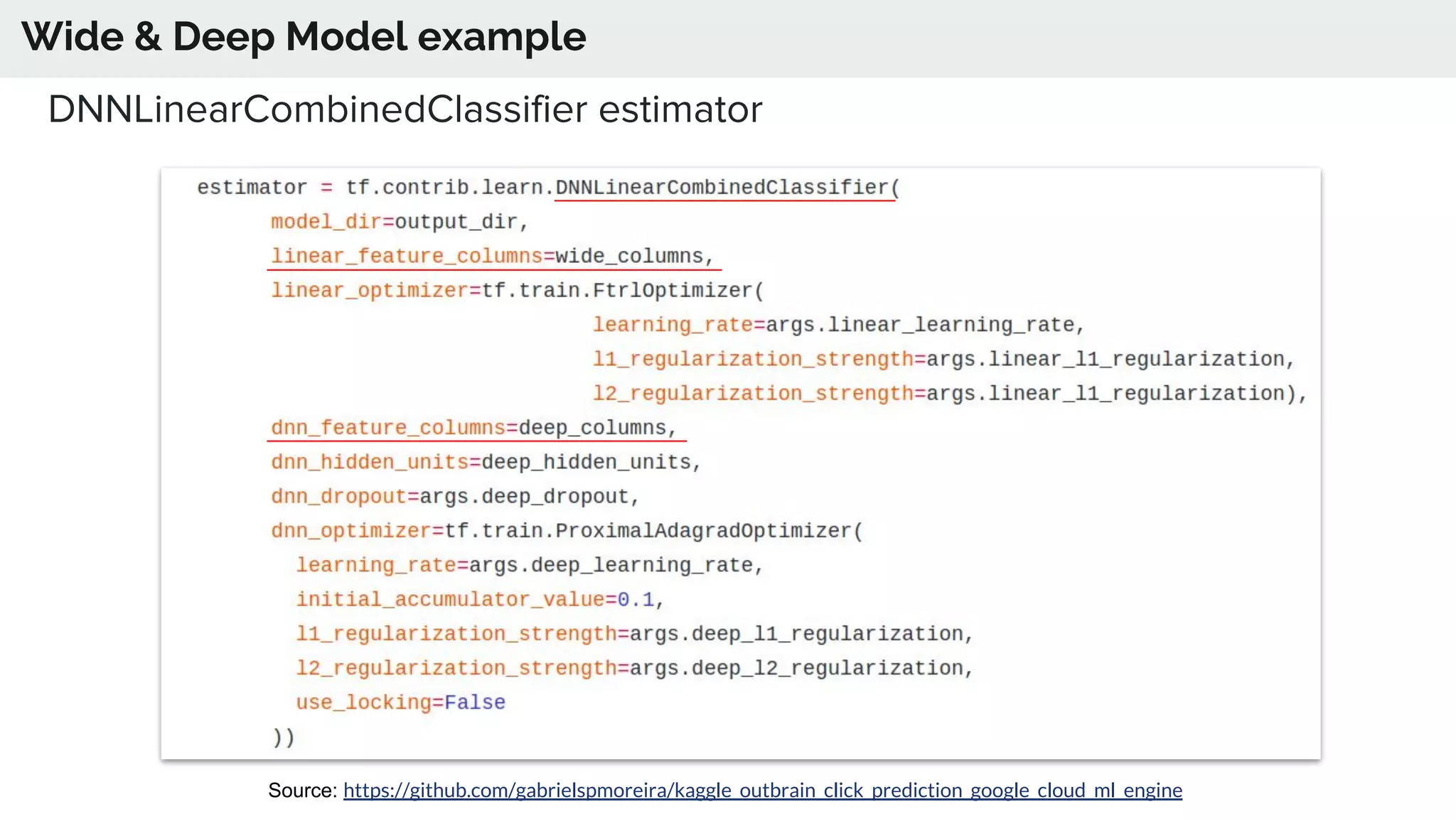
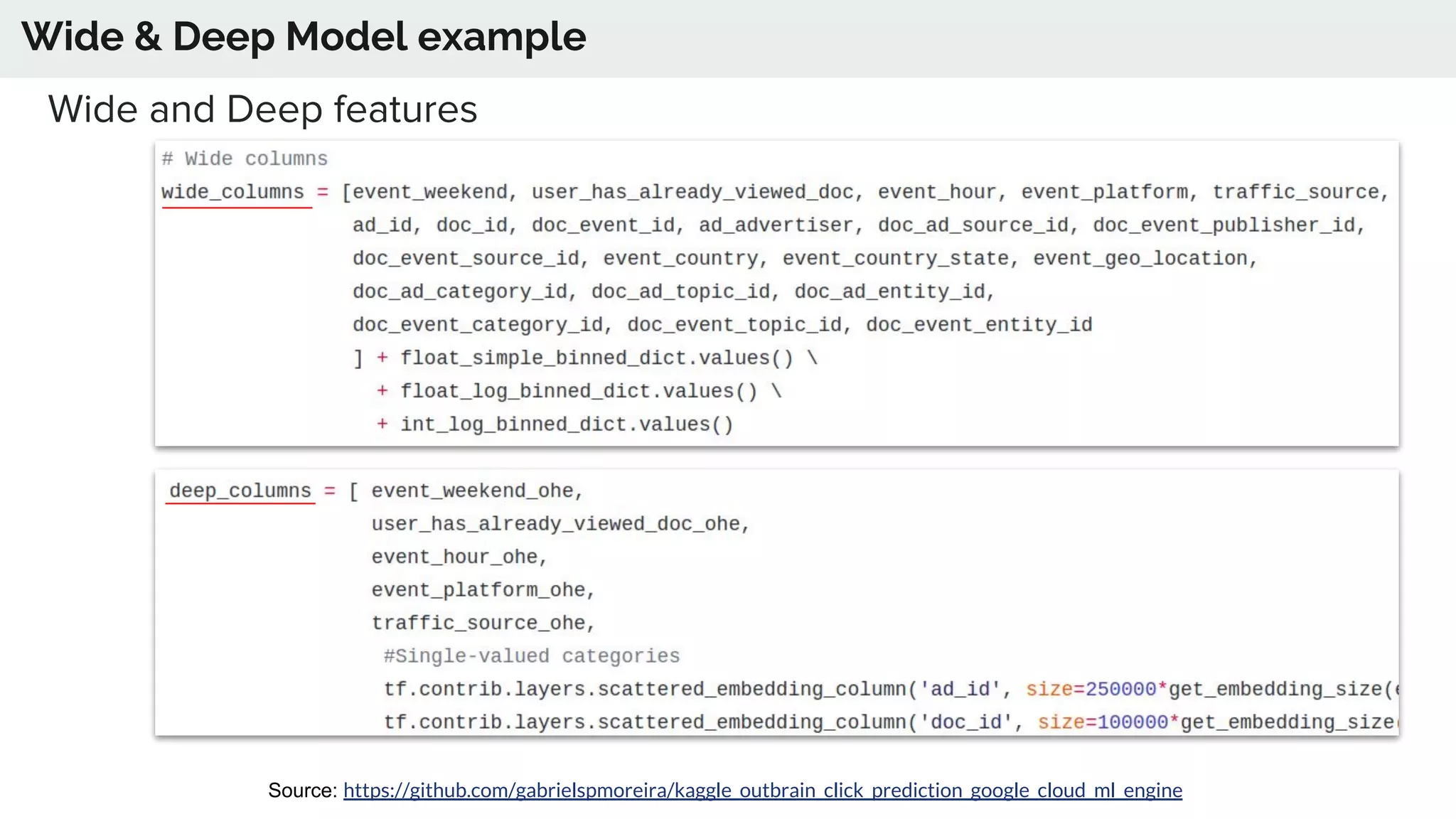
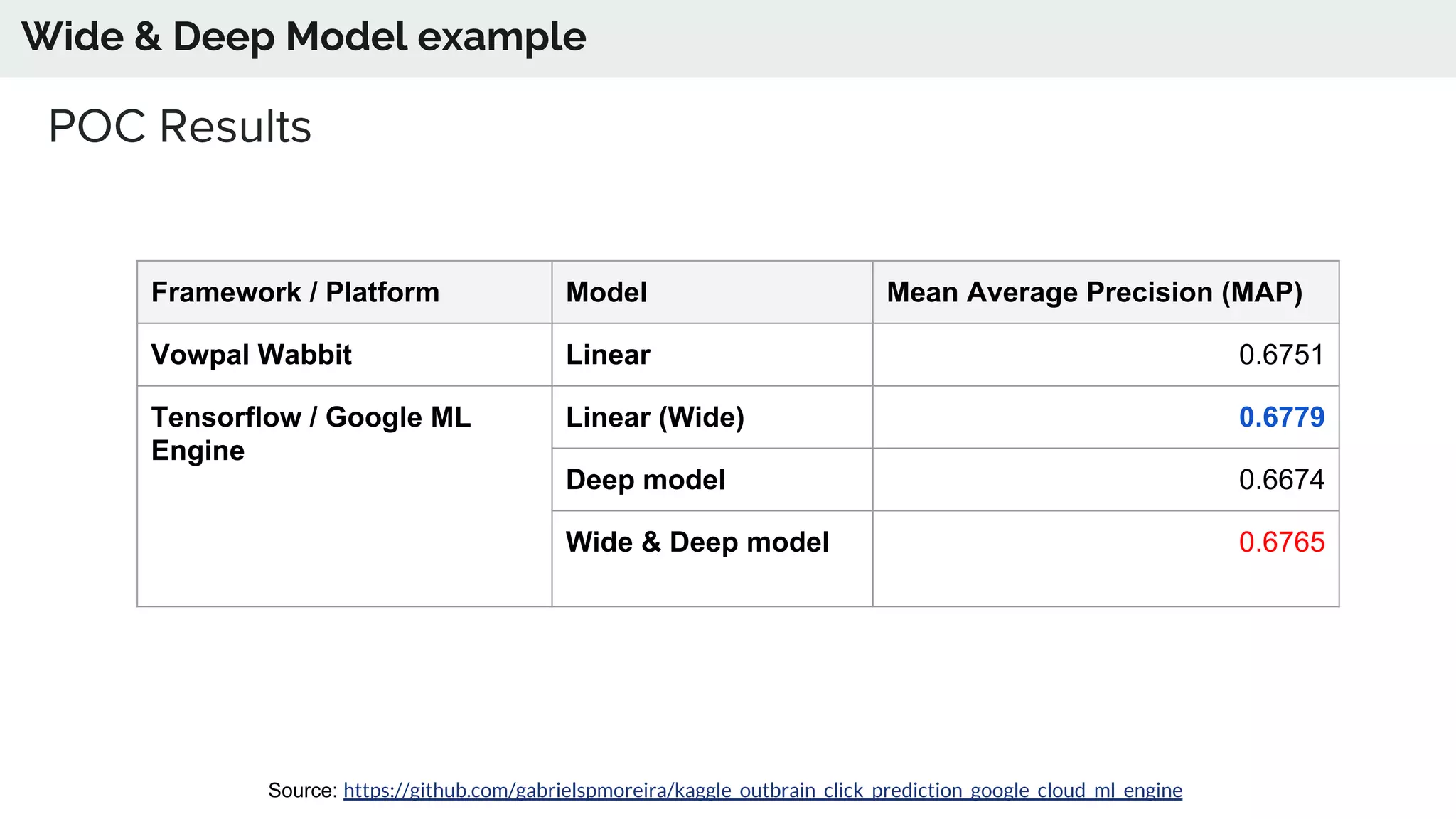
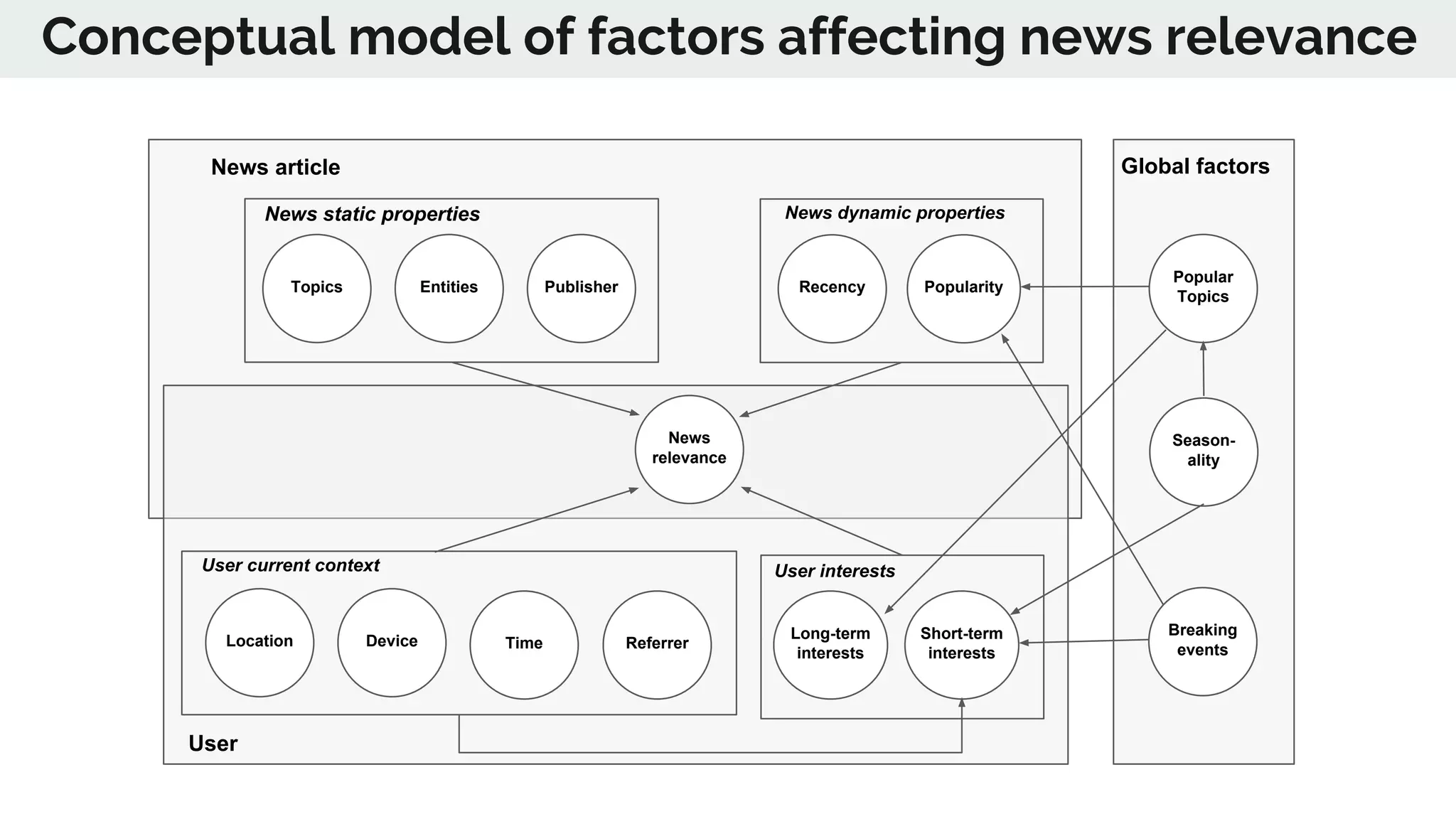
