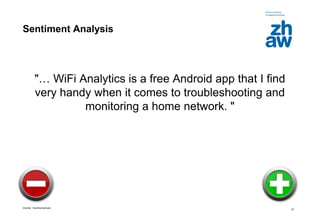
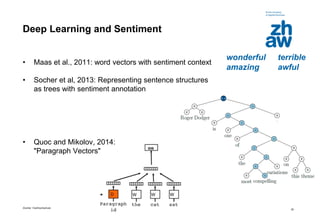
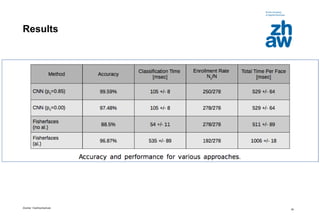
The document presents an overview of deep learning, detailing its advancements, successful applications in various fields such as computer vision and natural language processing, and current market trends. It highlights the significance of neural networks, particularly convolutional and recurrent networks, and outlines two specific use cases: text analytics and face recognition. Additionally, the document discusses the technical aspects of deep learning implementation and the impact of hardware investments on research and applications.






![Zürcher Fachhochschule
13
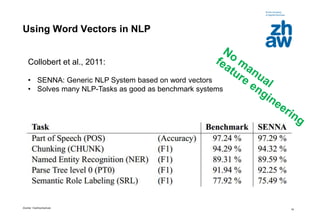
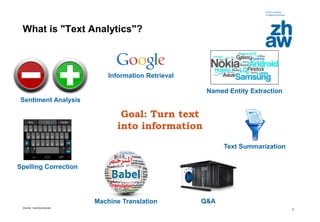
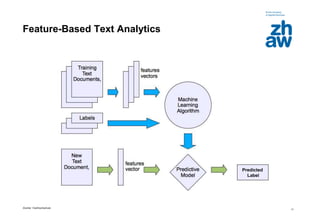
Feature-Based Text Analytics
Most Important Issues
• Requires large annotated corpora
• Depends on good features
[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150415deeplearningstdmcielpauc-150416023025-conversion-gate01/85/Deep-Learning-ZHAW-Datalab-with-Mark-Cieliebak-Yves-Pauchard-13-320.jpg)


![Zürcher Fachhochschule
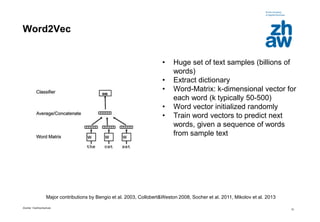
17
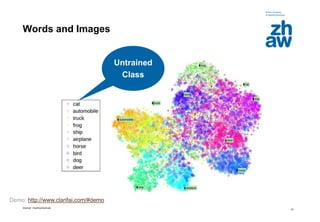
Relations Learned by Word2Vec
[11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150415deeplearningstdmcielpauc-150416023025-conversion-gate01/85/Deep-Learning-ZHAW-Datalab-with-Mark-Cieliebak-Yves-Pauchard-17-320.jpg)