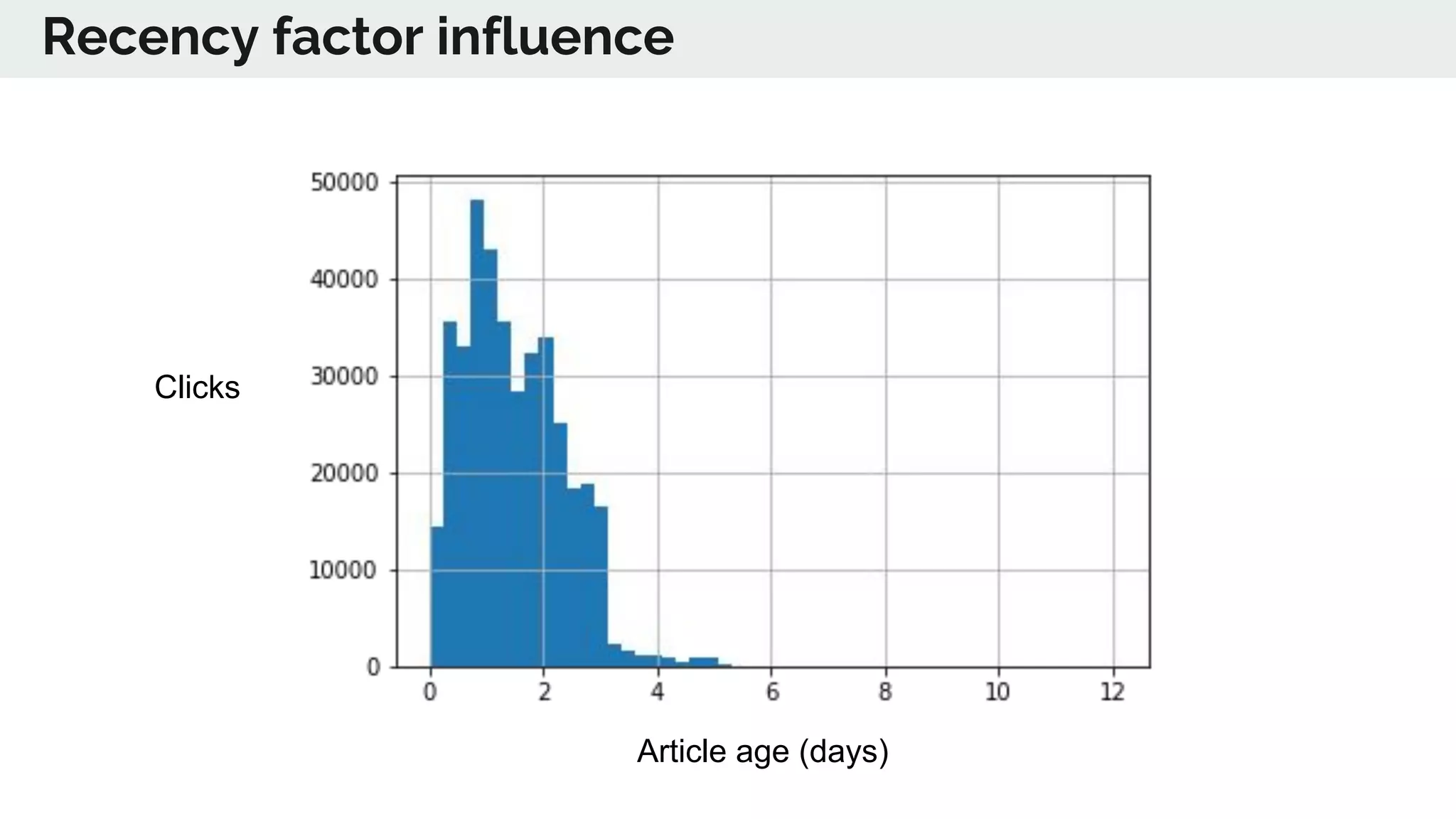
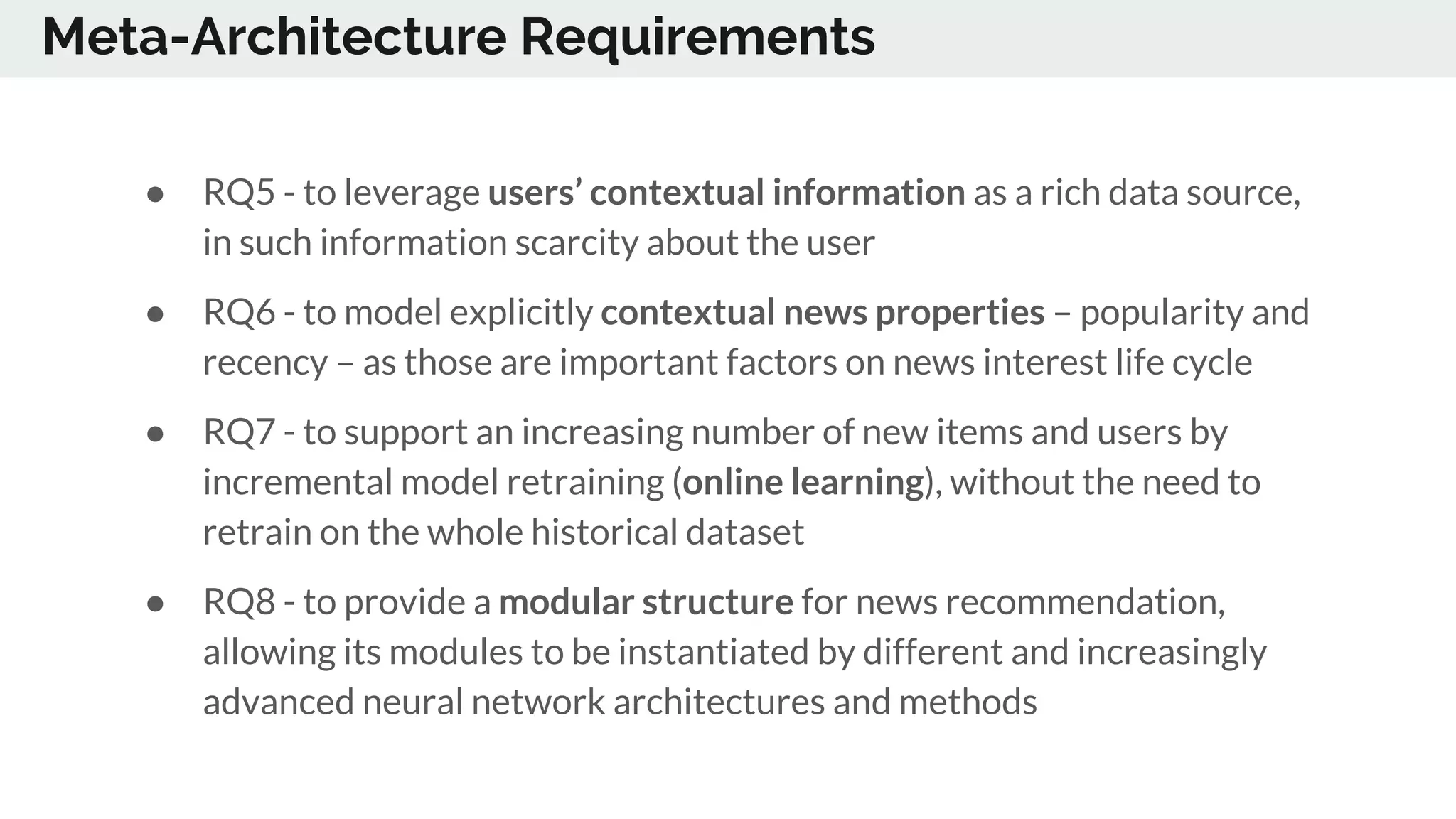
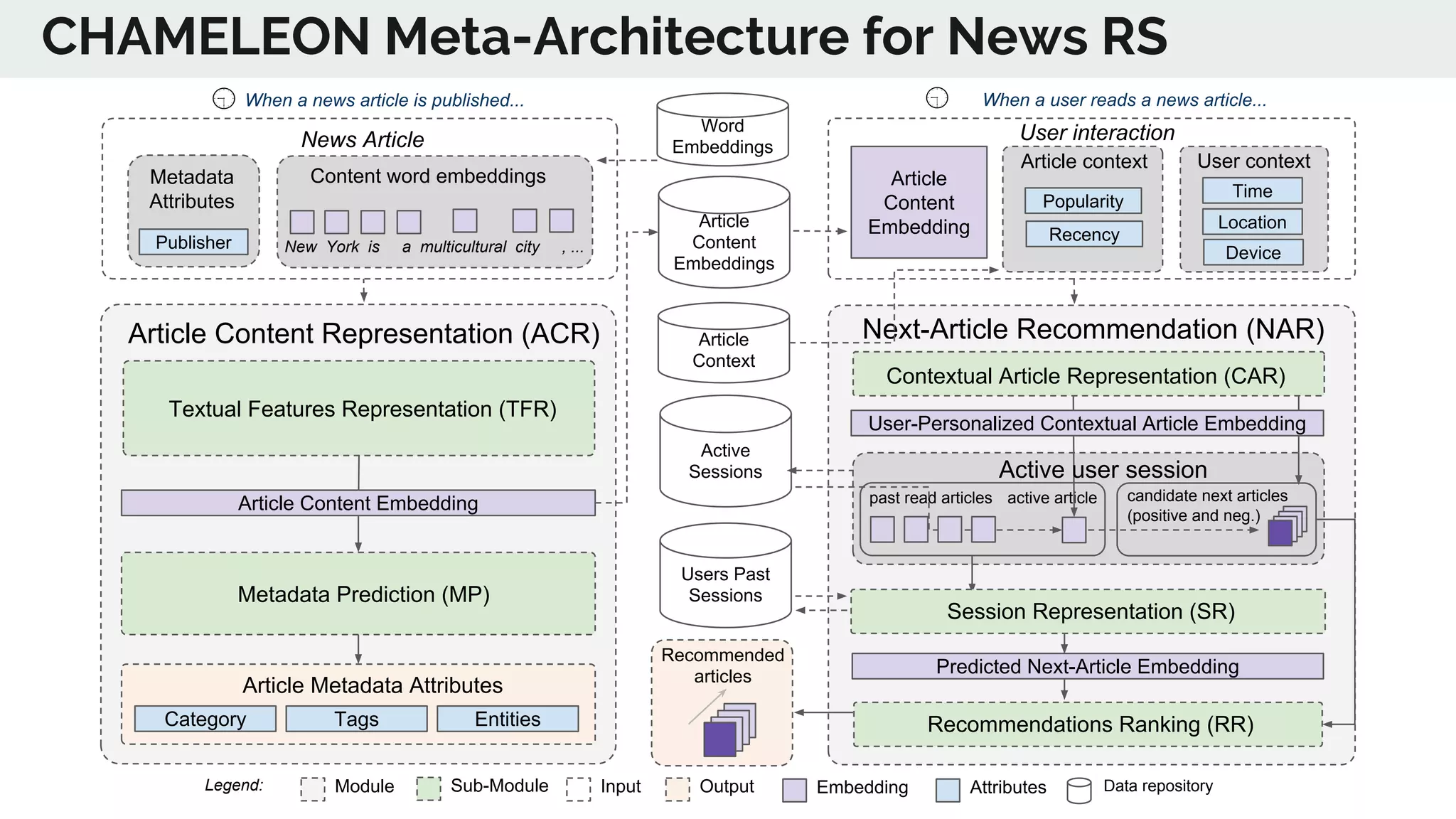
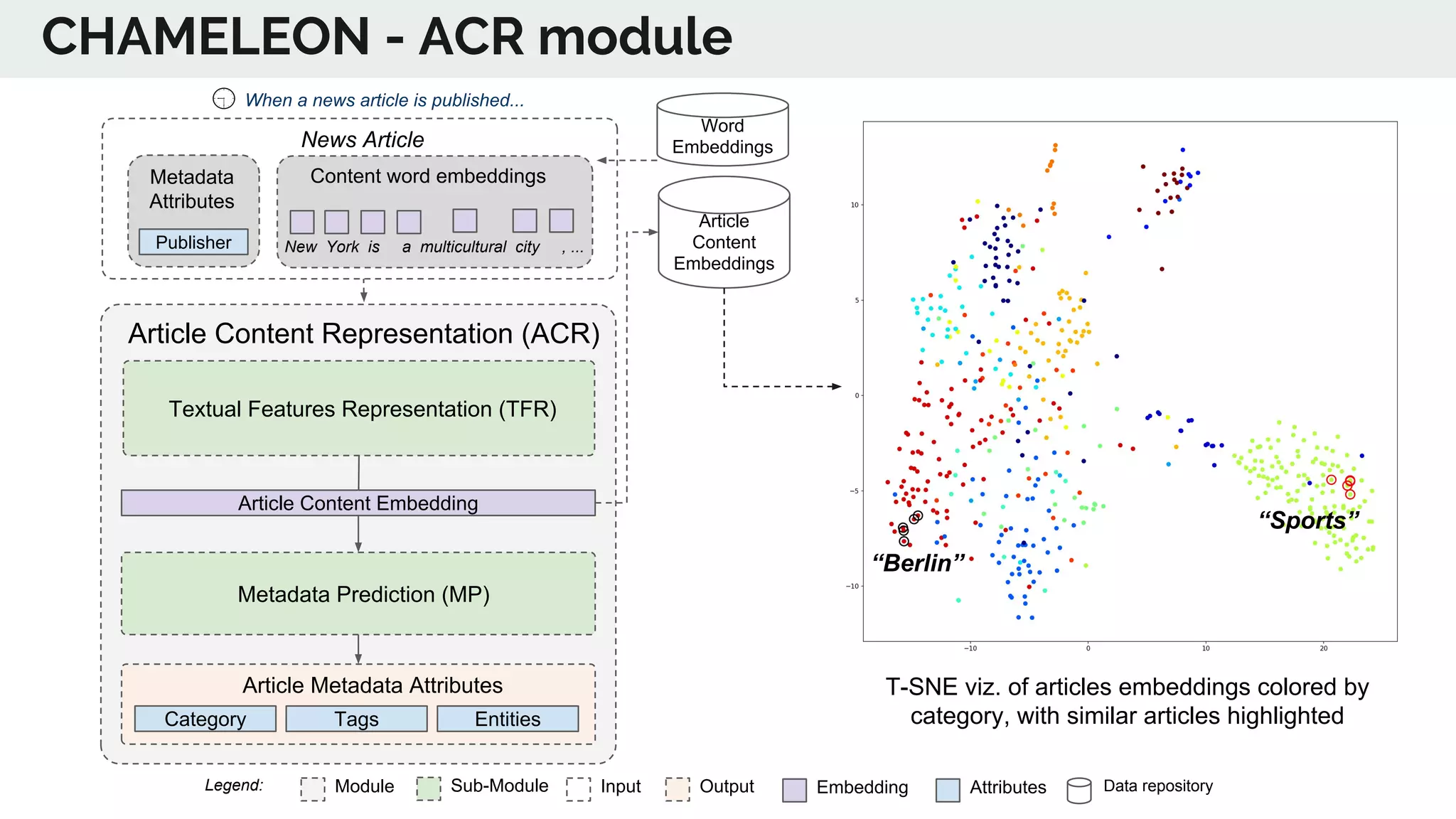
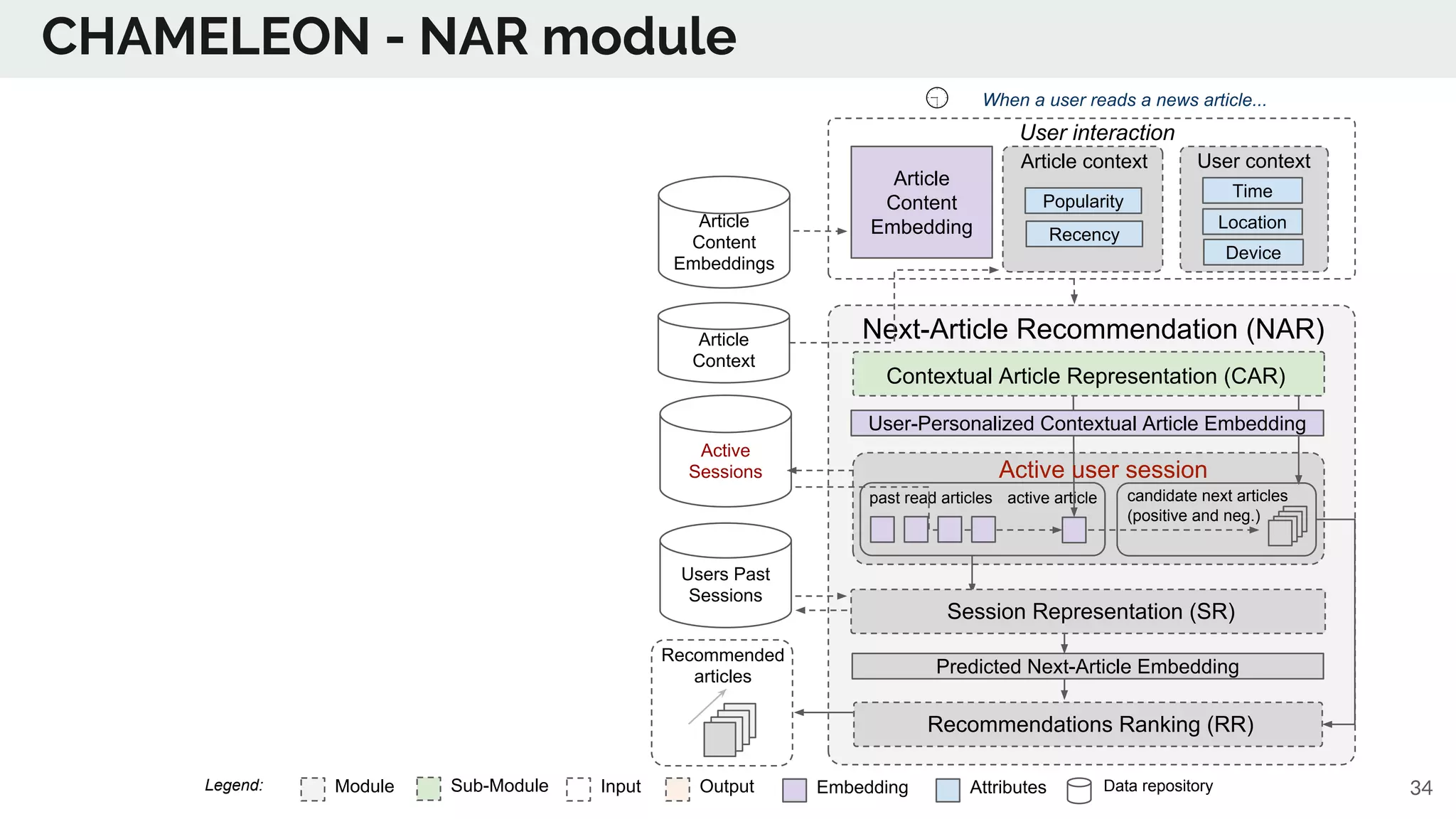
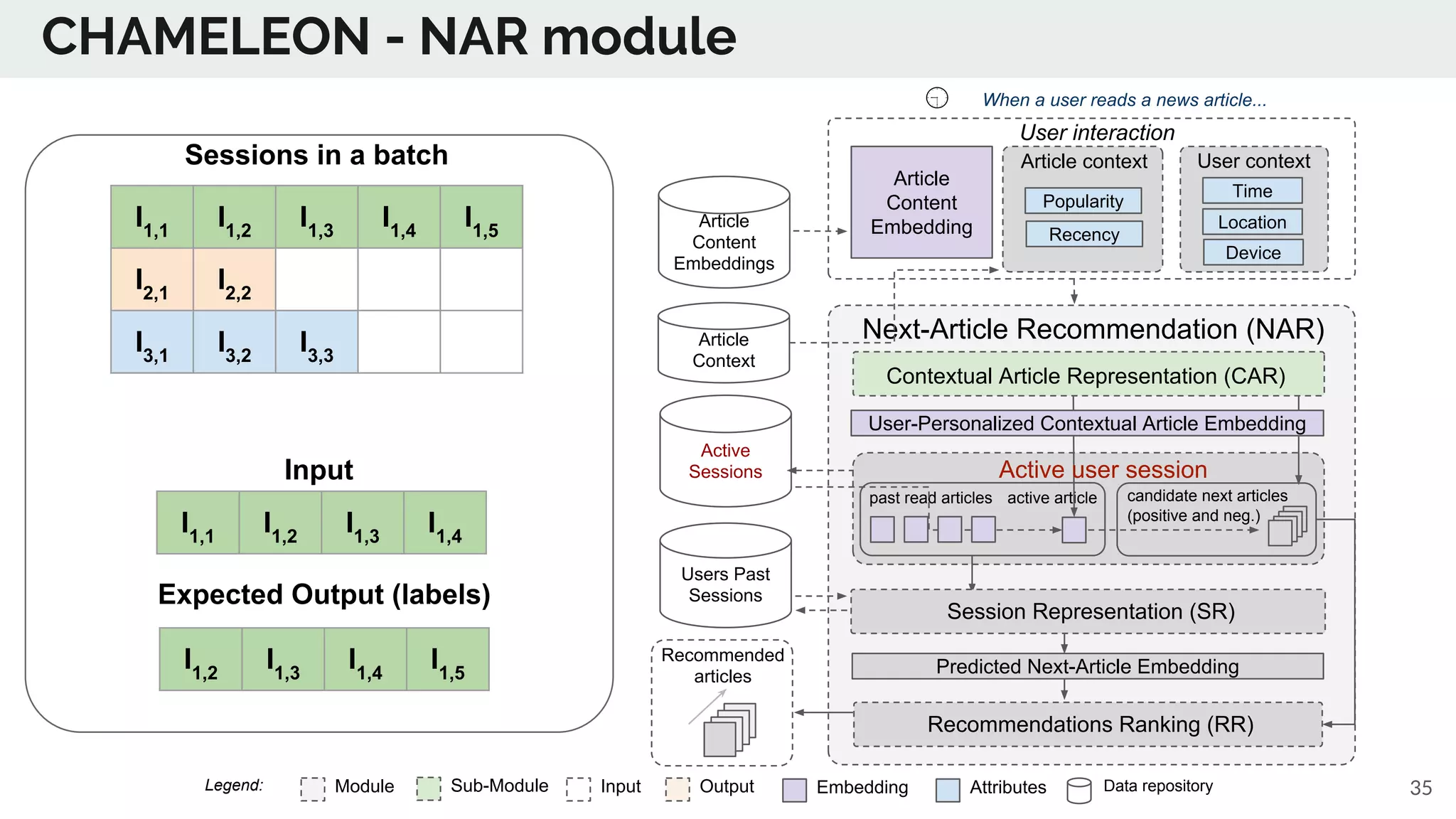
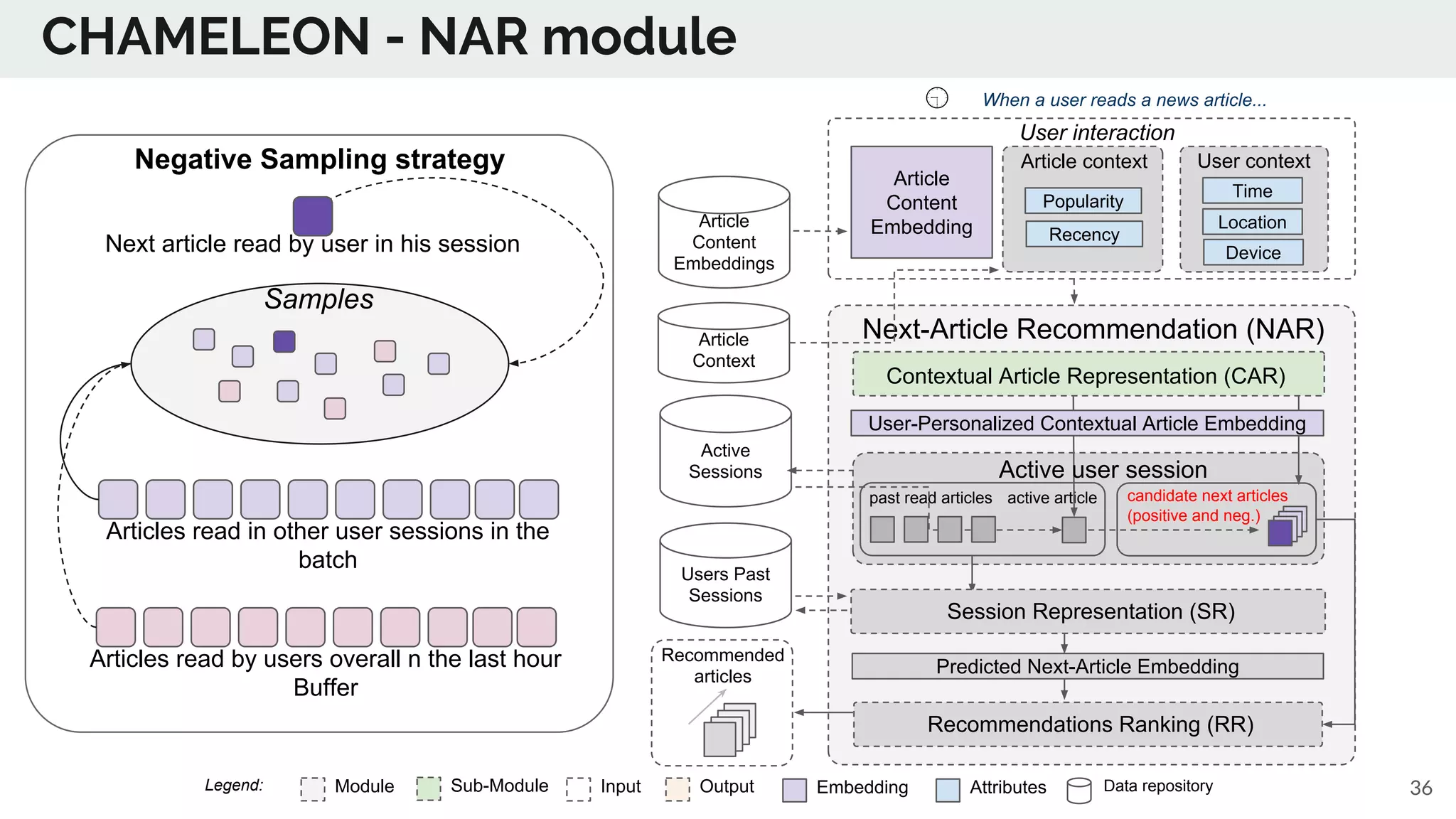
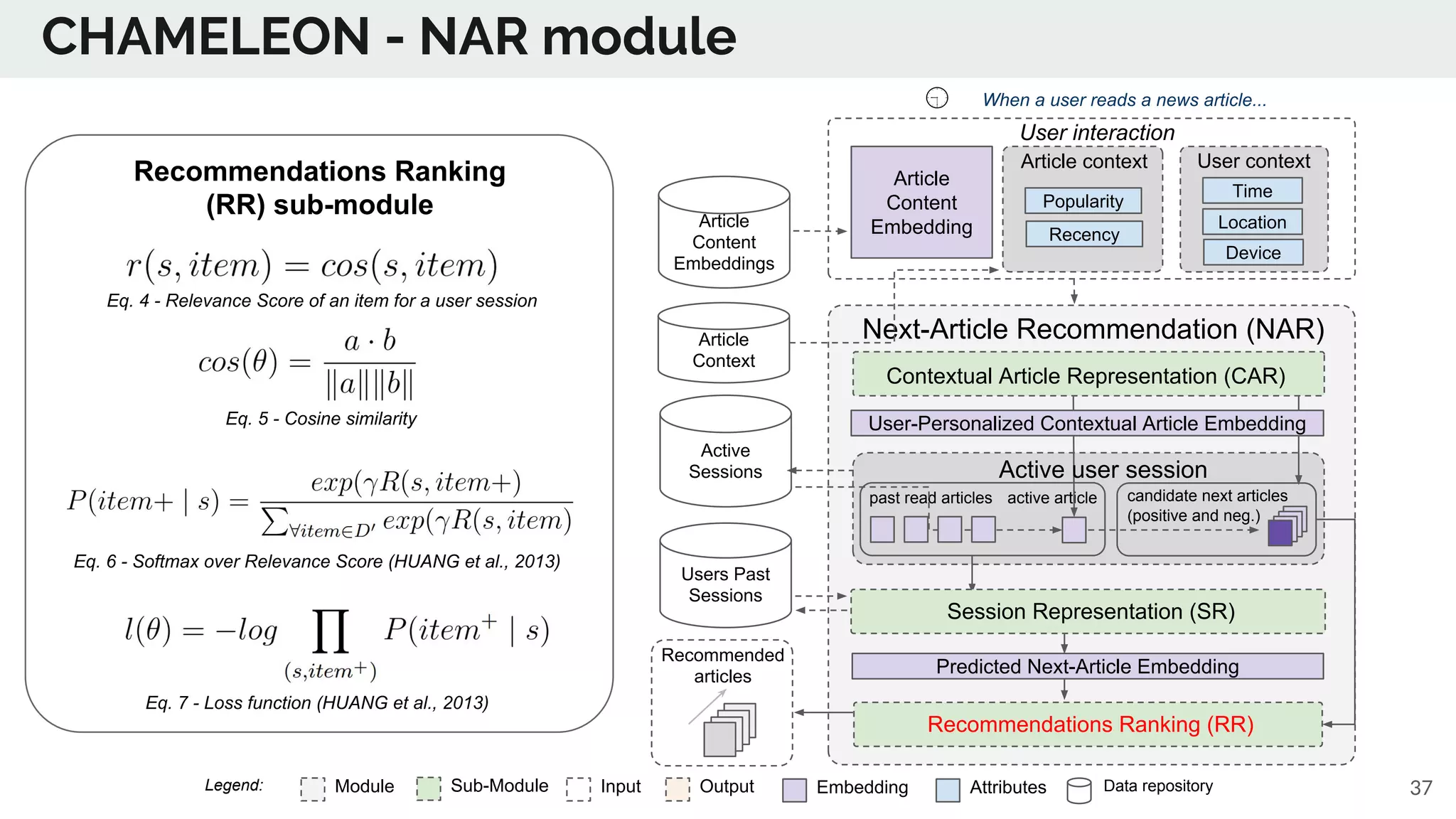
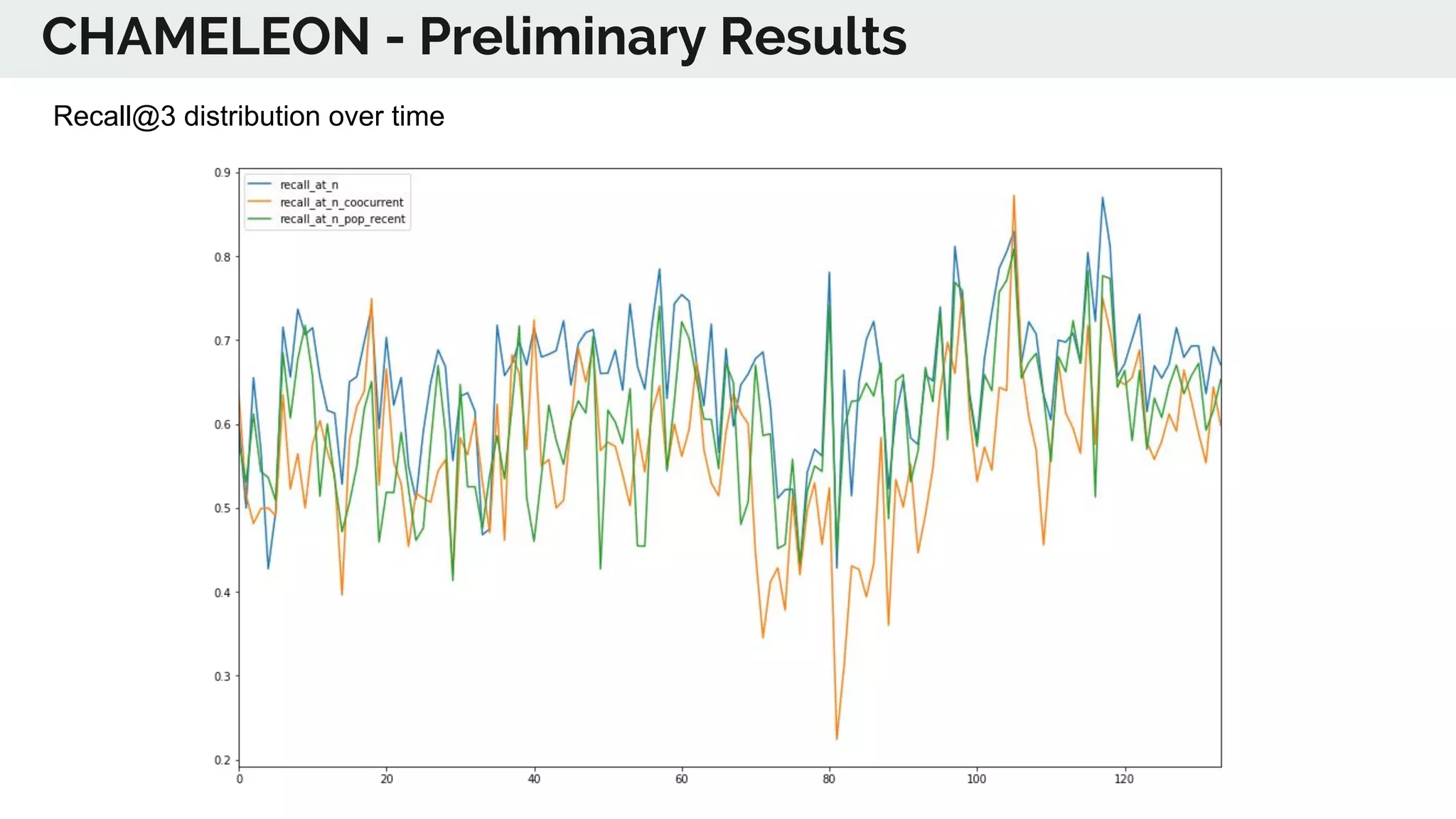
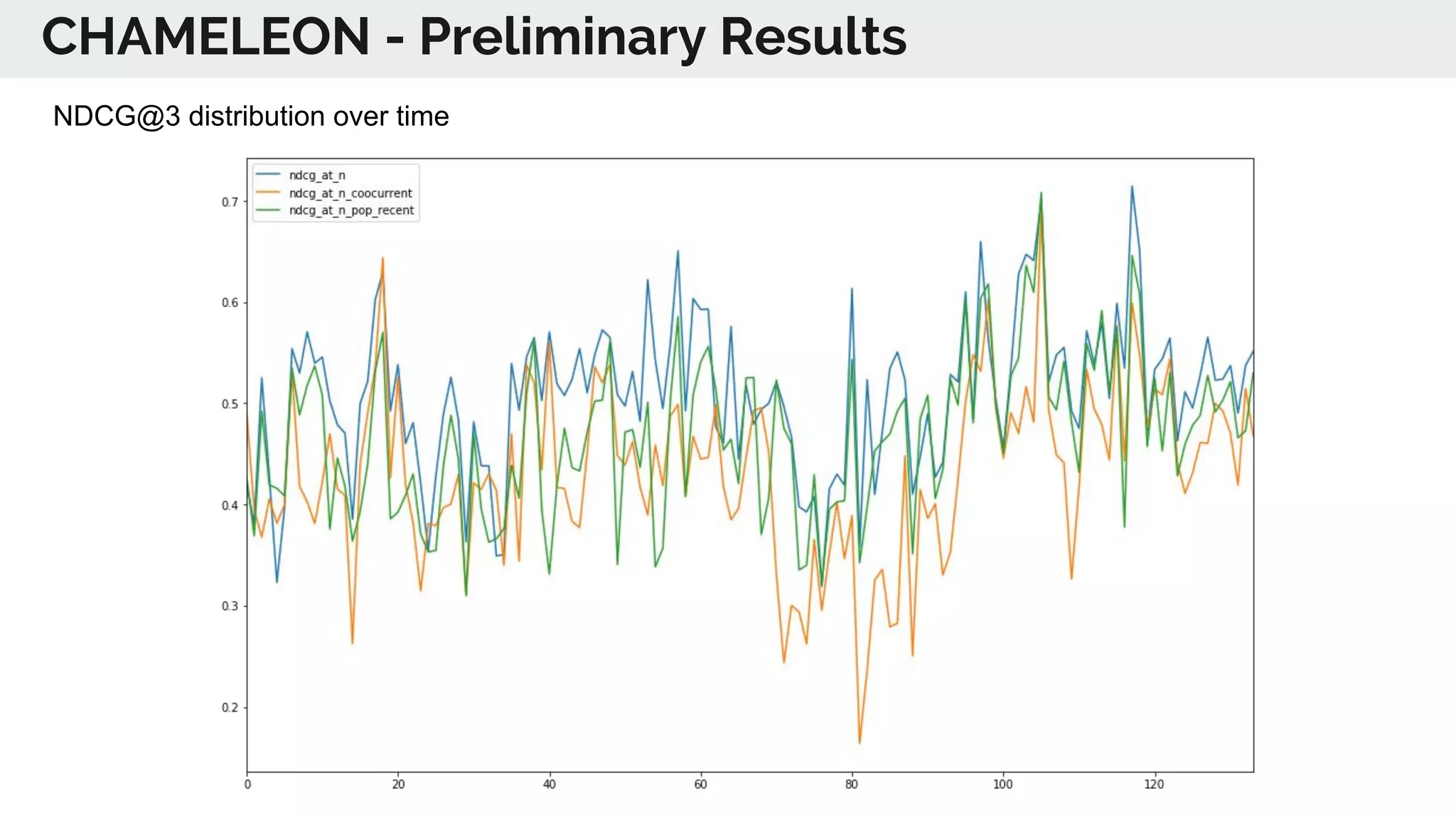
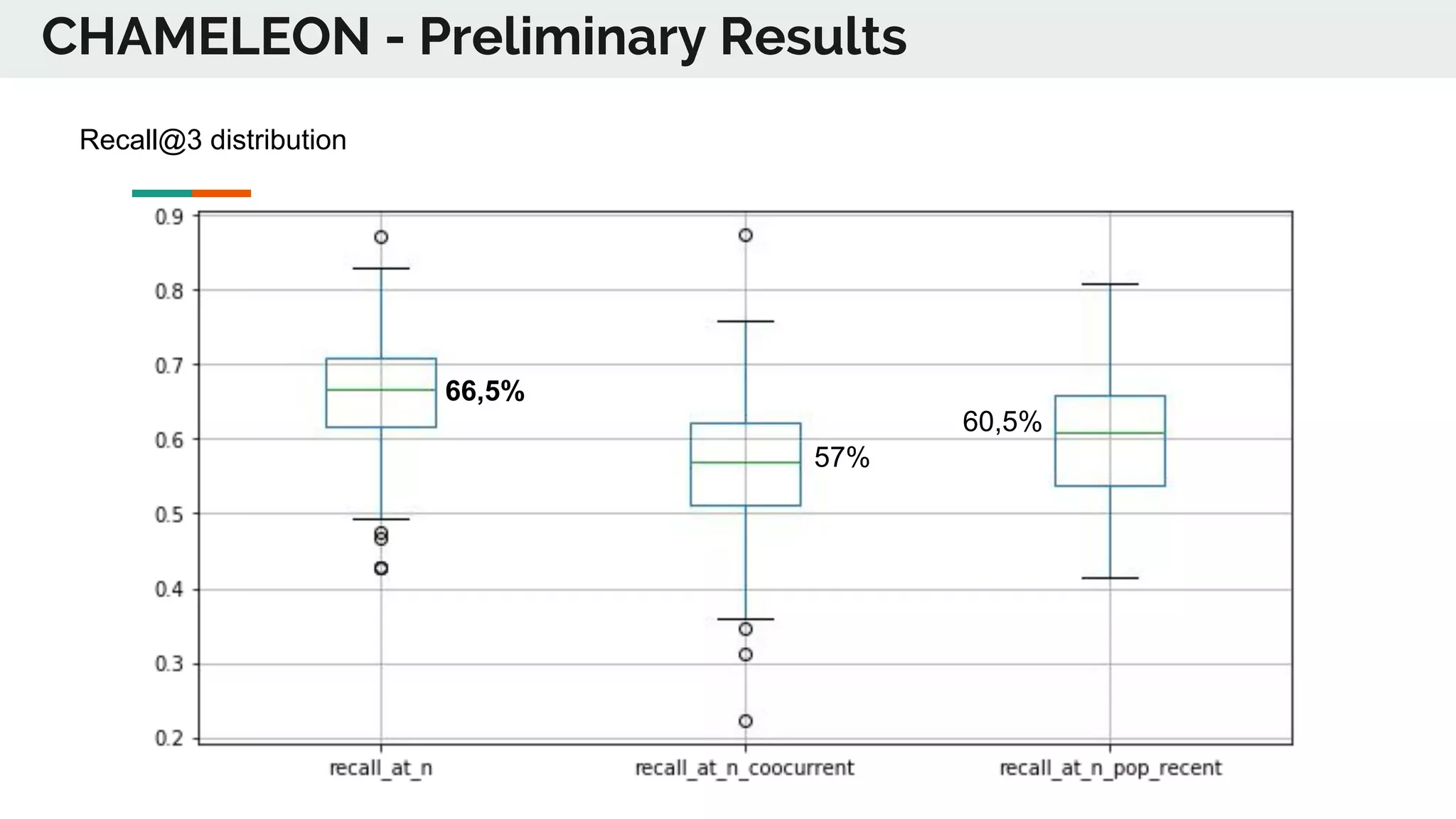
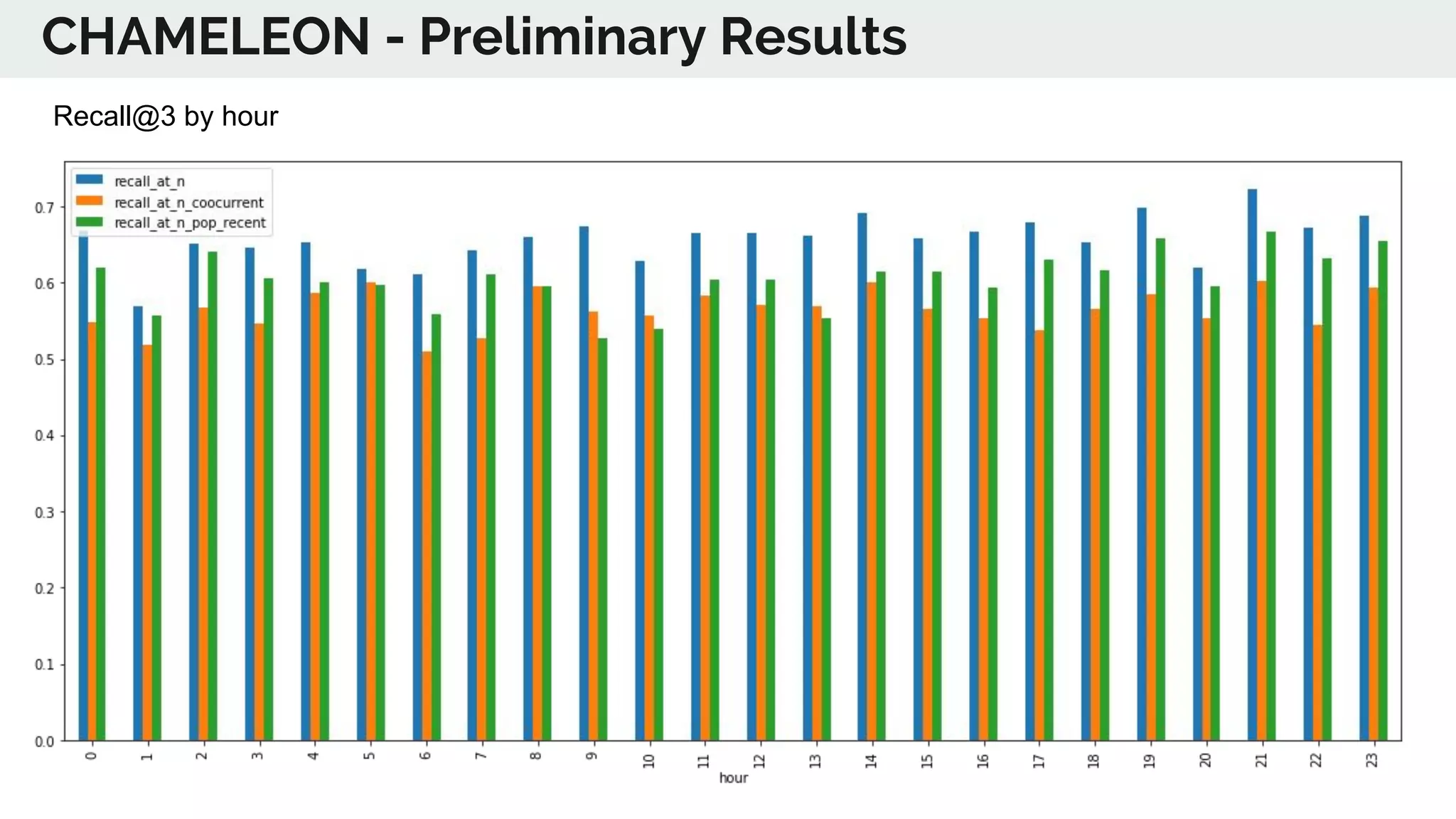
The document discusses the advancements in deep recommender systems, highlighting the transition towards using deep learning for improved recommendation accuracy through various methods like collaborative filtering and item embeddings. It outlines the challenges and evolution of news recommender systems while proposing a comprehensive meta-architecture to enhance recommendation quality in dynamic environments. Research objectives focus on personalizing news recommendations and leveraging user context and session information to meet users' shifting interests effectively.